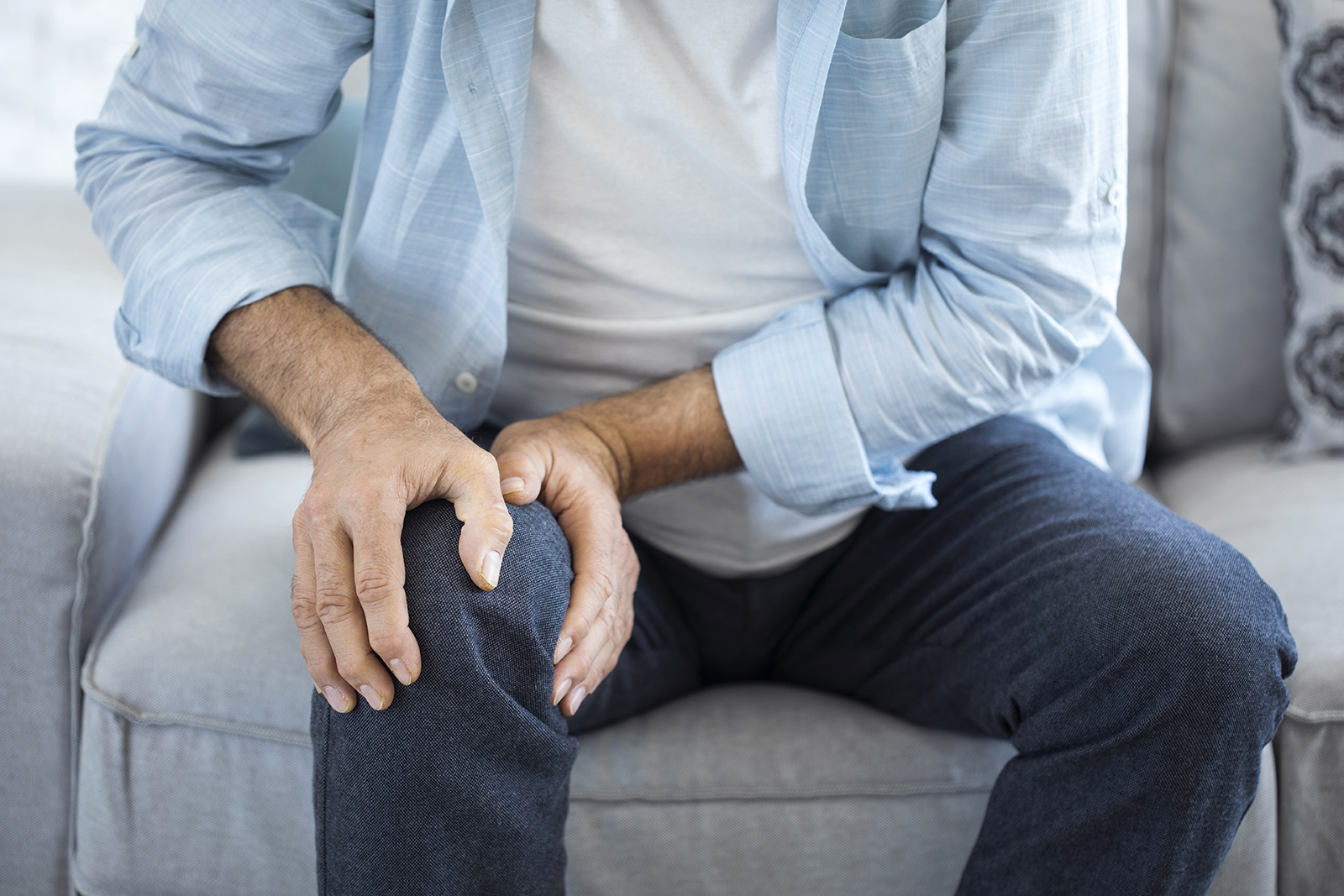
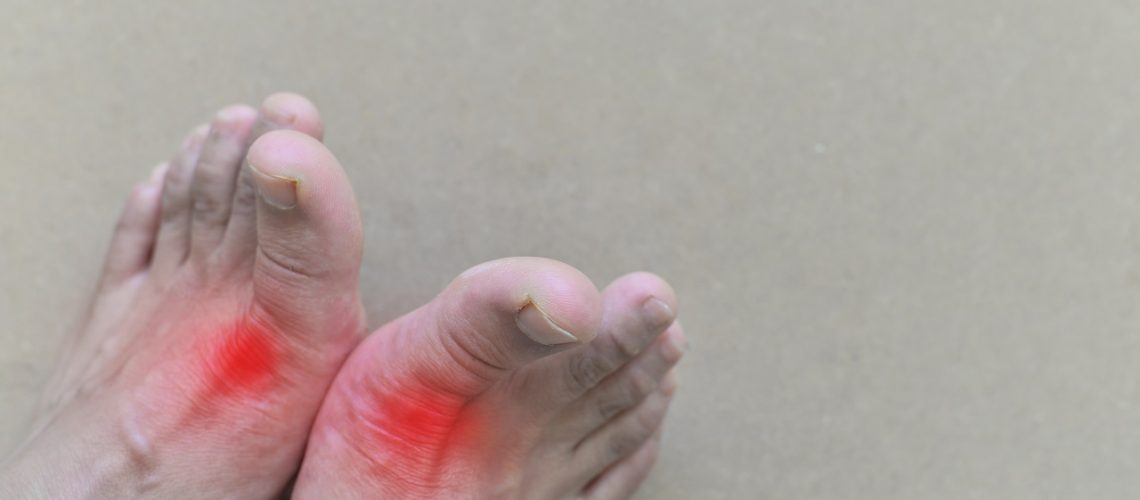
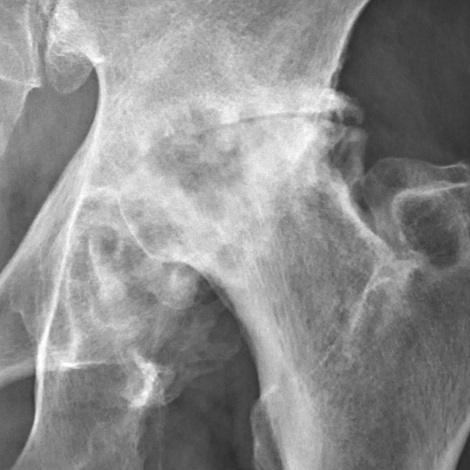
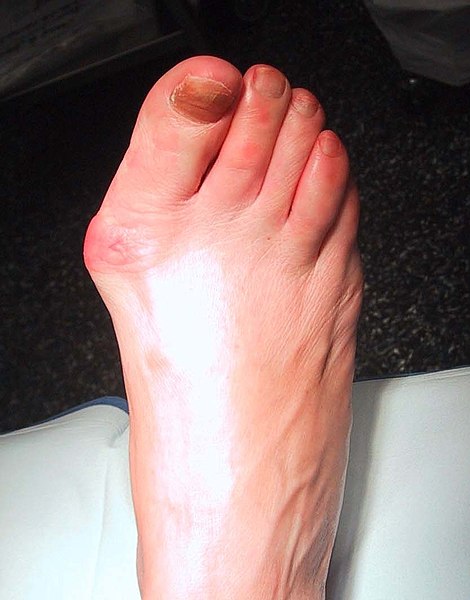
Gout is a metabolic disease that mainly affects adult men, but also women in the post-menopausal period. It is due to excess uric acid, which precipitates as monosodium urate crystals in the joints. The most commonly felt symptom is acute arthritis, but it is very important to make the differential diagnosis with other forms of acute arthritis such as psoriatic arthritis, septic arthritis, etc. The treatment of gout is a chronic therapy which uses specific drugs, although there is nondrug therapy aimed at controlling weight and limiting intake of purine-rich foods.
Tips dietary
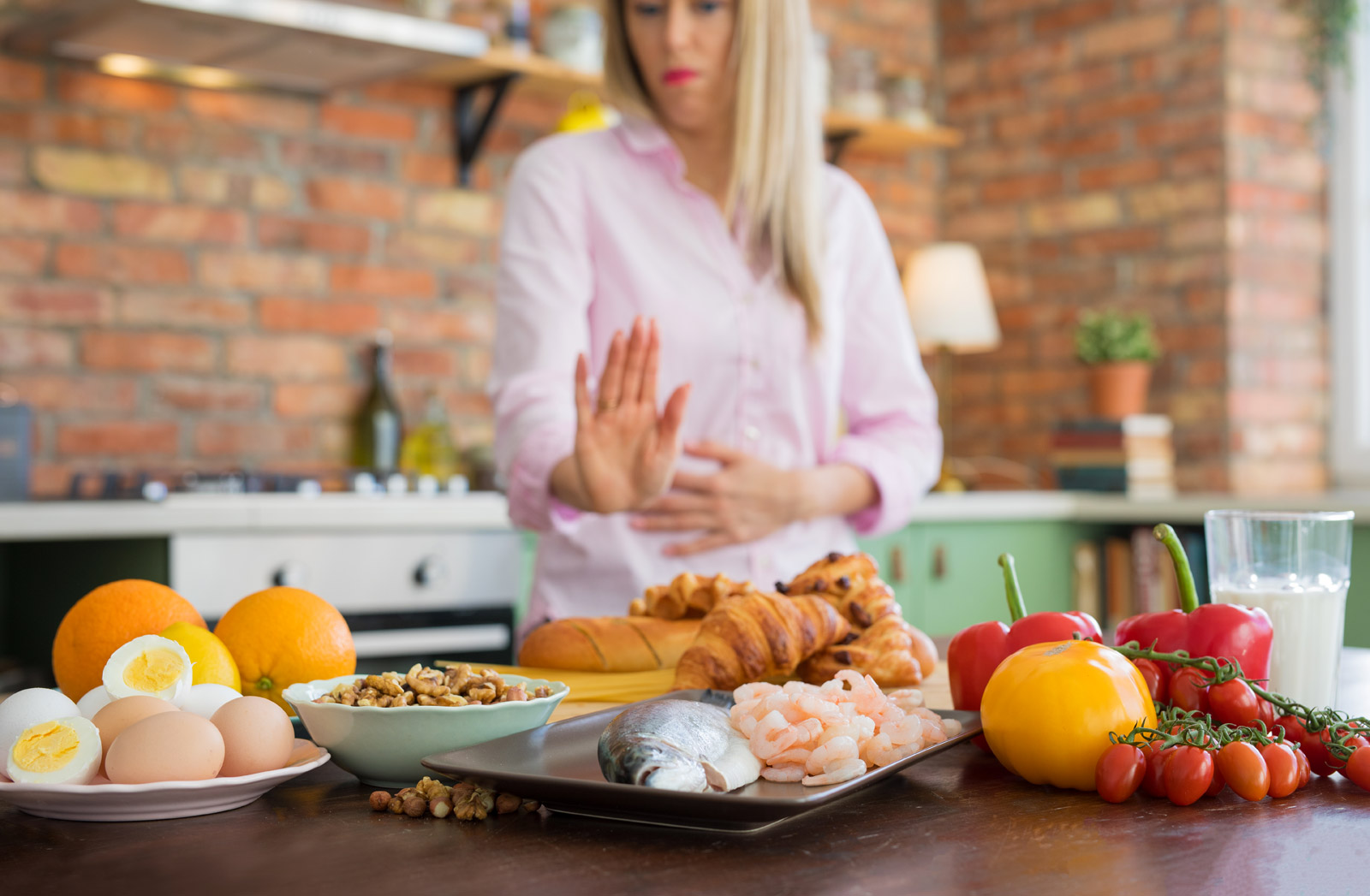
The patients who present with gout are given drug therapy for reduce uricemia, but it is advisable to avoid the consumption of foods with high purine content. It is absolutely necessary to avoid anchovies, sweetbreads, herring, brains, liver, shellfish, kidney, sardines and game.Is then important to limit consumption of eel, asparagus, beef, lamb, pork, cauliflower, wheat, mushrooms, legumes, bread and whole grains, fish, poultry and spinach. Foods to be used are coffee, tea, milk, cheese, fruits, seasoning fats, nuts, white flour breads and cereals, eggs, sugar and sweets.
Patients with overweight problems need to lose weight gradually. It is also helpful to ensure good diuresis by trying to avoid alcoholic beverages.
Source: Handbook of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition by Franco Contaldo et al.