Computed tomography, abbreviated as CT, still often commonly referred to as CAT (computerized axial tomography) despite the evolution of the method, is an imaging investigation that provides very detailed three-dimensional structural information of the internal organs of the human body, making use of ionizing radiation (X-rays).
Description
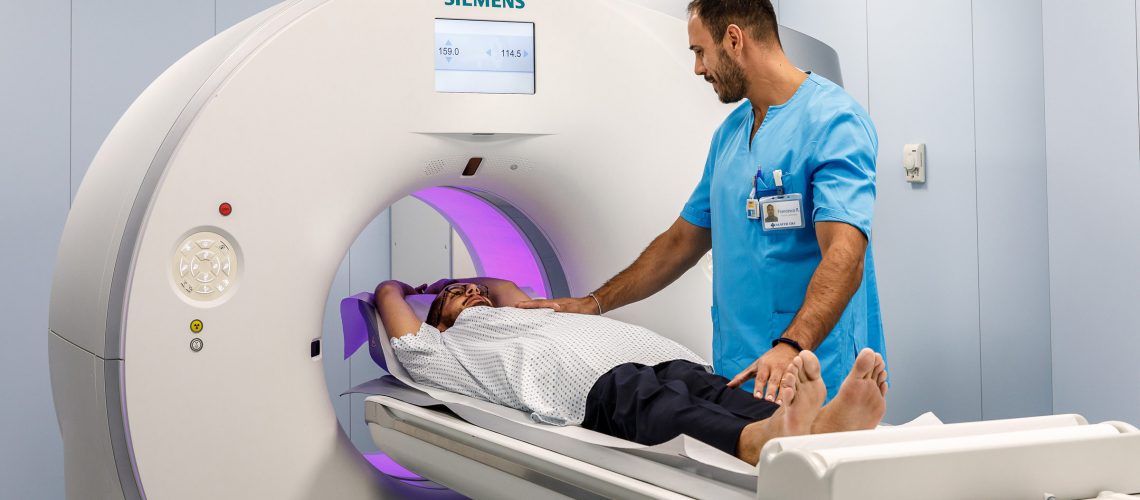
To perform the CT scan, it is, first of all, necessary to remove all metal or other objects (earrings, rings, bracelets, chains, glasses, etc.), undress and put on the gown provided by the health care personnel.
Then, one should lie down on the couch of the CT apparatus and get into the position indicated by the doctors, which should be held stably throughout the evaluation, following precisely the doctors’ requests regarding breathing. When the correct position has been assumed, the crib begins to slide, going through a structure similar to a large doughnut with a hole in it, stopping in places at the areas to be analyzed.
At this stage, the CT scan circle administers ionizing radiation while special sensors acquire signals from the body tissues examined; in doing so, the circle rotates on itself to acquire information in all directions in space.
The collected signals are transduced into electrical pulses and sent to a computer that integrates and processes them, turning them into three-dimensional images, displayed on the monitor, which can be further processed to optimize their resolution and photographed to fix the most interesting aspects for clinical purposes.
The duration of the CT scan varies according to the extent and complexity of the area of the body to be examined (encephalon, chest, abdomen, limbs, etc.), as well as the type of instrument used (newer or older) and the patient’s ability to maintain the required position. On average, the total duration of the evaluation is about 30 minutes. The examination is completely painless.
In some cases, to improve the diagnostic ability of the CT scan, a contrast agent is to be used, which, depending on the case and the purpose of the investigation, will have to be taken by mouth (liquid) or injected into a vein or inserted into the rectum, a few minutes before lying down on the instrument bed.
When needed
Now widely used in clinical practice, CT scanning is considered a Level 2 evaluation, to be used when other simpler, cheaper, and harmless techniques do not allow to specify the diagnosis with a sufficient degree of accuracy and in planning interventional procedures.
One of the main reasons for limiting the use of CT scans relates to the fact that the proportion of ionizing radiation administered during the examination, while not harmful when considering a single evaluation, is not negligible (amounting to about 30 times that used in performing X-rays), and the accumulation of the effects of X-rays administered in numerous subsequent CT scans, even years apart, could damage the body’s tissues and promote the development of fibrosis or tumors.
The main indications for performing CT include:
- Diagnosis of muscle and bone diseases, such as sarcomas, bone tumors, and complex fractures;
- Clarification of the location (and relationship to neighboring tissues/organs) of a tumor, site of infection, or blood clot (thrombus);
- Planning for an invasive procedure such as a delicate surgery or biopsy;
- Accurate identification of the area where a tumor is present to be treated with radiation therapy;
- Detection and monitoring of tumors, heart disease (coronary angiography with CT), lung nodules, and liver masses;
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of specific therapies, particularly cancer therapies;
- Accurate detection and localization of injuries and bleeding to internal organs.
Special Warnings
By itself, CT scan has no particular contraindications. However, in view of the use of ionizing radiation, it is important for women of childbearing age to be certain that they are not pregnant at the time the examination is performed. Conversely, although the radiation dose used is not likely to harm the fetus, if possible, it is preferable to postpone the evaluation or opt for an alternative diagnostic method (ultrasound or MRI).
The contrast medium used for CT scanning is generally harmless, but some people may develop hypersensitivity reactions (with onset of itching and skin rash) or true allergies: if you have had such experiences in previous examinations with contrast medium (even other than CT) or you are intolerant or allergic to particular drugs, it is important to inform your health care provider already while scheduling your CT appointment.