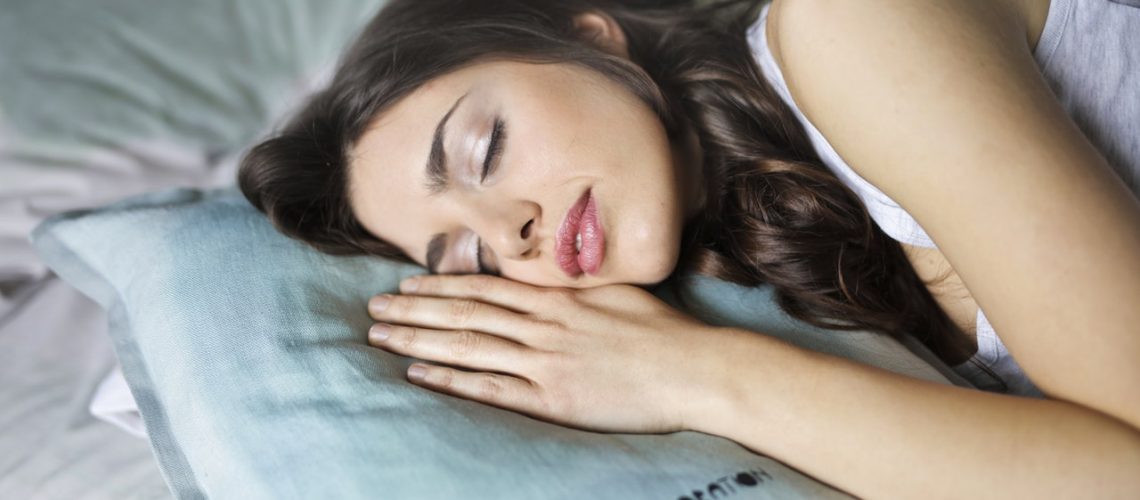
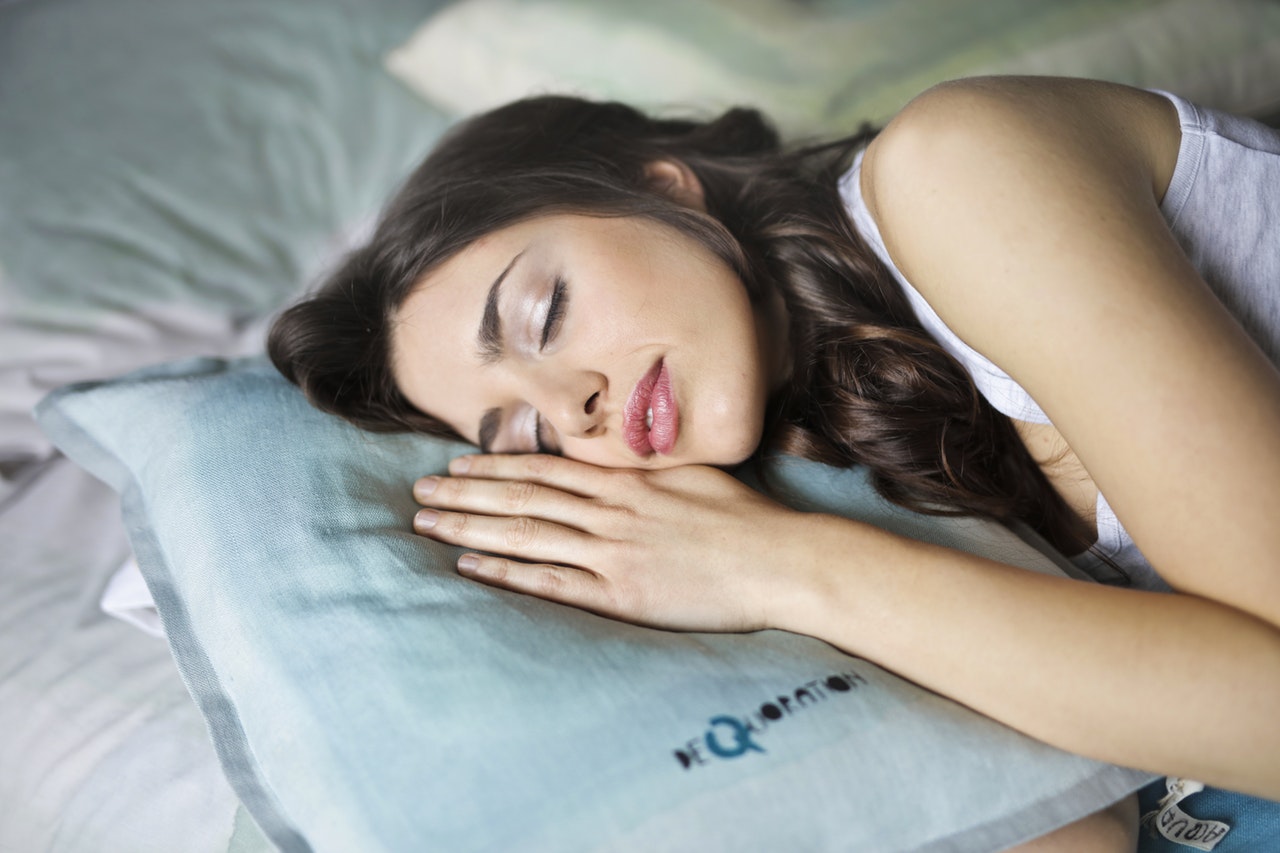
The brain, even when we sleep, works. Various research now agrees in assigning the sleeping brain a central role in memory fixation and thus in learning. The demonstration of this apparent paradox comes from research
on the “nap”: volunteers tested for mnemonic retrieval of a list of words learned, whether, between learning
of the list and recovery, they had interjected a nap of about ninety minutes, remembered more words than those who had not slept. This phenomenon has even been found in very young children, as shown by a group of psychologists from Germany’s Ruhr University, who recently published in PNAS a study conducted on children between 6 and 12 months of age. Children’s brains at this age have already developed a strong imitative capacity. The researchers used this skill to test whether napping could improve memorization of simple actions with objects. Children who had slept more than half an hour, after ‘exposure to object manipulation, were more capable, in reproducing these actions, than those who had slept less than half an hour.
The most surprising data, however, come from studies of adults. In fact, the paradox is that memory consolidation, a purely cognitive and therefore demanding activity, occurs when we are in the depths of deep sleep, when the brain machine is at its lowest oxygen consumption, blood flow is slow and the electroencephalogram shows large, slow and very slow waves.It is known that during sleep, our brain activity is highly variable: cycles alternate, of about an hour and a half each, containing phases dominated by slow and very slow electric waves and instead phases characterized by mixed, fast-dominated waves. The latter is called the REM (Rapid Eye Movement ) phase because fast waves are accompanied by rapid eye movements. At this stage we have very detailed and consistent dreams , which have an easier time being remembered. At the electroencephalus gramma, the brain shows a profile very similar to that of wakefulness. Therefore, for a long time REM phase was thought to be the one most related to nighttime cognitive activity. Instead, it is now clear that it is the slow and ultralow wave phase, called Slow Wave Sleep, which is part of the broader Non -REM phase, that is implicated in nighttime memorization. Bjorn Rasch and Jan Born, neuroscientists at the University of Zurich, in an extensive review in Physiological Review, document that exposure to an odor, during a cognitive learning task, prompts memory consolidation only if the same people are re-exposed to the same odor while in the deep sleep stage and not REM sleep. But what are the hypothesized brain mechanisms?
Fixation of a memory is a process that requires the cooperation of two brain areas: the cortex and the hippocampus. The former fixes attention on the object to be memorized, frames it, gives it a code and then transfers this initial encoding to the hippocampus, which will consolidate the trace and then transfer it back to the cortex, where it can be integrated into the various drawers of our memory and remain available for further recall. In this dialogue, the two areas go at different speeds: the cortex is characterized by fast waves and theta waves, which are relatively slow waves, have a rhythm (4 -8 Herz) but are more than twice as fast as the slow waves, the deltas (1-4 Herz), which instead dominate the hippocampus and the deep phase of sleep. During wakefulness then, the first phase of memorization would occur in the sign of theta waves, while during deep sleep, the hippocampus would consolidate the memory with slow and ultralow activity (less than 1 Herz).
What evidence do we have for this explanation? The application of a transcranial current (absolutely painless operation) with delta frequency, on the area of the head that corresponds to the prefrontal cortex during the first stage of sleep, increases the memory of an exercise done before sleep. If a theta frequency is administered instead, the memory is suppressed. But conversely, if a theta frequency is administered during wakefulness, when one is engaged in learning, memory is improved. Further evidence came on March 15 when a group of Austrian neuroscientists hadimproved in the Journal of Cognitive Neurosciencethat theta activity during learning is directly related to the ability to remember after a night’s sleep. In essence, say the researchers,during slow-wave sleep, the hippocampus selects memories to save and those to throw away and does so by following a label that has been affixed to them during wakefulness, the theta label. Finally, there is another type of
Sleep and Memory
And that is the immune one. Volunteers who received a single dose of hepatitis A vaccine, if they did not sleep the night after the vaccine, the antibody level (indicating vaccination efficiency), checked after four weeks, is much lower than that of their colleagues who slept .
The arms and legs of memory
It is well known that we Italians are good communicators and use gestures a lot to emphasize or complete a message. This characteristic, which might appear to be a simple trait of the Latin costume, more expansive and physical than that of the global north, now acquires a new dimension in the light of cognitive neuroscience. In fact, gestures, in addition to playing a communicative role, also play a role in ‘cognitive processing and memory. We have a body of evidence showing that, when recalling an event, gesticulation can promote recall of details better than when gesticulation is interdicted. In addition, gesticulation, prior to recall of previously learned words, helps recall performance. Other studies have documented an effect of gesticulation on working memory. This renewed interest on the relationship between body, cognition and memory has important clinical basis. Indeed, it has long been known that neurological and psychiatric disorders often go hand in hand with motor impairments and, conversely, that motor disorders go hand in hand with psychiatric impairments.
A typical feature of depression is impaired memory and motor slowing, just as motor impairments are common in psychotic and anxiety disorders. Conversely, Parkinson’s, which is the typical disease of the basal ganglia motor system, frequently presents with depressive disorders and/or worsening of cognitive performance and memory. Finally, it is well established by numerous controlled clinical trials that structured exercise has positive effects on major depression and anxiety disorders, dementia, and other neurodegenerative disorders. A recent randomized controlled trial published in Neurology by an interdisciplinary group at the University of Iowa documented that aerobic activity improves not only fitness, motor function, and fatigue, but also mood, cognition, and memory in people with Parkinson’s disease. Extensive animal and human research has documented that physical activity induces the release in the brain of three neurotransmitters critical for memory, such as dopamine, serot onin, and norepinephrine . At the same time, cannabinoids and brain growth and plasticity factors (IGF-1) put into the circulatory stream by muscle contraction reach the brain. One finding established by human research is the physical activity-induced increase in Brain-Derived Nerve Factor (BDNF), an increase that corresponds to improved memory retrieval capacity.
by Francesco Bottaccioli