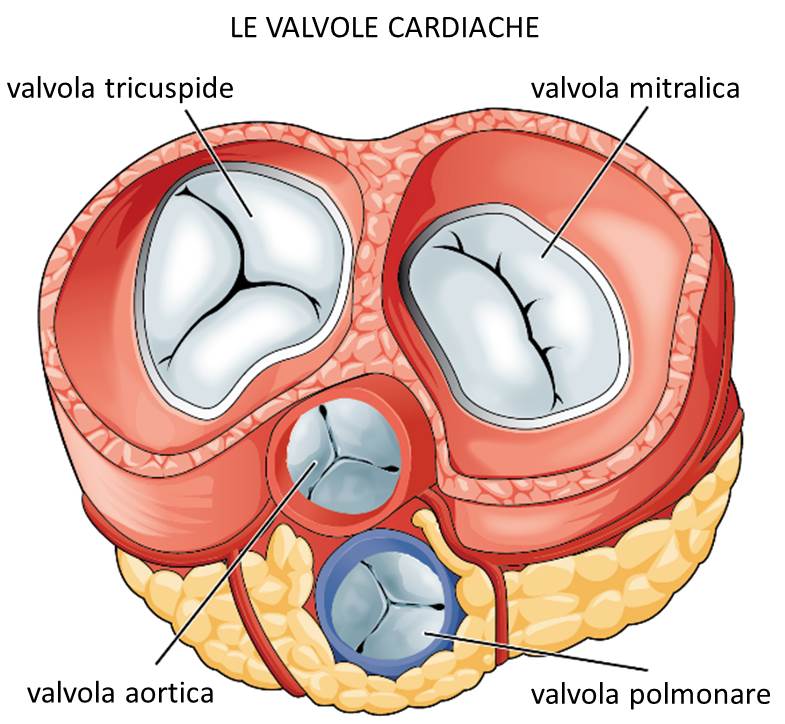
Body water is distributed in two different compartments: intracellular and extracellular, which in turn is divided into intra and extravascular or interstitial.
Electrolytes are distributed differently in the two compartments: usually potassium and phosphorus are found in the intracellular, and sodium and chlorine in the extracellular. The concentration of electrolytes in fluids is called osmolarity. This ranges between 275 and 290 mosm/kg and is provided by an average daily water intake of about 40 ml per kg of body weight. It is obvious that it is not enough to take only water, but also electrolytes in the right proportions.
Malnutrition occurs when the intake of nutrients does not match the nutritional, qualitative and quantitative needs of an organism. The main causes of malnutrition are:
- Excess food
- Poor food quality
- Food insufficiency
- Increased need or inadequately compensated losses
Source: Handbook of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition by Franco Contaldo et al.