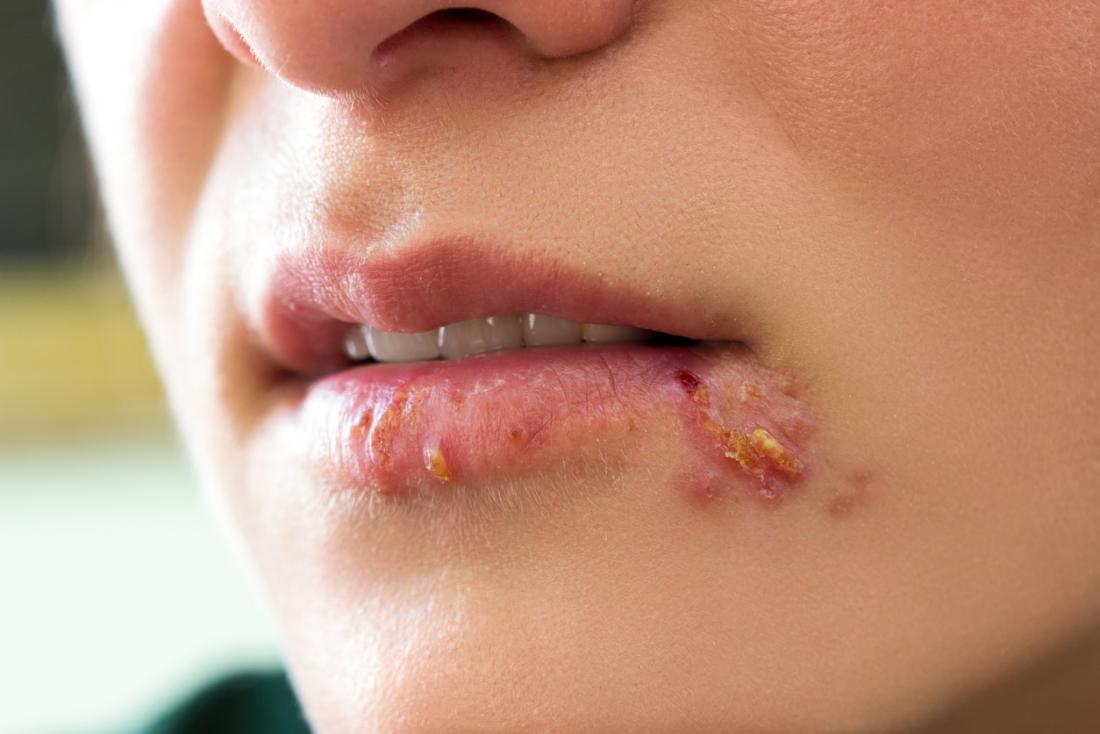
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease caused by human herpes virus 1 or 2. Causes ulcerative genital lesions. Diagnosis is clinical with laboratory confirmation by culture tests, PCR (polymerase chain reaction), or serological tests. Treatment is with antiviral drugs.
Genital herpes is the most prevalent sexually transmitted ulcerative disease in developed countries. It is caused by human herpes viruses 1 (herpes simplex virus-1) or 2 (herpes simplex virus-2), which are two of the 8 types of herpesviruses that infect humans.
After initial infection, the herpes simplex virus remains dormant in nerve ganglia from which it can periodically reactivate. When the virus emerges, it may or may not cause symptoms (i.e., genital lesions). Transmission can occur through contact with lesions or, more often, through skin-to-skin contact with sexual partners when lesions are not obvious (called asymptomatic shedding).