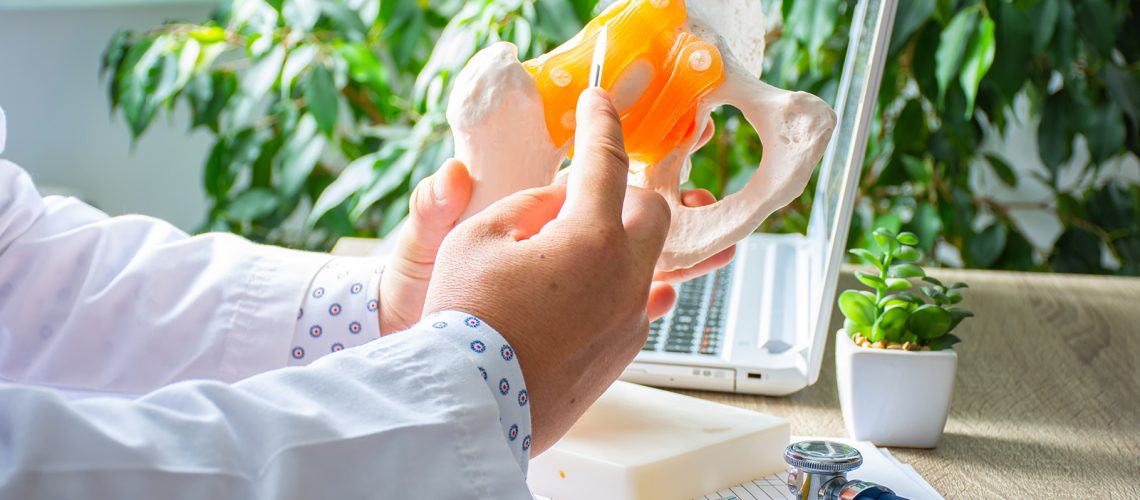
In some more complicated cases, especially when the following is present a severe condition of arthritis or even injuries or even in those cases where surgery can intervene to repair damage to tendons, cartilage or ligaments, or correct fractures or arthritis problems, conservatively repairing a hip joint compromised by femoral epiphysis, but in many other cases resorting to the hip replacement surgery (hip arthroplasty) may be an option to consider.
However, the prospects for the durability of the prosthesis over time must be considered on the one hand and what the condition of the patient with a worsening hip problem might be on the other.
Complications resulting from a hip disorder include difficulty or inability to walk properly, and often the need for continued medication treatments to relieve chronic pain.
Cases of acquired hip deformities that become established as a result of the disorder and pain are not uncommon.
There can be several surgical interventions to correct the hip disorder that vary based on the type and extent of the disorder.
Surgery is necessary in cases of hip fracture, a complicated and serious condition at any age because of the real risks to the patient’s life.
Hip fracture can occur in several ways. Usually a hip fracture occurs in the spherical part of the bone (the femur) and can be located in different places. Sometimes the fracture may involve thesocket or acetabulum. If the fracture occurs at the femoral neck, the rupture that occurs occurs near the junction point where the head of the bone joins its socket, posing serious risks of blockage of blood circulation to the hip head, compromising the network of blood vessels.
Another type of fracture is what is called an intertrochanteric fracture, which occurs at a greater distance from the joint and does not compromise blood flow to the femur.
Intracapsular fracture goes to the parts that make up the sphere and the orbit in which it moves, it may involve a risk of impairment of the vascular network that goes to irrigate the spherical part of the bone.
Several causes of hip fracture can occur:
- The fall from height or as a result of impact on a hard surface.
- Trauma from a traffic accident, or from an investment or motor vehicle collision.
- As a result of the damage produced by a disease such as osteoporosis, due to the loss of bone tissue.
- For damage caused by an obesity condition, which can produce excessive pressure on the hip.
There are risk factors for hip fracture, including:
- osteoporosis, a risk particularly present in ethnic Asians.
- The female gender, being more frequently affected by osteoporosis women are at greater risk of hip fracture.
- Age: after age 60, the risk of hip fracture increases. Over the years bone density, strength and endurance may decrease, exposing weaker bones to the risk of fracture, also sometimes accomplice to decreased perception of obstacles due to vision and balance problems.
- Insufficient nutrition in which important supports such as protein, vitamin D, and calcium are lacking as malnutrition, a condition that can increase the risk of fractures.
Symptoms of a broken hip may include:
- Hip and groin pain.
- The leg corresponding to the sore hip appears shorter than the other.
- Inability to load the leg and walk.
- Inflamed state of the hip and bruising in the external area.
Diagnosis of hip fracture
Although on physical examination there will be obvious signs such as bruising and swelling and sometimes a deformed appearance of the involved part, the diagnosis can be made after some diagnostic imaging tests, such as radiographs, MRI, or comuterized tomogrphy.
MRI, diferently from X-rays, is able to highlight with greater precision and detail any injured parts of the hip.
In addition, imaging investigation by CT scan can provide detailed images of the bone, ma nce of the tissues and muscles around the fracture point.
There can be several surgical interventions to correct the hip disorder that vary based on the type and extent of the disorder.
Surgery is necessary in cases of hip fracture, a complicated and serious condition at any age because of the real risks to the patient’s life.
Types of hip fracture:
- a hip fracture usually occurs in the spherical portion (femur) of the hip joint and but can occur elsewhere as well. Sometimes, the socket or acetabulum may fracture.
- Femoral neck fracture: this type of fracture occurs in the femur near the junction between the head of the bone and the orbit. A femoral neck fracture can cause an abrupt interruption of blood circulation in the spherical part of the hip by damaging the network of blood vessels.
- Intertrochanteric hip fracture: an intertrochanteric hip fracture occurs further from the joint and does not involve circulatory blockage of vessels to the femur.
- Intracapsular fracture: this fracture affects the ball and socket parts of the hip. It can also cause rupture of blood vessels located near the sphere.
Several causes of hip fracture can occur:
Potential causes include:
- Fall on a hard surface or from a great height.
- Traumatic event to the hip, such as from a car accident.
- A disease such as osteoporosis, due to the loss of bone tissue.
- Obesity, in which the pressure exerted on the bones becomes excessive.
Some people are at greater risk of hip fracture in the following cases:
- as a recurrence of an equal event that has already occurred, which results in a considerable increase in risk.
- In people of Asian ethnicity, the risk increases due to the greater presence of osteoporosis.
- In female persons, due to greater exposure to osteoporosis.
- In people of advanced age, among whom after age 60 the risk of hip fracture is more substantial, due to the effect of decreased bone strength and density, febìnomenon also accentuated by decreased visual and balance maintenance abilities.
- In people who are malnourished due to deficiency of important nutrients for bone health, such as protein, vitamin D, and calcium.
Symptoms of a broken hip may include:
- Pain in the hip and groin area.
- The affected leg is shorter than the healthy leg.
- Inability to walk or load weight or pressure on the affected hip and leg.
- Hip inflammation.
- Bruises.
A broken hip can be life-threatening, so medical attention should be sought if a break is suspected.