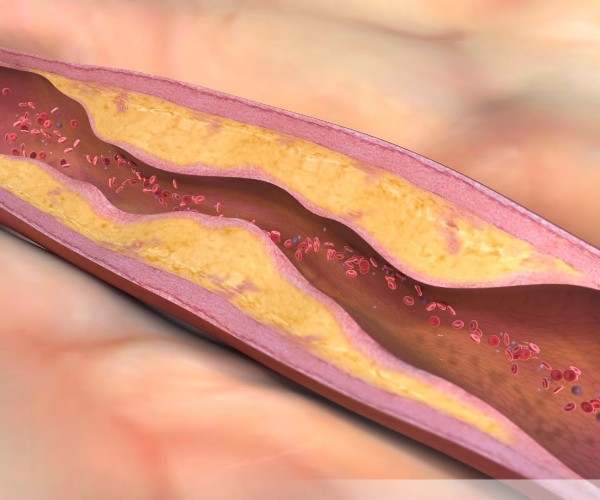
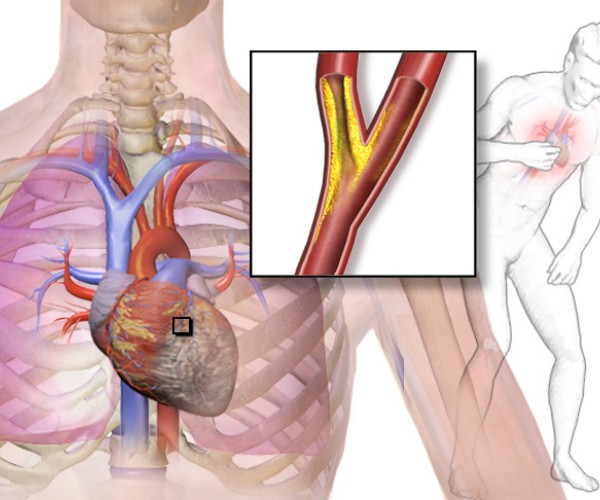
Once circulation has been restored in the patient suffering from Cardiac Arrest, following hospital discharge, one must wait for subsequent outcomes by ensuring that, in addition to spontaneous circulatory restoration, no neurological damage occurs.
Survival data also depend on some favorable factors such as:
- Rapid and effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Treatment performed n an emergency department with the possibility equipped with patient monitoring
- Initial rhythm of ventricular fibrillation
- Defibrillation performed for time of ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia
- Post-arrest treatment, such as circulatory enhancement therapy and use of cardiac catheterization
- In adults, maintaining a body temperature of 32 to 36°C over 24 hours, preventing the occurrence of hyperthermia
![]() Health Daily – Cardiac arrest. Hypothermia after resuscitation protects the brain
Health Daily – Cardiac arrest. Hypothermia after resuscitation protects the brain