With this maneuver, the apneist returns the eardrums to a neutral position, which, due to the external pressure, which reduces the volumes of the air zones of our body, would tend to introflex to the point of injury or rupture if they were not rebalanced.
Ambient pressure, which increases with depth, causes a reduction in the volume of the aerial parts of our body (lesson 3), compensating the ears reconstitute the original volumes, keeping the eardrum in a neutral position.
The freediver’s mask must also be compensated for: it is filled with air, which decreases in volume as one descends into depth. If we did not compensate for it, an at first annoying and then painful and finally dangerous vacuum situation would be created in it and that, sucker-like, could pull and even make the athlete’s eyes squint.
Compensation is a maneuver that should be carried out most frequently in the first few meters of descent in which (first 10 meters) there is a halving of the volume of the aerial parts (see lecture 3, Boyle’s law), which is the most important reduction we see in a deep descent; as we descend, reductions will continue to occur, but in a less than proportional manner, and the time required between clearances will lengthen.
It will, however, become more and more difficult, since as the volume of air contained in our lungs also becomes smaller and smaller, it will gradually become more and more difficult to bring to the ears the proper amount to perform this maneuver.
To facilitate subsequent compensations, it is advisable for the freediver to start with the ears already compensated, right from the flip, and never get to that muffled and/or painful feeling forcing us to perform such a maneuver, but anticipating these moments: by the time we come to feel pain, it is often late and compensation would require such an effort that would certainly, in the first place, affect the state of relaxation and then, in many cases, it would not succeed or might even cause some harm to the apneist.
For the same reasons, it is advisable to always have a well-compensated mask, insufflate a trickle of air through the nose, and make sure that the compensatory sequence is always mask-ear, and this is because a compensated mask, facilitates the maneuver involving the ears. An uncompensated, vacuum mask, on the other hand, would tend to pull air, plunger-like, through the nose and make it more complicated to rebalance volumes and reposition the eardrum into proper shape.





Valsalva maneuver:
You bring your hands to your nose, hold it and blow: air cannot come out of the nose, nor out of the mouth, which must be closed, so it naturally goes to the ears. It is an effective compensation that directly connects the air in the lungs with the tympanic membrane.
Marcante Odaglia or Frenzel maneuver:
This technique assumes, unlike the previous one, that at the time we put our hands to our nose and blow, with our mouth closed, the glottis is also closed and the soft palate is open.
In most cases it is done without the knowledge that this is happening, but there are huge differences between the two maneuvers.
The latter is gentler and more relaxing than the former and that is intuitive, as more effort is required with the latter, as air has to reach from the bottom of the lungs to the ears, while with Frenzel It is the air in our mouths that needs to be brought to the eardrums: the shorter path it has to travel, requires the use of fewer muscles, thus less effort, and the execution is also faster and more effective.
The muscles involved in compensation can also be trained, through tubal gymnastics, which can be, for example, done by inflating a balloon with the nose. One can then exercise the tongue, extroverting and introflexing it to the fullest extent, the jaws (mandibular exercises) or the cheeks (blowing on a candle gradually farther away or through a narrow straw).
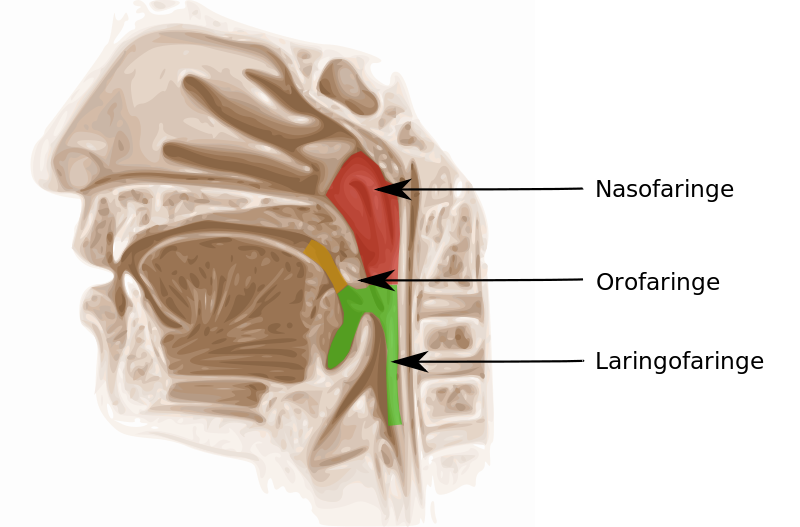
There are compensatory maneuvers for more EXPERIENCED freedivers: the floodingmaneuver, which, however, has many contraindications and therefore is no longer used today and the Mouth Fill. With the former, freedivers, upon reaching a certain depth, would remove the nose plug and let the sea flood the air-containing parts of the oropharyngeal cavity. Since these were now, these, filled with water, which is a liquid, thus incompressible and not subject to volume reduction under pressure, they circumvented the obstacle or problem of compensation.
The Mouth Fill è A maneuver by which the apneist keeps the Eustachian tubes open at all times, managing the air in his mouth, which he continues to recharge, taking it from the lungs, up to a certain altitude beyond which it is no longer possible for him to recharge, due to the volume reduction that also takes place within them. The athlete must be good at managing the glottis and leaving the soft palate open, while the mandibles, cheeks and tongue constantly keep air pressure towards the ears.
by Mariafelicia Carraturo
www.feliciacarraturo.it