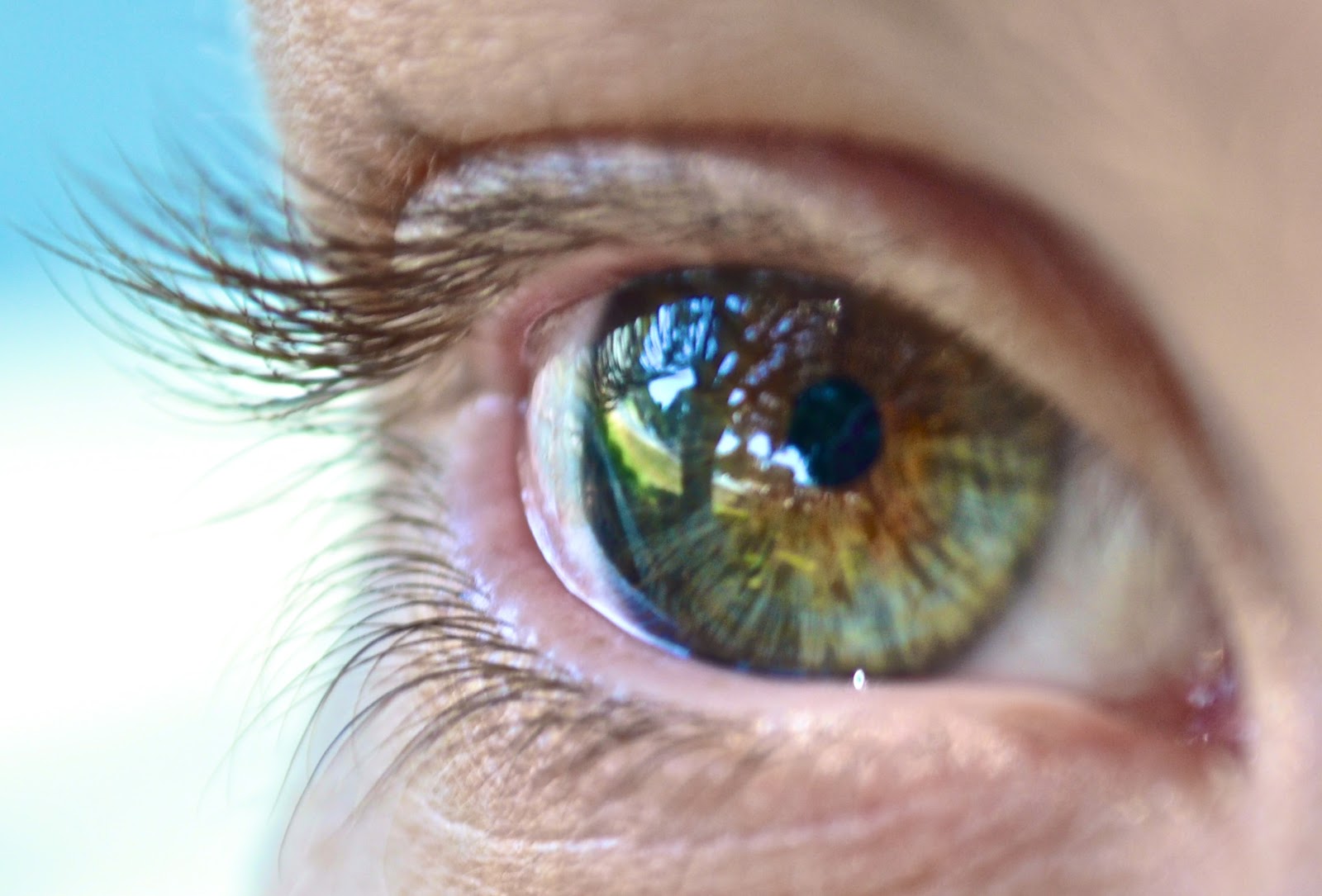
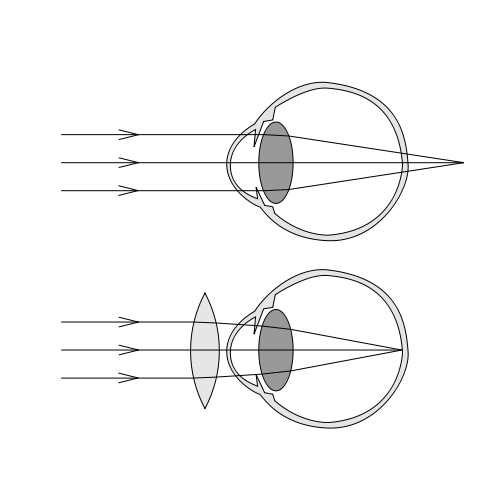
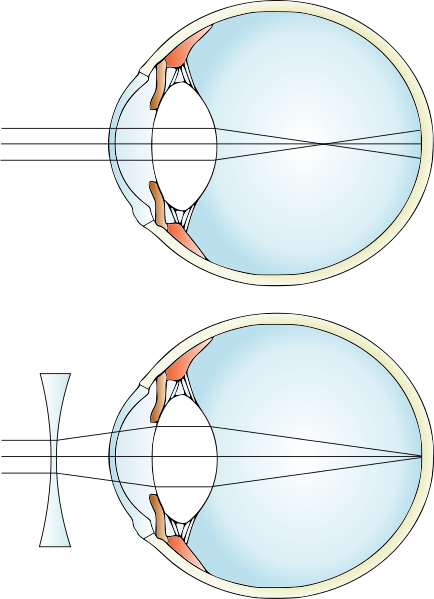
Hypermetropia indicates a visual defect, which causes blurred vision of near objects and sharp vision of distant objects. It is possible that the patient with hypermetropia may not realize it right away, as the hypermetropic person, like the emmetropic person with no vision defects, by changing the shape of the lens is able to remedy the condition. This involves the use of the so-called “accommodation reflex,” which is characterized by the modification of the globularity of the lens according to the proximity or distance of visual targets. Usually with age, accommodation decreases and hypermetropia occurs.
Causes of hypermetropia
Hypermetropia can be caused by several circumstances, but usually the most likely one is heredity. Other causes could be:
- The diameter of the bulb shorter than normal
- A lower than normal curvature of the lens surface
- Absence of the crystalline lens
What are the symptoms?
As with any condition, hypermetropia can also cause cert ain symptoms. These can be:
- Burning
- Tearing
- Hypersensitivity to light
- Headache and eye pain subsequent to reading, writing, or computer work.
How to remedy hypermetopia?
In hypermetropic patients, it often happens that images are focused behind the retina and in this way newspaper characters, for example, appear blurred, while more distant objects are brought into focus. Removing the problem, at least for the time being, is impossible, but there are several options to remedy hypermetropia. Contact lenses, corrective eyeglasses, and laser surgery can safely prevent the individual from feeling uncomfortable. Regarding the last option, Lasik is a surgical technique to treat farsightedness, which involves removing layers of the cornea to make the surface more curved.