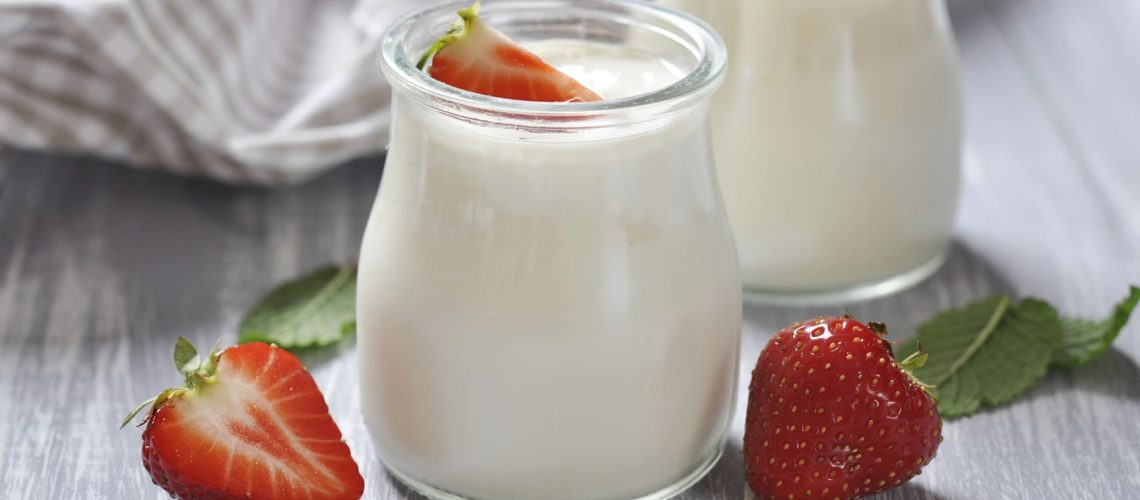
Yogurt is one of those foods that are very often underestimated but, on the contrary, are rich in nutrients that are essential for the well-being of our bodies, both in adulthood, but also and especially for young children. In fact, parents often do not give due importance to Yogurt, even though it represents a food that should always be present as part of a complete diet for their child. It represents a good substitute for milk; in fact, it can be included from the earliest stages of weaning, as it helps meet the calcium requirements of infants.
The nutritional values
As already anticipated, Yogurt is a food rich in nutritional values that provide for the well-being of our body. In addition to being highly digestible and with excellent satiating power, it is rich in high biological value protein, contains a higher availability of iron and zinc, and, in addition, has levels of folic acid 10 times higher than those of milk. Yogurt, moreover, is a popular food for both adults and toddlers. In fact, it is used by mothers mainly to make fruit more palatable for their children, but also for making tasty low-fat desserts that are ideal for healthy eating.
Yogurt and Sports
Yogurt is also highly recommended for those who engage in sports activity, both before and after exercise. If taken before exertion (soccer, gymnastics, swimming, dancing, etc…) it does not burden digestion but consistently provides the calories required by physical exertion. If taken after exercise, on the other hand, it replaces consumption without unnecessarily overloading the body or interfering with normal eating rhythms, allowing you to arrive at the next meal with a proper sense of appetite.
A health ally
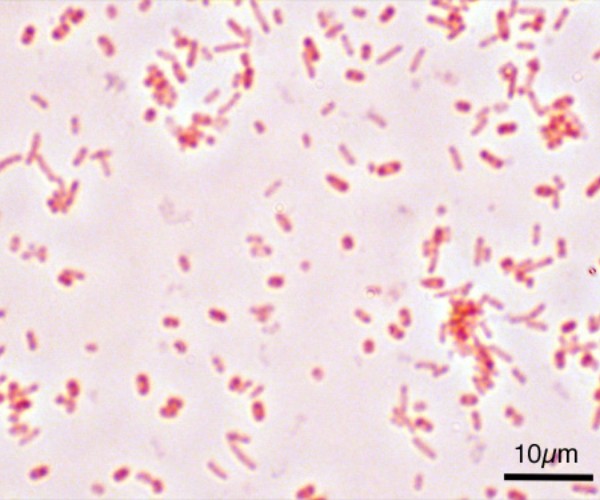
There are many physical benefits that come from regular intake of Yogurt, and they affect multiple parts of our bodies. To begin with, Yogurt is an ally for preventing tooth decay and, most importantly, for controlling bowel activity in both constipation and diarrhea. This is due to the presence of two lactic acid bacteria (food microorganisms used in the production of fermented milk) which implement the transformation of milk into yogurt. These are milk enzymes that, until the product expires, are alive and viable in very large quantities (about 10 million live enzymes per gram of Yogurt). Streptococcus Thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus are the milk enzymes that carry out the transformation from milk to yogurt.
In the face of often wrong situations and lifestyles, whether due to stress, poor diet, drug use or otherwise, the normal balance of the bacterial flora can be easily altered, and this is where the lactic acid bacteria in general and, specifically, those contained in the Yogurt assume a key role in rebalancing the bacterial flora and bringing it back to a state of normalcy.