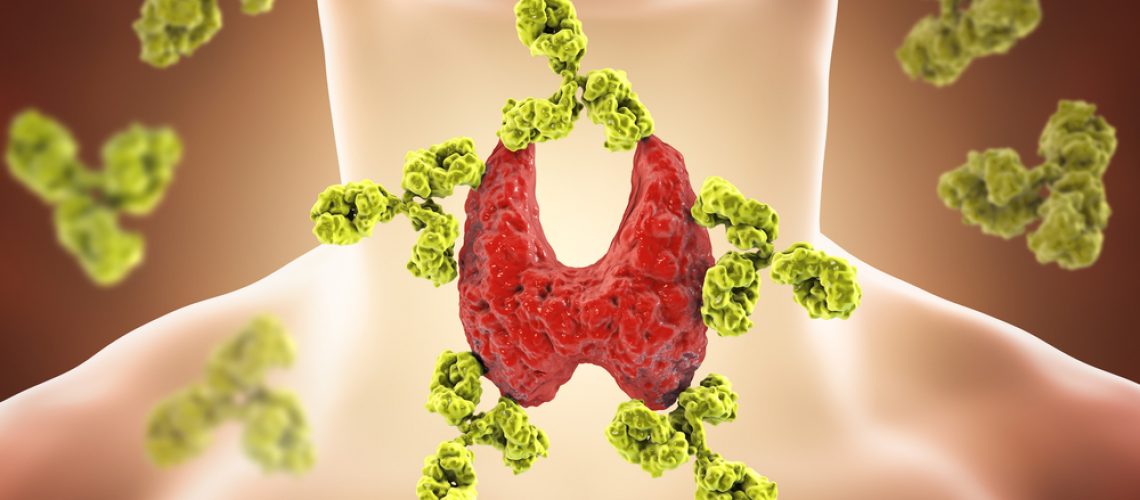
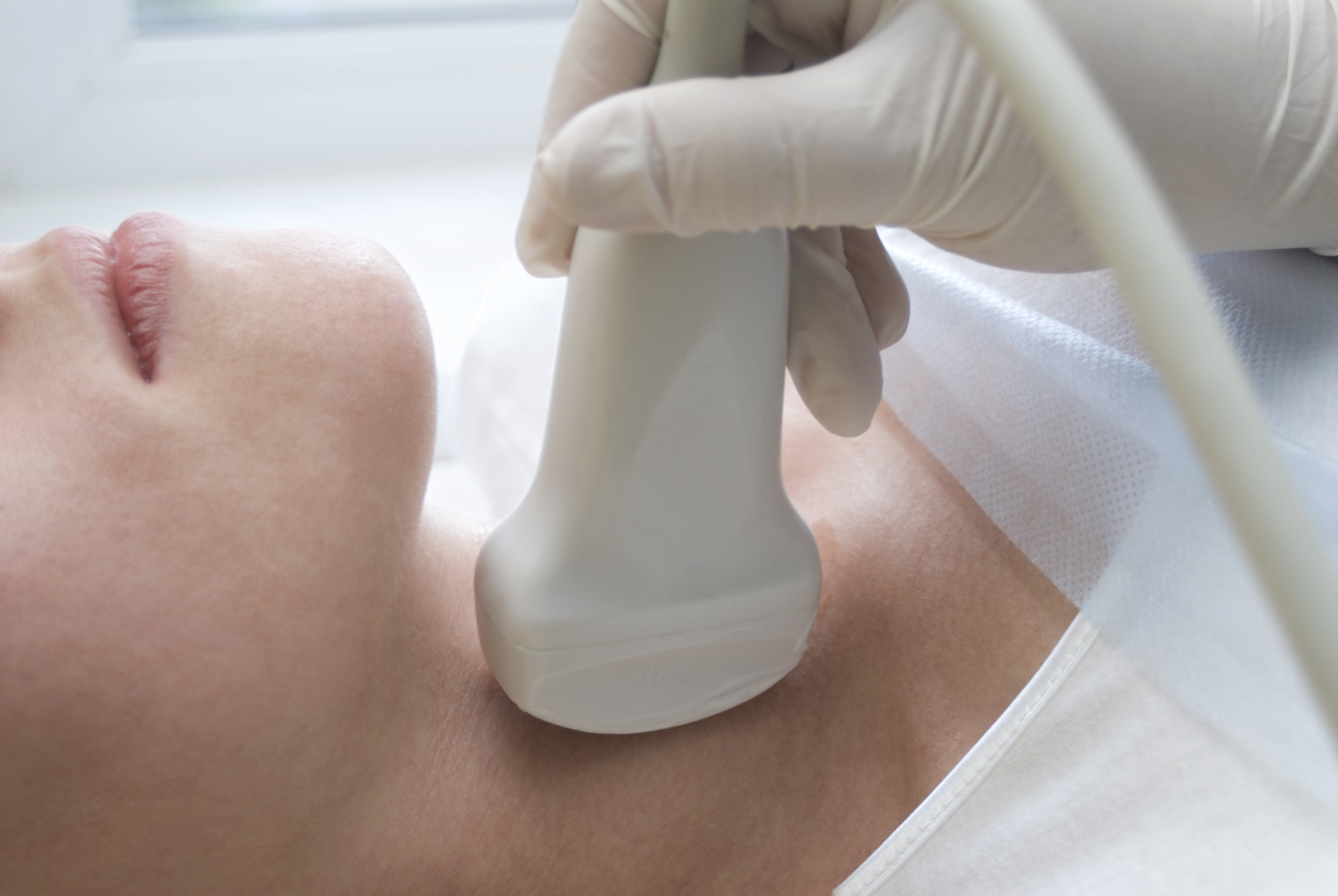
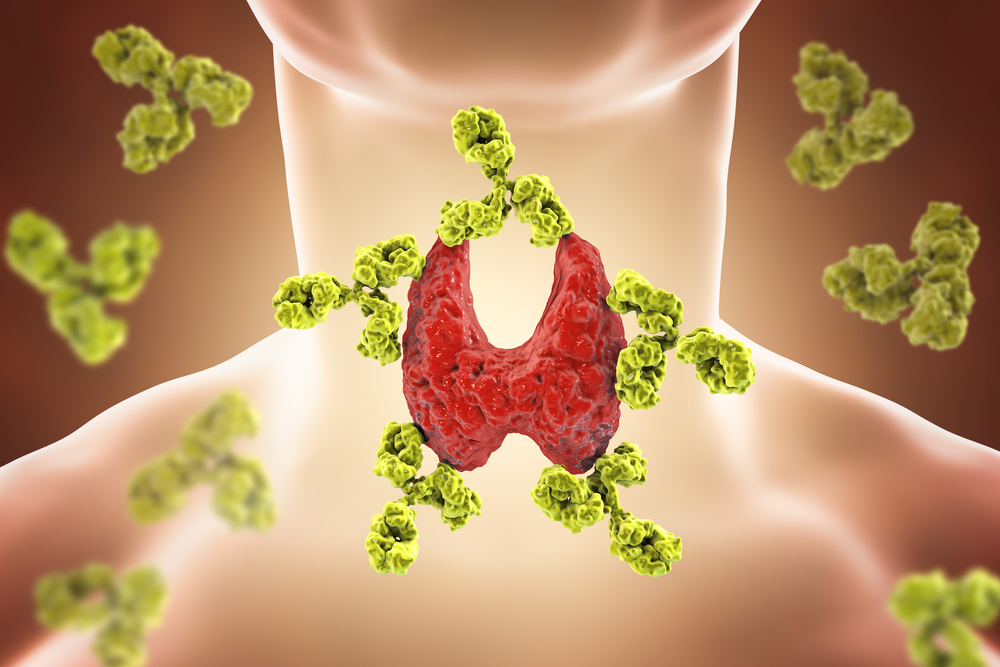
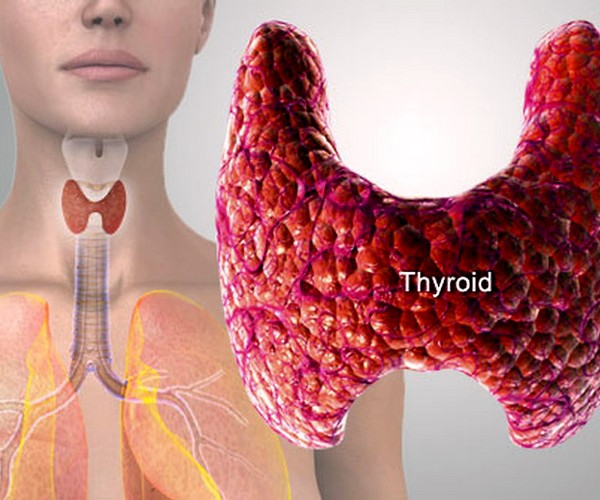
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland, causing it to become chronically inflamed and gradually degenerate and lose function, resulting in the development of hypothyroidism (a condition characterized by insufficient thyroid hormone production and related metabolic imbalance).
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the leading cause of hypothyroidism in adult women, with peak onset between the ages of 40 and 50, being almost endemic in some geographical areas.
Men can also be affected by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, but less frequently, similar to other autoimmune diseases.