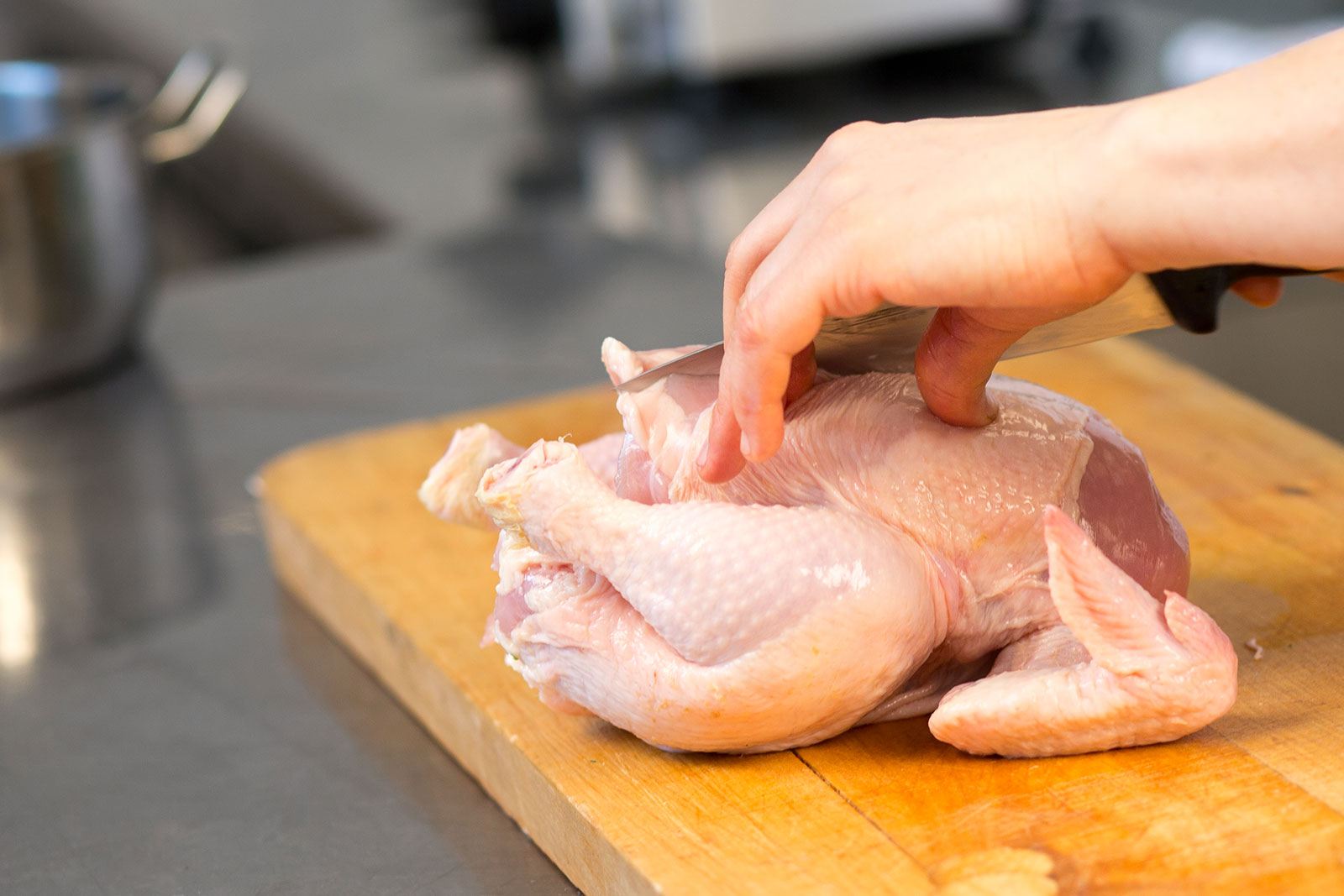
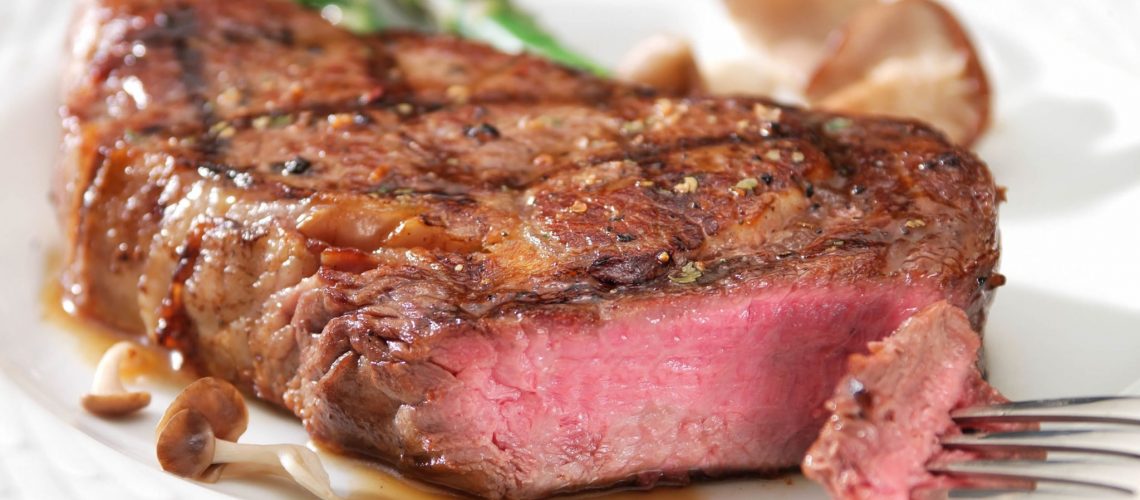
Meat has always been one of the most consumed and appreciated foods by humans, not only for its taste but also and especially for its many nutritious properties, which are essential for the growth and development of our bodies. Meat, despite its high nutritional value, should still be included in a varied and balanced diet, to avoid arising in food problems and deficiencies due to the lack of other foods important to the body or, conversely, problems due to too much consumption of meat itself. However, this food is essential in weaning and the very early stages of children‘ s growth, as they have very high protein requirements to develop healthy and strong. Due to the presence of iron also, meat helps prevent and treat any anemia due to its possible deficiency, and it stimulates the body’s immune system by helping it effectively fight infections.
Meat is also rich in “noble” proteins, that is, all those proteins that help ensure and regulate the growth of the human body, as well as provide all the essential amino acids that the body cannot synthesize on its own. These proteins also are extremely important for the construction and maintenance of all cells, mucous membranes, and muscles. In addition to protein, meat is also rich in
vitamins
, among which are certainly those of the B group, especially vitamin B12, which is important in red blood cell formation, nerve function and energy transformation processes.
Meat in the Mediterranean diet
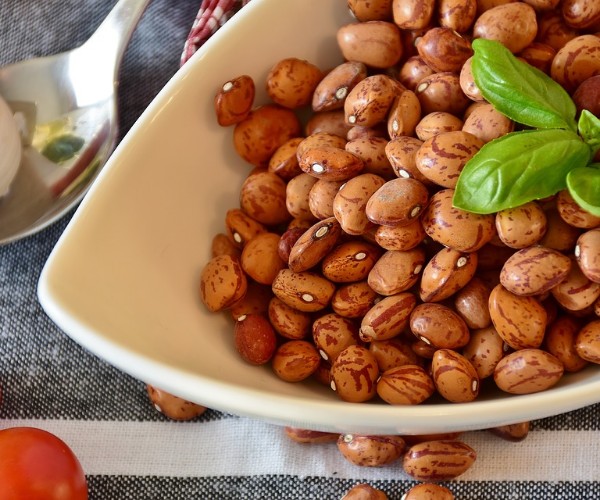
A proper diet cannot be based on the intake of a few specific foods, but must include a broad swath of foods so that the body is provided with all the nutrients it needs to develop and grow in the best possible way. For this reason, meat is included in the
Mediterranean
, one of the dietary patterns most corroborated by nutritionists precisely because of its variety of foods and nutrients. Recognized and appreciated by all major scientific communities, the Mediterranean diet is considered the ideal dietary style for safeguarding the body’s well-being and preserving it from major chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity and cancer, as well as decreasing cardiovascular disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. The basic elements of the Mediterranean diet, besides meat of course (in not excessive amounts), are: vegetables, legumes, fresh and dried fruits, olive oil , cereals and fish, and sweets in more moderate amounts.
Returning to meat, Italian meats are among the most controlled in the world, thanks to strict regulations and one of the most structured health systems in the world, with continuous inspections and controls throughout the processing phase.