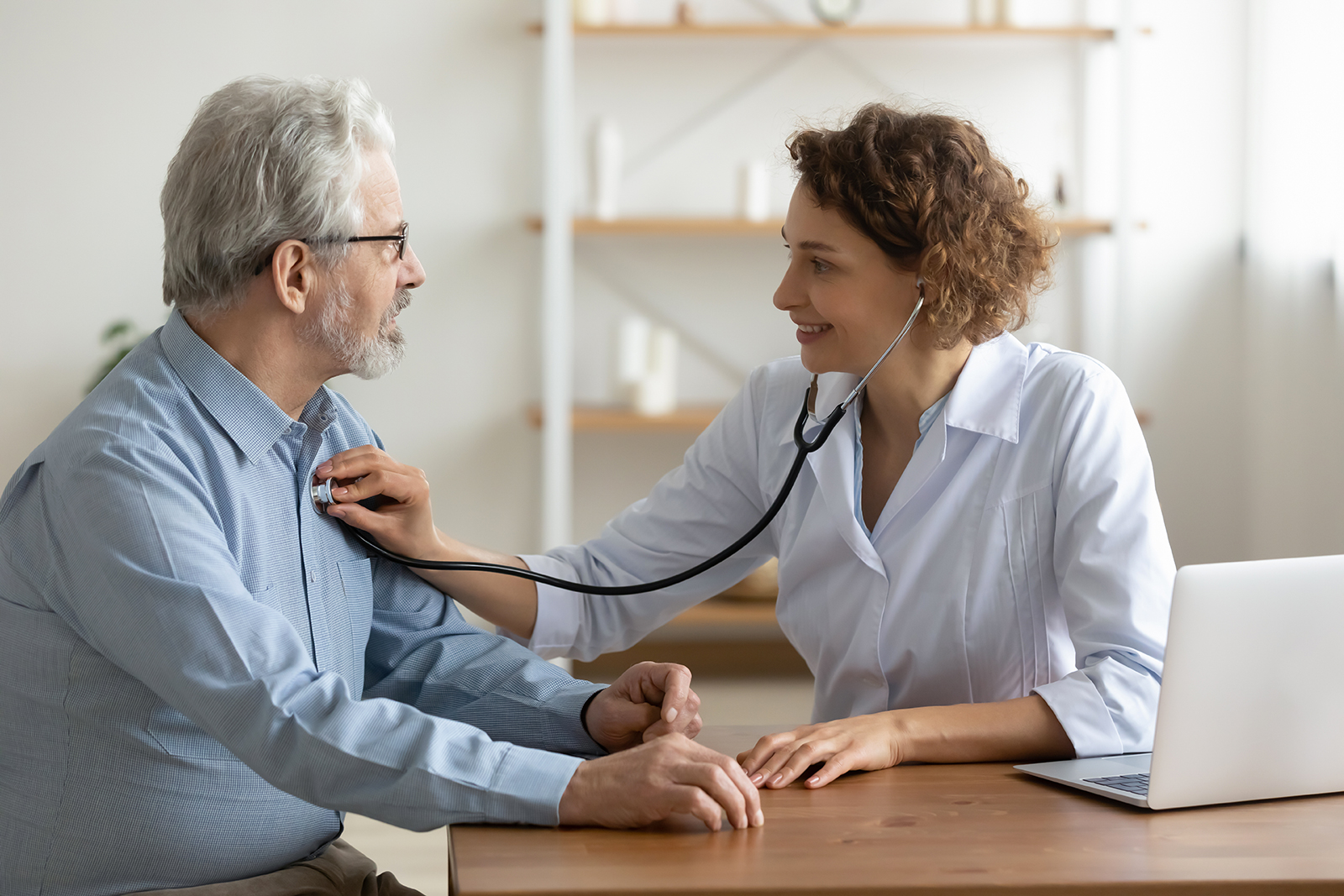
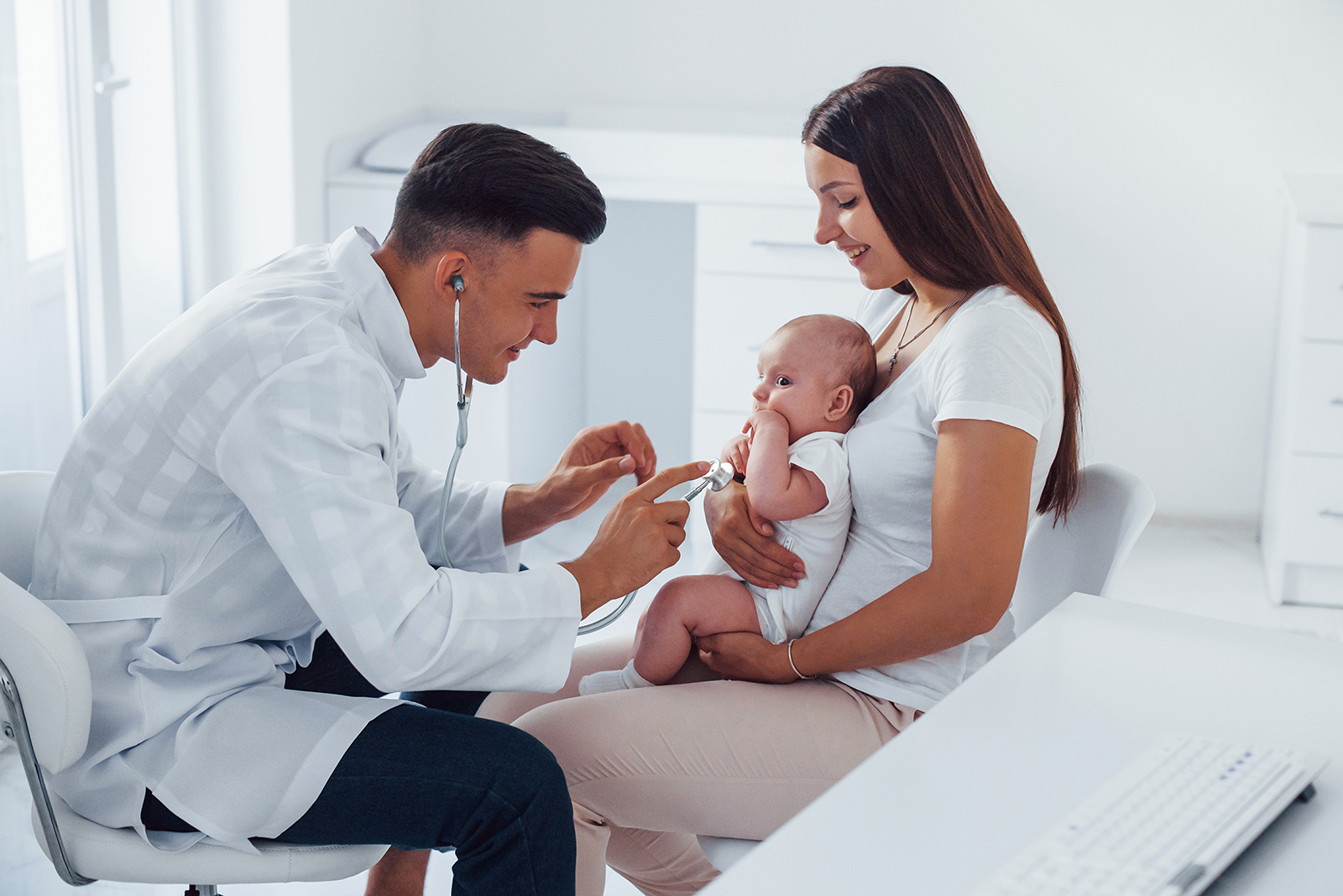
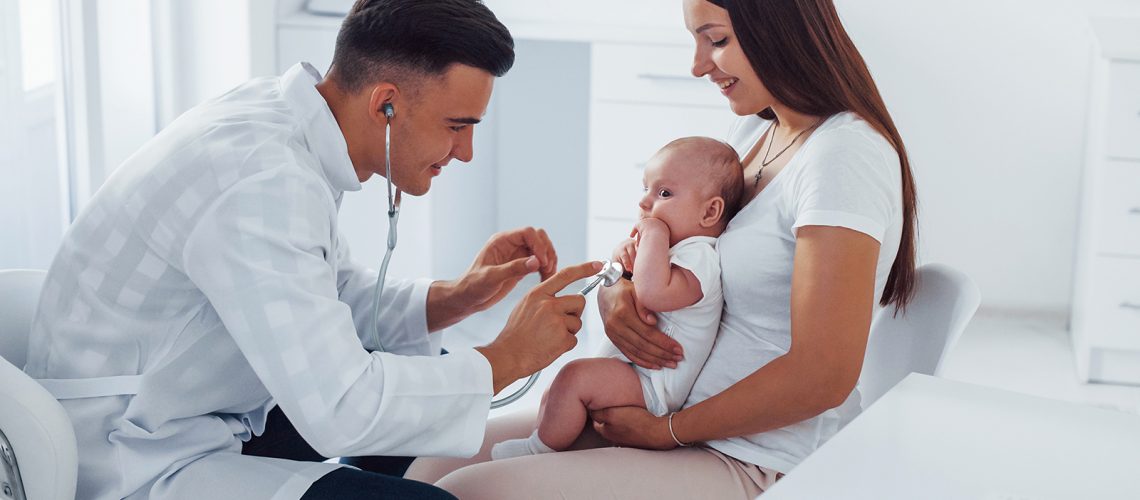
A child’s illness arouses anxiety in parents and the urgency of interventions to free him or her from a distressed state as soon as possible. This is further amplified when faced with a very young child who cannot put into words how he or she feels or ask what is happening to him or her.
There is first and foremost a need to find an explanation about the causes of the disease, inform parents about the causes, prognosis, and appropriate therapeutic interventions, and translate all this into language that can be understood and assimilated by the child.
The pediatrician and other professionals are within a complex relational mosaic that concerns both aspects related to the diagnosis and the correct understanding and adherence to the therapeutic program (medical history, lifestyles, moods, etc.) as well as the reception and containment of anxieties, fears, anxieties of the parents and finally an adequate level of communication with the child.
The most difficult experiences for a child to endure are not always the illness itself or its treatment but being frightened of unfamiliar things or, in the case of hospitalization, being away from home in an unfamiliar world populated by strange smells, sounds, practices and instruments.
What to do, for example, when convincing a child to undergo medical treatment?
The best attitude is to devote time to him: time to listen but also time for storytelling, for example through the use of fairy tales with animals or fantastic subjects with which the child can easily identify and which in a metaphorical way address and overcome difficulties similar to those experienced by him in actuality.
For older children, a notebook in which they can write down thoughts, questions, concerns about medications or curative interventions might also be helpful.
The notebook may be a kind of Ariadne’s thread for adults (doctor and parents) to navigate the labyrinth of the child’s state of mind, as well as a channel of communication with him.
Indeed, it must be remembered that a pediatrician’s educational intervention with a sick child should aim to prevent future difficulties and ensure acceptance of the disease in its limitations and chronicity, as well as to stimulate autonomy in general and foster socialization and confidence in one’s own potential. Only in this way can illness become a growth experience and not just an event with more or less traumatic contours.
Taken from: Management of emotional crisis in pediatrics.
Author: Maria Esposito Salsano, pediatrician.