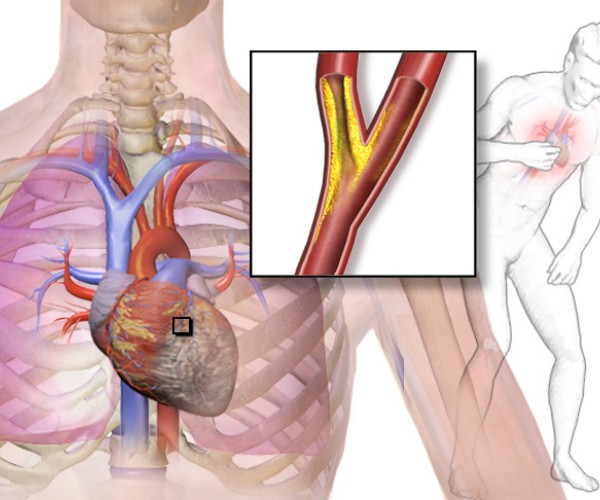
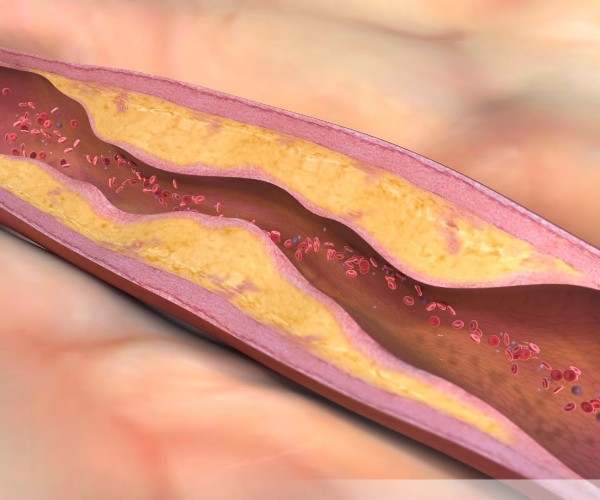
Embolism lung is a serious complication to be suspected in cases of dyspnea, in a patient at risk of deep vein thrombosis.
I Main symptoms are: sudden dyspnea, chest pain, syncope, tachycardia, hyperventilation, cyanosis, atrial and ventricular gallop, status of agitation and lung rales. Unfortunately, there are no specific tests, for to which the suspicion of pulmonary embolism should be based on the conditions of risk present and the results of investigations such as arterial blood gas analysis and radioisotopic scintigraphy.
Regarding the therapy to be carried out on the patient, heparin infusion, treatment of shock e/o decompensation as well as any alterations in acid-base balance, oxygen therapy, and morphine to reduce pain and anxiety are required.
Source: Medical Guard Handbook edited by Piercarlo Salari