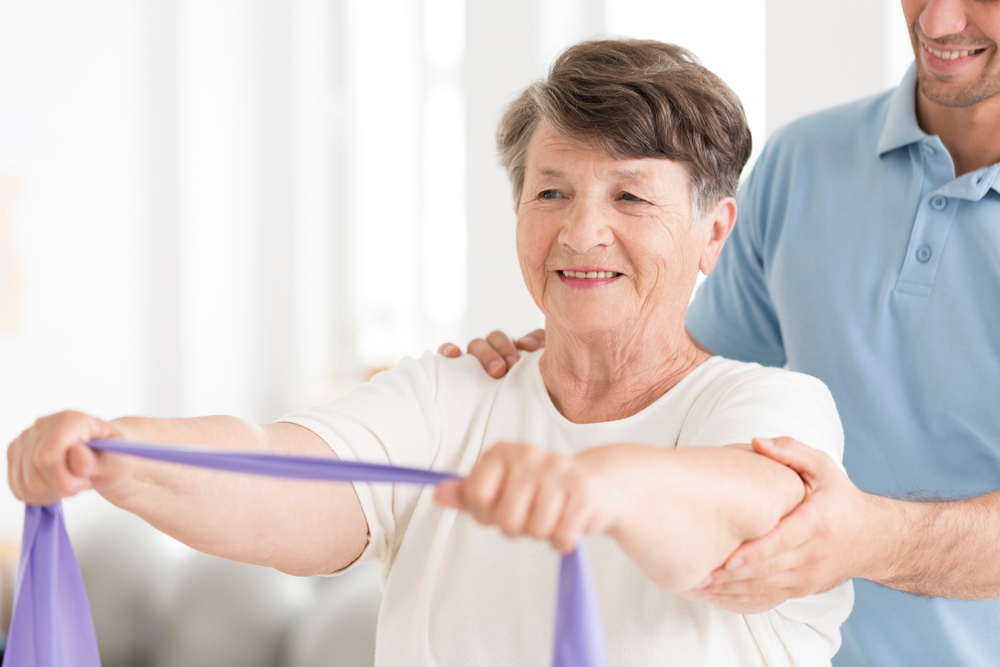
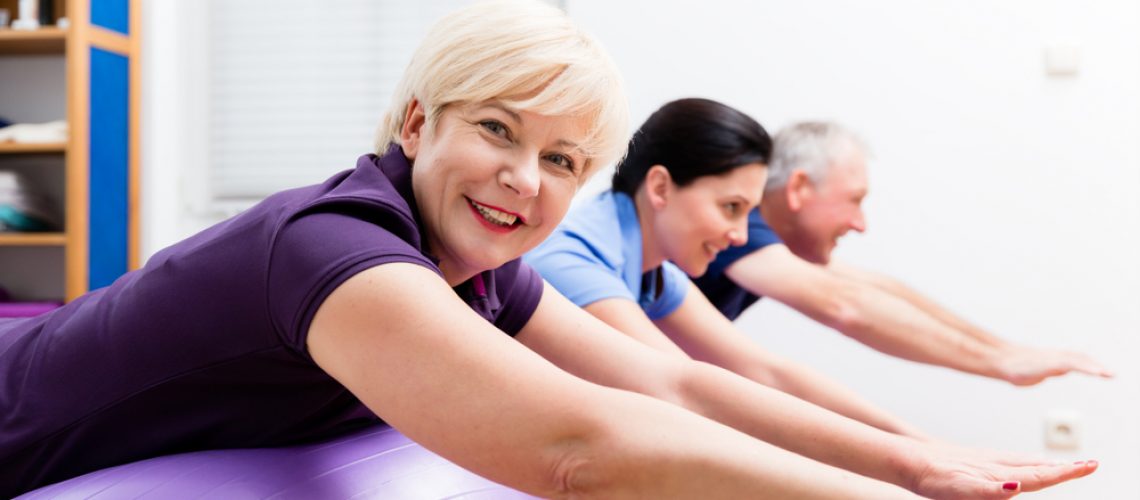
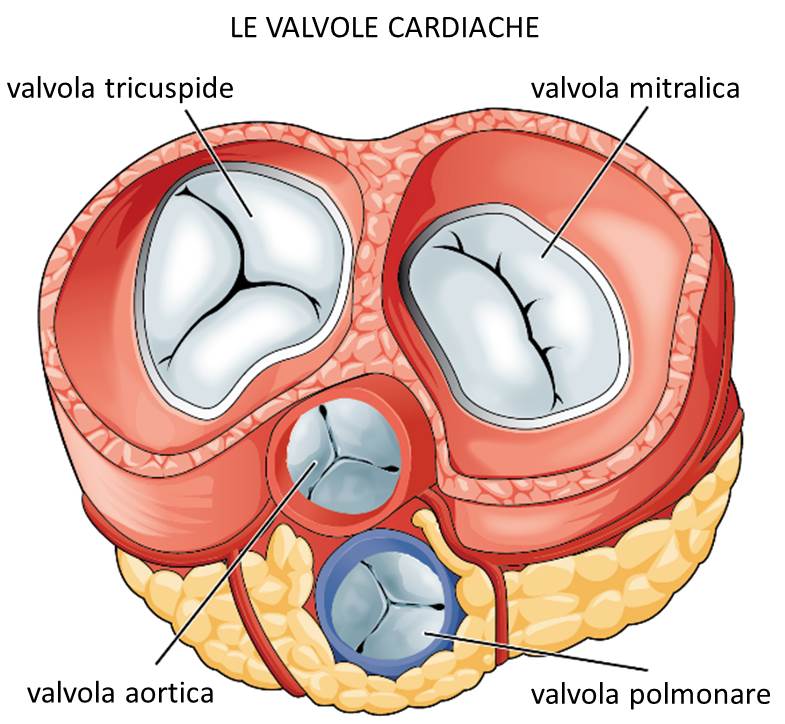
Cardiac rehabilitation according to a currently accepted definition in Europe, the United States and Canada is “the sum total of interventions carried out on the patient to ensure the best physical and psycho-social condition.” Such improvement enables patients with chronic heart disease to resume their role in society. The main goal is to normalize the elements of disability, established subsequent to acute cardiac events. Usually, ideal candidates for physical training are patients in the low or intermediate risk range. Those who undergo the training can achieve the following benefits:
- Reduced mortality.
- Improved exercise tolerance.
- Better overall feeling of well-being.
- A more frequent return to work.
For these reasons, rehabilitation through physical training is an essential component of the coronary artery disease patient’s care program. In the United States, only 11% of those affected by a coronary event underwent rehabilitation, but in recent years the percentage has risen to nearly 40%. As for Italy, the exact figures are not known. The benefits brought by cardiac rehabilitation on cardiovascular mortality rates may be less significant than documented by major trials, performed a few years ago. Therefore, the importance of exercise can be traced back to its effect on mortality, but also to its role as a catalytic event, promoting other aspects of rehabilitation.
A physical rehabilitative training program includes the following stages:
- Medical evaluation
- Risk stratification
- Exercise prescription
- Patient education
- Information aimed at patients about their disease
Physical training also sets short-term and long-term goals.
Source: Mediserve Cardiovascular Rehabilitation