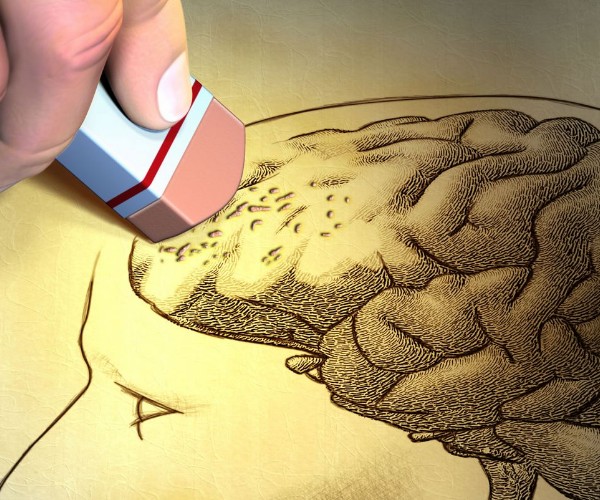
Stroke is a serious disease that occurs as a result of the reduction, or interruption, of blood flow to the brain (by which we mean the brain, cerebellum, and brainstem enclosed in the brainbox) and the subsequent death of brain cells.
Two forms are distinguished: the most common, ischemic stroke, occurs when a blood clot obstructs an artery carrying blood to the brain; hemorrhagic stroke is caused by the rupture of an artery.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted for a short time.