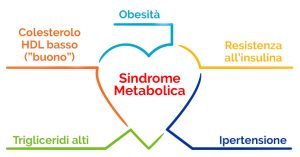
Sudden cardiac arrest comes mainly from cardiac pathology, such as from existing cardiovascular disease or coronary syndromes, representing the first and most obvious consequence of heart disease. There may be additional causes capable of cardiac arrest, such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure or even metabolic disorders.
CORONARY SYNDROME
 Acute coronary syndromes (heart attack; myocardial infarction; unstable angina)
Acute coronary syndromes (heart attack; myocardial infarction; unstable angina) Cardiac arrest: causes, symptoms and treatment
Cardiac arrest: causes, symptoms and treatment
PATIENT AT RISK
CARDIAC ARREST

RESPIRATORY FAILURE
CIRCULATORY SHOCK
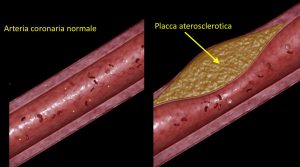
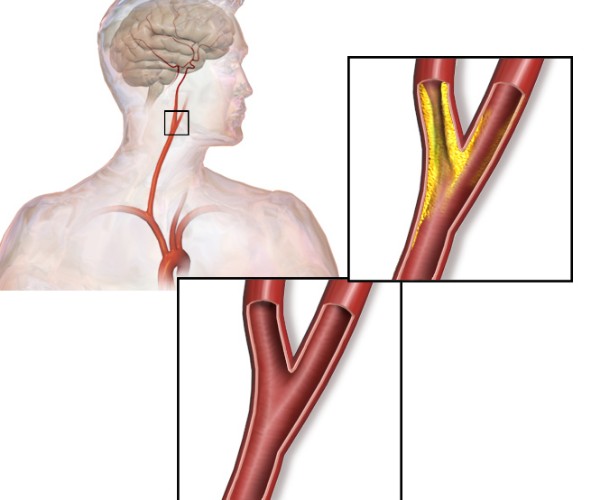
FRAMES OF CLOGGED ARTERIES
FROM CHOLESTEROL DEPOSITS