Cardamom
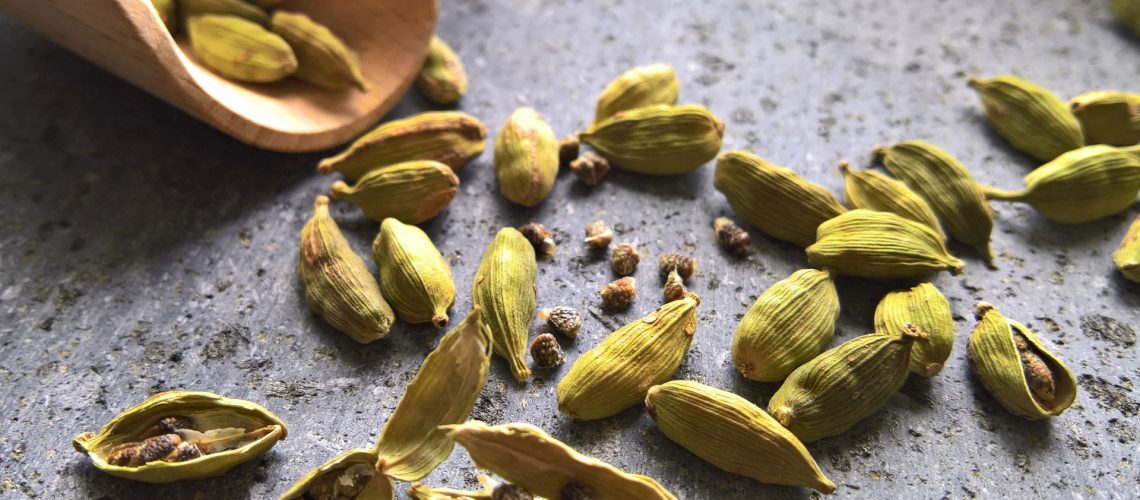
Refined, rare, fragrant, pungent taste, aroma somewhere between mint and eucalyptus. These are some of the characteristics that well describe cardamom. A spice belonging to the Zingiberaceae family, the same as ginger as you might guess from the assonance, among the most expensive in the world after saffron and vanilla. It is the seeds, contained in a capsule, that are ‘valuable’ for a variety of uses: in cooking, to spice dishes, flavor desserts and pastries in general, to give tea, coffee, liqueurs and beverages a sweet and sour taste, in medicine to treat some specific diseases, and in cosmetics in the form of essential oil.
‘His’ territory. Do not expect to find it in the wild on Italian soil: of course, you can grow it at home, on your balcony, and you will soon find out how or buy it in herbalist stores and dedicated stores. In fact, its origin is ‘far away’: it originates and is mainly grown in Nepal, India, Cylon depending on the variety. In fact, cardamom loves warm-humid climates, where it grows and grows to be able to reach 20 meters in height; it has long, narrow leaves and whitish flowers similar to orchids. But it is the fruit that attracts the most attention and interest: a green or brown capsule inside which are housed the seeds, 4 to 8 usually, also dark in color that can be used whole or ground. If you do not intend to grow it, it is best to buy it in pods because the seeds easily lose their aroma and then consume them ‘fresh,’ shelled at the time or dried. It should be stored in an airtight container to preserve its original qualities intact
Varieties. Cardamom is extracted from two plants:Elettaria, the most common and known by the scientific name Elettaria cardamomum, andAmoxmum. Specifically, Electaria is divided into other subspecies according to territoriality, viz. Elettaria cardamomum which is also the most prized and intensely flavored found in India’s Cardamom Hills, a region in Kerala and the Malabar coast where it can still be found in the wild, the Elettaria repens instead originating in Ceylon, Sri Lanka. While Amomum compactum, widespread mainly in Myanmar and Thailand, is the most bitter variety, known as black cardamom of Siam. To summarize: there is the milder, more aromatic green cardamom and the brown/black cardamom with a more bitter flavor, tending toward smoky, which is also the cheapest. Sometimes you can also find it white, but the seeds have been bleached and have a lower quality. Varieties also determine different uses:Elettaria cardamomum is used as a spice and in medicine. It is sometimes smoked and is the main food of the larvae of a type of moth, whileAmomum is an ingredient in traditional Tibetan, Indian, Chinese, Iranian, Korean and Vietnamese medicine.
An ancient spice. Even among the oldest in the world. It has been growing in India for more than 5,000 years and is also called “Capalga” and “Iliachi,” and has been used in the centuries since for different purposes. For example, the Ancient Egyptians used the seeds to brush their teeth or after pulping as a ‘means’ to freshen breath; in Europe, where it arrived by caravan routes, the Greeks and Romans employed it as a perfume; in the Middle Ages, however, it was used as a preservative for food. Today it is also widely used in cooking, especially in ethnic gastronomy, to give an aphrodisiac touch to foods: it is used as an aroma in the preparation of Turkish-style coffee, Arabic coffee, and Iranian tea; in Middle Eastern, Iranian, Turkish, and Indian cuisine it is among the favorite spices for flavoring desserts or is used in spice mixes. In India, cardamom is an integral part of garam masala, precisely a mixture of spices (our curry), or of the masala chai, a tea spiced with milk, as well as being used to flavor rice or mixed with betel leaves, a climbing shrub typical of India and Malaysia, and areca fruit, a kind of palmetto, to form betel precisely, a ‘patty’ useful for freshening breath and aiding digestion. Still in China, cardamom flavors roasted meat dishes, in Vietnam it is combined with broth for noodle soup called Phở, and finally in Ethiopian and Eritrean cuisine the seeds are used in the preparation of Himbasha, a celebratory bread. Among the Nordic countries, it is mainly used in Sweden, Finland, and Germany for the preparation of traditional dishes, breads, and baked goods, but it is also often combined with cinnamon and cloves. Finally in spirits it is added in some coffee or nut liqueurs, vermouth and bitters, but it can also be mixed into spicy or tropical fruit cocktails, with unusual outcomes.
Cardamom cultivation. If your passion is gardening and you love to see essences grow that will later flavor your dishes, here is how you should go about growing cardamom. There are some rules to follow, regarding:
Exposure. Cardamom should be placed in a shady yet bright location, that is, never directly exposed to sunlight. In fact, the ideal temperature for its cultivation is around 22°C, in areas with minimum temperatures below 10-16°C it should be grown in pots so that it can be easily sheltered in winter.
Terrain. It needs an acidic pH soil, with values between 5.1-5.5, which should be constantly moistened. In case the soil is very clayey, it should be lightened by mixing it with a good amount of sand. Most importantly, care should be taken to water/water the soil regularly from the resumption of the growing cycle, keeping it moist, never soggy or soggy. In winter, irrigation should be kept to a minimum and implemented only if the soil is dry, while in summer it should be more frequent to promote fruit ripening.
Fertilization. The soil should be treated with a specific granular fertilizer for acidophilic plants, distributed at the base of the head. In full soil, the plant needs supporting fertilization with mature manure mixed with plenty of peat. When to carry out fertilization? At the end of winter, mixing it into the substrate being careful not to damage the roots, then repeating it cyclically every 3 months.
Growing in pots. Regardless of the climate, it remains a good choice to grow cardamom in a pot that should be no less than 40cm deep and 30cm wide so as to encourage the plant’s growth. While re-potting in a larger pot, it should be done when the cardamom’s roots emerge from the water drainage holes of watering, using a fresh, loamy soil with a pH between 4.5 -7.
Sowing. It is recommended to use seeds collected from a plant at least 5 years old, which should then be layered on the surface of the potting soil 2.5 cm apart. Having done this, the seeds should be covered with a layer of soil two to three millimeters thick, mixed with a little sand, taking care to keep it moist until the seeds germinate, usually after about 30-45 days. Once nurtured, the new seedlings should be constantly watered and allowed to harden, and after about 90 days they can be transplanted outdoors or placed individually in a deep pot.
Propagation by rhizome division. Rhizomes, you may remember, are the shoots and should be chosen from well-developed plants. Having identified the most suitable one, we gently pull it out of the soil and divide the rhizomatous root into 2-3 portions, each should have well-formed secondary roots. This is because they will have to be interred instantly in a hole suitable for its size but never too deep so that it can take root and grow.
Planting. It is made in holes 2.5 to 4 cm deep, 15 to 45 cm apart, depending on the width of the soil. After planting, the roots should be covered with soil set aside and compacted by hand to the height of the collar.
***
Clip
What do you still need to know? Certainly what are the best ways to harvest, store, or risk cardamom. Let’s go in order, then: the berries or capsules should be harvested while they are still green and unopened and placed to dry in the sun for a few days. They are then opened manually and the seeds are extracted, which in turn must be allowed to dry for about 15 30 days. Generally, berries are harvested 5-6 times within a year, 35-45 days apart, the time required for ripening. When they are ready, store the seeds in airtight glass jars in a dark, cool place.
Pay attention to pruning; you will only need to remove dry stems and damaged leaves. Cardamom is a hardy plant and is rarely attacked by pests, while do not neglect root rot, which can easily occur due to waterlogging in the soil, and keep an eye on the color of the leaves: if they turn brown, it means they are exposed to intense sunlight and the ambient humidity is not adequate for the plant if they turn yellow, the growing medium is too low in nutrients. An excellent ‘treatment’ is misting with water when the growing environment is too dry. Instead if you need to support the stems, tie them to supports driven into the ground at a distance of 5 cm from the base.