HOW TO RECOGNIZE THEM
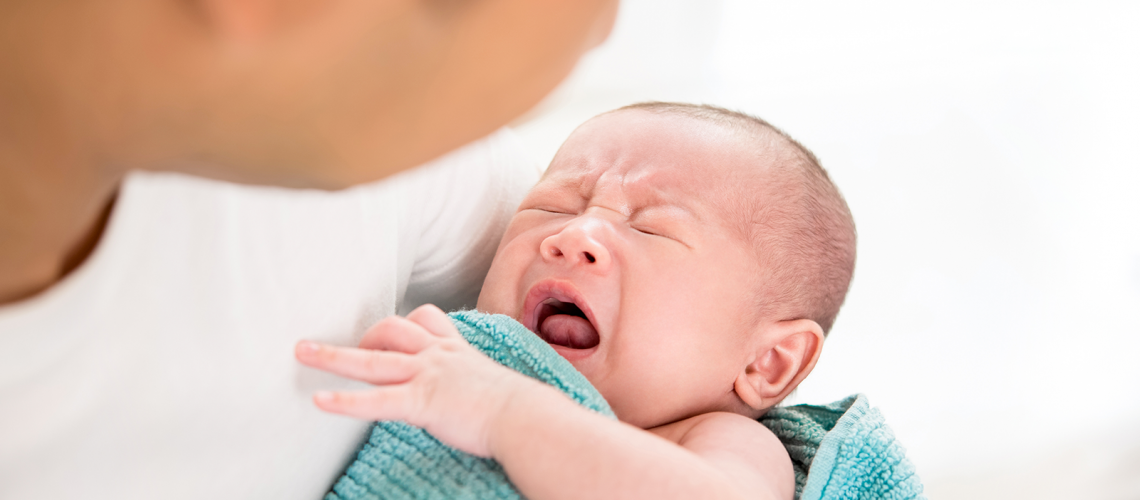
Gas colic is defined as an acute, benign event that affects about 50% of infants (most often in the first 6 weeks of life). Based on data from the literature, colic occurs on average in at least one in five infants.
Colic usually arises after a feeding, particularly in the evening hours: the infant screams, cries, fusses, alternately flexes his legs over his abdomen, which is tense and sore to the touch, and arches his back.
Gas emission may occur during crying, which is sometimes associated with resolution of the episode. They tend to occur mainly in the evening hours and can vary in duration. Although it is a common disorder in infancy, colic often causes serious concern for parents and can even foster depression in mothers, who feel disoriented and helpless.
All of the following criteria must be met for diagnosis:
- Age less than 5 months;
- onset with recurrent and prolonged episodes of irritability, agitation, or crying reported by parents in the absence of obvious causes that cannot be prevented or resolved;
- Absence of growth arrest, fever, or pathological signs.
In any case, this is a diagnosis of exclusion that is made only after other possible hypotheses or causes have been ruled out. On the other hand, in less than 5% of infants with acute crying, an underlying organic disease is really present.
ASPECTS TO BE EVALUATED AND REPORTED
- Timetable and possible periodicity of colic.
- Association with particular stimuli and/or environmental or food elements.
- Possible presence of family tensions or concerns.
- Infant’s reaction to any remedies taken (e.g., massage).
- Presence of other digestive complaints (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea) and/or abdominal pain/reactivity outside of episodes.
CAUSES AND MECHANISMS
Among the possible factors suggested were:
- Gastrointestinal immaturity.
- A change in mother-child bonding and gastrointestinal failure with fermentation in the intestines and flatulence, but rightly no specific cause has been identified. Some hypotheses suggest analteration in intestinal bacterial flora, others a possible food intolerance (which, moreover, in atopic children could also manifest in this way) or digestive difficulty, and still others propose a socio-psychological hypothesis, with the mother-child relationship being the focal point).
It is therefore likely that infant colic is the consequence of a synergistic interaction between biological and behavioral factors. Colic generally does not result in long-term complications but induces frustration in parents, amplifies postpartum depression, and is a cause of doctor visits and stress for the family
CARE AND PREVENTION
If the crying lasts too long or occurs with excessive frequency and especially if fever, decreased liveliness, and/or enlargement of the abdomen occur, the pediatrician should be consulted. Quite different, however, is the situation with crying and fussing after meals, which calms down at least temporarily in two or three minutes by picking up the baby. Colic, in fact, is benign and, depending on the case, as evidenced by numerous traditional remedies, benefits from manipulation (massage on the abdomen clockwise around the navel, rocking) and the use of probiotics. Preventive use of preparations that can promote gas expulsion (e.g., simethicone-based) or homeopathic or herbal medicines is common.