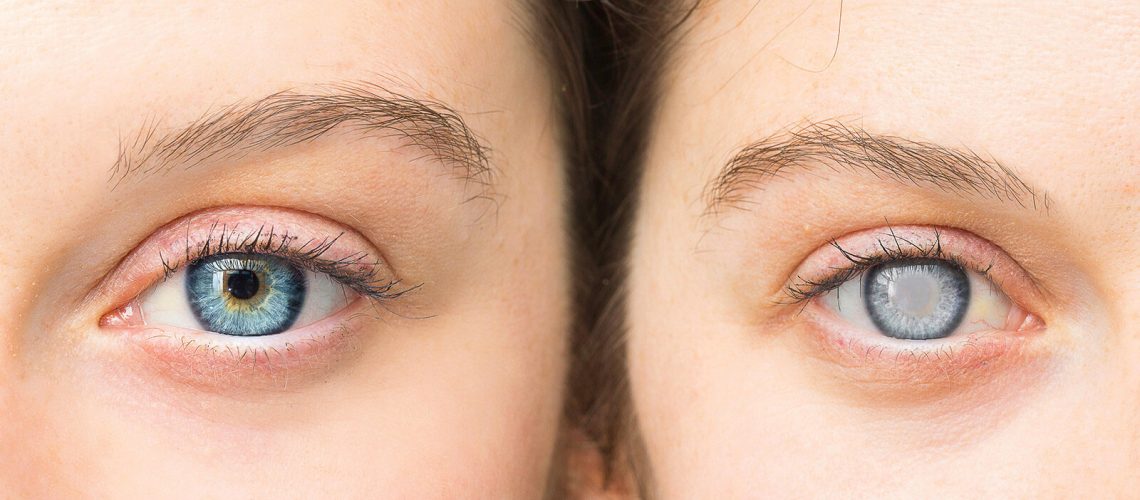
A cataract is a gradual and progressive clouding of the lens inside the eye.
It does not cause pain, but it can reduce light to the point of blocking it, making clear vision increasingly difficult, until complete blindness occurs.
Cataract is an eye infection whose causes are not known, although it is known that risk factors increase with advancing age, in the presence of eye injuries, as a result of diseases such as diabetes, following the use of drugs such as corticosteroids, and habits such as smoking and alcohol.
Cataracts can be diagnosed by a microscopic eye examination with pupil dilation to give the ophthalmologist a chance to observe the condition of the retina and optic nerve
The phenomenon of cataracts is usually related toaging, but sometimes it also occurs in young or , at any rate, not yet elderly people.
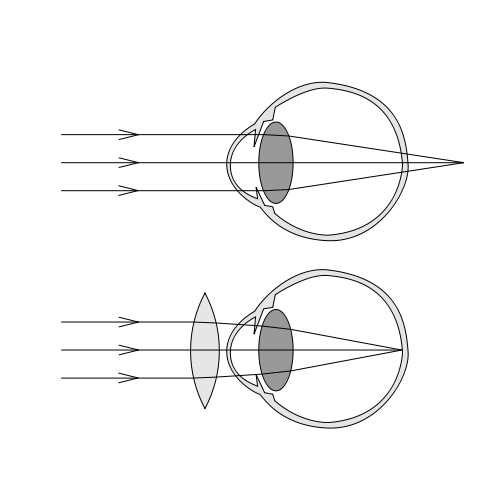
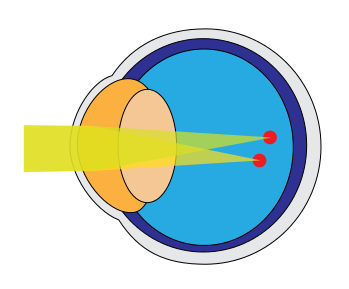
Cataracts can impair vision because they are an obstacle to the passage of light, which normally, passing through the lens, transmits and fixes sharp vision on the retina and from there reaches the brain through the optic nerve, but if there is a cataract obstructing the passage of light then theimage appears blurred and fuzzy.
Just as with cataracts, an eye affected by myopia can give a blurred image, although cataracts are accompanied by other symptoms, such as blurring of images from both near and far, with veiled or smoky vision, which greatly limits the range of motion of those affected, such as driving a car, especially at night.
There are many symptoms caused by cataracts:
- Cataracts can cause a doubled image to be seen even when looking from only one eye.
- Bright glare is another of the recurrent symptoms of cataracts, where glare due to increased sensitivity to light is very common. Sunlight, house lights or even car lights during night driving can be dazzling to the eye.
- Color perception may also be altered and impaired by cataracts, so much so that one shade of color cannot be distinguished from another, appearing some colors completely faded and others altered.
Since cataracts can be compared to a kind of additional lens, they can give the sufferer the impression that he or she no longer needs reading glasses, acting as the cataract itself as a magnifying glass, but only as long as it does not increase in thickness, blurring vision completely.
When there is a gradual and consistent loss of vision due to the presence of cataracts, a surgery of removal, which takes place on an outpatient basis, during which the opaque lens is removed and replaced by an artificial lens, either in one eye or both, at two different times. This is a safely effective intervention that restores a clear and no longer blurred vision condition.
Significant advances and developments in cataract surgery have also meant that both near and far vision can be corrected, sometimes making it possible to reduce or completely eliminate reading glasses once the surgery has been performed. The best results after cataract removal surgery may become apparent after a couple of months.