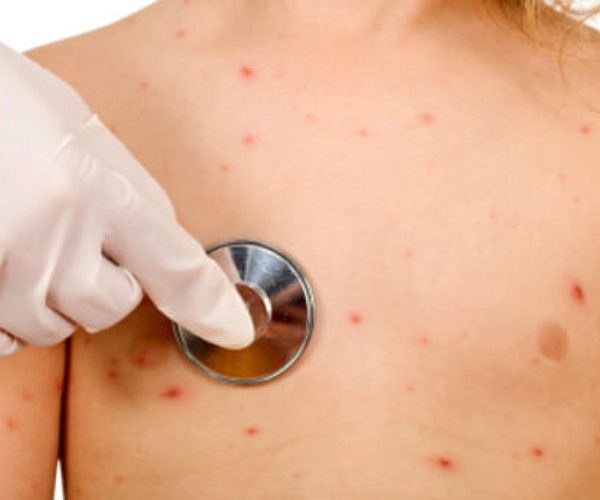
The St. Anthony’s Fire, also called St. Anthony’s rash or Herpes zoster according to scientific nomenclature, is a viral disease that affects individuals who have contracted chickenpox in the past, as it represents a reactivation of the virus that is generally not completely eliminated from the body, but remains dormant in certain parts of the nervous system. This virus owes its particular name to the ancient tradition, which originated in the Middle Ages but was especially present in the modern age, of invoking St. Anthony the Abbot to ask for healing from illness. Shingles can also affect young people, but it occurs more frequently from age 40 and up.
Symptomatology and contagion
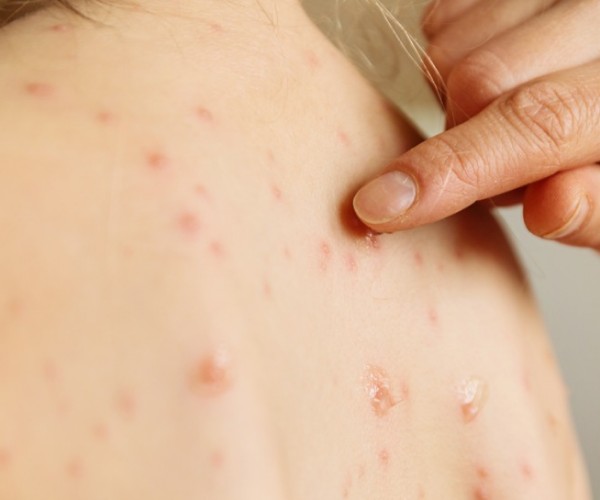
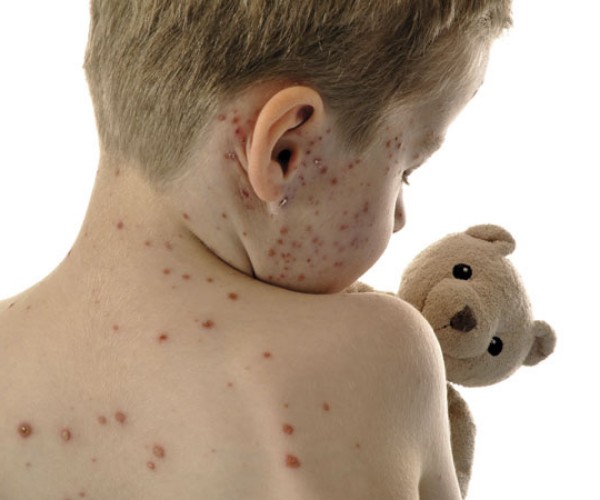
The specific cause that triggers shingles is not yet known: the immune system should suppress the reactivation of the latent virus, however in many cases this does not happen, especially in people with weak immune systems, due to old age, psychological stress and other risk factors. Shingles infection can only occur through direct contact and not through the air, but what is actually transmitted is the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which precisely triggers chickenpox in individuals who have never had it. The first symptoms of the virus, such as headache and fever, are very general and therefore can be mistaken for a simple flu. Specific symptoms of shingles such as burning, tingling, itching, and severe pain appear later, especially for people of advanced age, and after a few days a reddening of the skin(skin rash) followed by the appearance of blisters. Depending on the area affected by the virus, there may be additional complications: in the case where it affects the eye area, it is called ophthalmic herpes, while if it affects the ear area, one can contract Ramsay Hunt Syndrome type II.
Treatments and vaccination
The
vaccine
against chickenpox, which has become mandatory in Italy, obviously also helps to ward off the risk of shingles; however, according to some studies, since an adult in contact with a child who has contracted chickenpox develops immunity for shingles, the spread of the vaccine helps in a sense to spread the latent virus. There is also a specific vaccine for shingles (Zostavax), aimed at adults who have contracted chickenpox in the past, which according to some U.S. studies reduces the risk of being affected by the virus by 50-70%. For those who have already contracted the virus, however, treatment with prescription antivirals can help reduce the duration and intensity of symptoms until complete regression of the infection, which generally occurs after 2-4 weeks.