The
Parkinson’s disease
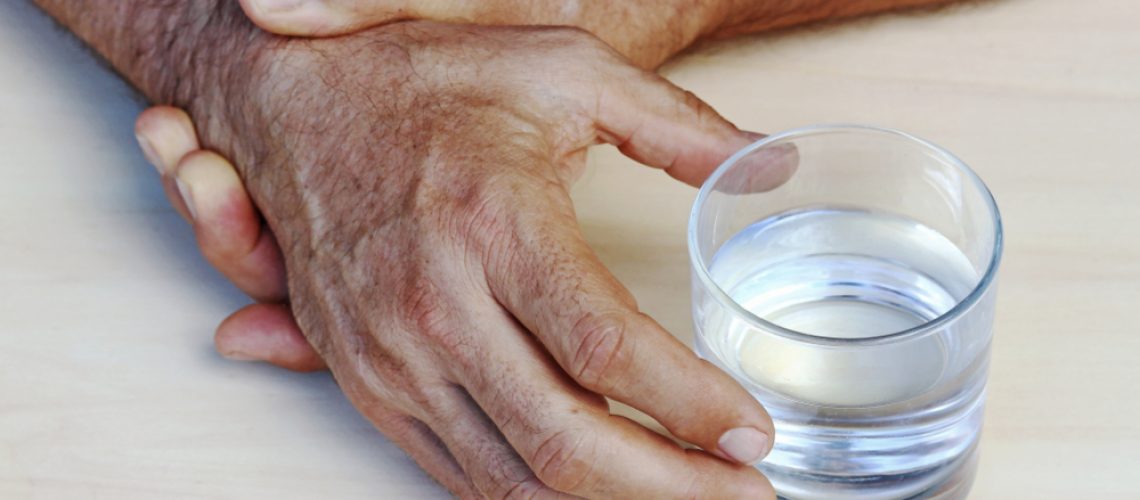
is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system, first described in 1817 by an English physician, James Parkinson. It is characterized by three main symptoms: slowness of movement, rigidity and tremor. The causes are related to degeneration of certain structures in the central nervous system, where dopamine, the main neurotransmitter essential for controlling bodily movements, is produced. Treatment of the disease still relies on drugs that can either supply the deficient dopamine through its precursor, L-DOPA, or stimulate the cells on which this transmitter acts, the dopaminergic cells. Unfortunately, due to the processes of neuro-degeneration, inherent in Parkinson’s disease, these drugs gradually lose their effectiveness over time.
A pioneering program involving an experimental and innovative drug treatment to be applied directly to the brains of people with the disease was published in the latest issue of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease in February 2019.
The hope: to restore cells damaged in the course of the disease.
The study is based on providing Parkinson’s disease-compromised brains with increased levels of a naturally occurring growth factor, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), which has been shown to be able to regenerate the brain cells impaired dopaminergic pathways in individuals with this condition.
Six patients took part in the initial pilot study that mainly evaluated the safety of the treatment approach. Another 35 people then participated in the actual study, which was carried out in a double-blind manner for the duration of nine months: half of the randomly selected subjects received monthly infusions of GDNF, while the other half were treated with placebo infusions.
A specially designed delivery system using robot-assisted neurosurgery was implanted in each subject to carry out the monthly infusions. This delivery system made it possible to deliver high-dose infusions of GDNF every four weeks directly to disease-affected brain areas with pinpoint accuracy through a transcutaneous port mounted on the skull behind the ear. The high compliance rate (99.1%) in participants recruited throughout the United Kingdom demonstrated that the drug delivery system, by repeated cerebral infusion, is feasible and tolerable.
After 18 months of therapy, all of the patients who had received GDNF showed improvement in disease-affected brain areas and related symptoms with a moderate to major rating from the researchers compared with the initial condition. This improvement was also observed in those subjects who were initially placed in the placebo group and then switched to GDNF treatment. GDNF administration proved to be safe throughout the study period.
The study’s principal investigator, Dr. Alan L. Whone of Bristol Medical School at the University of Bristol, UK, stated that: “ In GDNF-treated subjects The improvement in disease-affected areas went beyond what has ever been seen before” and then added that: “High doses of GDNF are able to awaken and restore dopaminergic brain cells, which are progressively impaired in the course of Parkinson’s disease.”.
Even in light of the neurodegenerative process underlying Parkinson’s disease, the drugs currently in use are likely to gradually lose their effectiveness. Therefore, there is no doubt that this study, if confirmed by subsequent evaluations, represents a decisive breakthrough in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
Source: Alan L. Whone et al:“Extended Treatment with Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Parkinson’s Disease” published online in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, in advance of Volume 9, Issue 2 (April 2019) by IOS Press