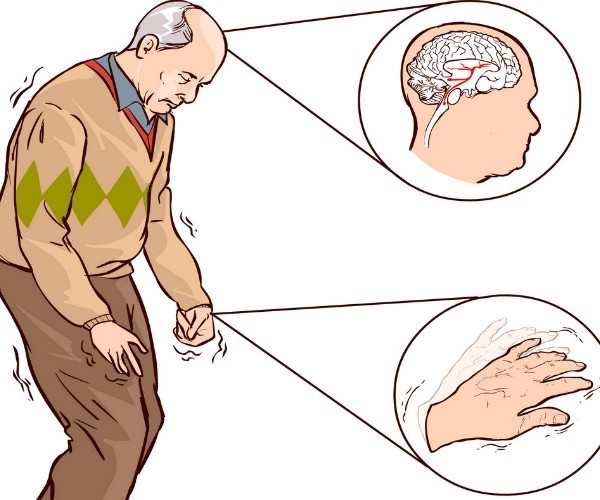
Memory is a function of the central nervous system that enables all animal beings to be able to make the best use of knowledge from experience: thus, old and new difficulties or problems from the outside world can be dealt with in an increasingly appropriate way.
In humankind in particular, memory has assumed a fundamental value both in the dissemination of language and in the development of culture.
The basis of memory is first and foremost learning, the ability to acquire new information from the outside world. This information, stored in particular brain areas, can be retrieved and used.
The three different moments underlying mnemonic processes are:
1 – the acquisition of new information or experiences from the outside world;
2 – the consolidation and preservation of information;
3 – the recall and use of archived information.
One of the most important aspects of memory is the consolidation of acquired information, which takes place through formation of new proteins, activation of genes, and changes in synapses and dendrites.
VARIOUS FORMS OF MEMORY
Based on how long information is stored in brain structures, two different forms of memory can be distinguished:
1 – short-term memory
2 – long-term memory
In short-term memory, information is retained only for a short period of time, seconds or minutes; in long-term memory, information is also available for long intervals of time, even years.
SHORT-TERM MEMORY
Short-term memory is the ability to retain and recall a memory acquired shortly before for only a very short time interval (thirty seconds to two minutes). Within short-term memory, there is what is known as immediate memory or working memory, which allows information to be stored and used only to implement a particular task.
LONG-TERM MEMORY
It is the process of learning that is completed with the preservation and subsequent consolidation of the acquired information. This process can occur actively with the individual’s personal commitment, but also without direct participation. It is also worth noting the distinction of long-term memory into implicit and explicit.
Implicit memory, also called procedural memory, is that related to the performance of activities, such as swimming, riding a bicycle or playing a musical instrument. It is closely related to training and is recalled to mind unconsciously. Explicit memory, also called declarative memory, is related to events, people, situations, places or objects. It is called to mind consciously and always needs awareness. It is the memory of spoken language or related to previous experiences. Forms of explicit memory are:
– episodic or autobiographical memory, which is about personal experiences or events in one’s life;
– semantic memory, which refers to notions, concepts or general cultural knowledge. However, not all memories are stored. Proper memorization requires a selection of information, which is based both on the subject’s interest in a particular topic or event and on his or her ability to pay attention and concentrate. Long-term memory, as opposed to short-term memory, involves a whole series of changes to neurons, synapses and dendrites. Processes of neurogenesis, with formations of new neurons, are probably also involved in a particular encephalic structure called the hippocampus, which, contrary to common belief, continues to produce new neurons throughout life.