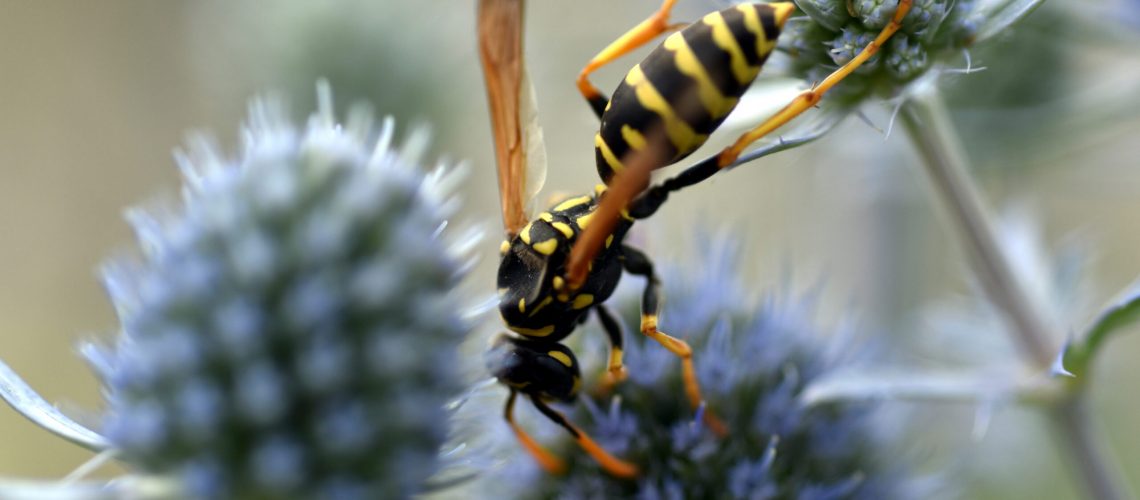
Wasp and other insect bites are common, especially during the warmer months when people stay outdoors longer. Generally, most people recover quickly and without complications. Wasps, bees, and hornets, are equipped with a stinger that has self-defense functions. The stinger of a wasp contains a poisonous substance, which is transmitted to the victim during a sting.
However, even when the stinger is not left after the sting the wasp venom can act causing the stung person significant pain and irritation.
It is also possible to have a serious reaction if you are allergic to the poison. In both cases, timely treatment is important to alleviate symptoms and complications.
But what are the symptoms of a wasp sting, or a hornet’s sting?
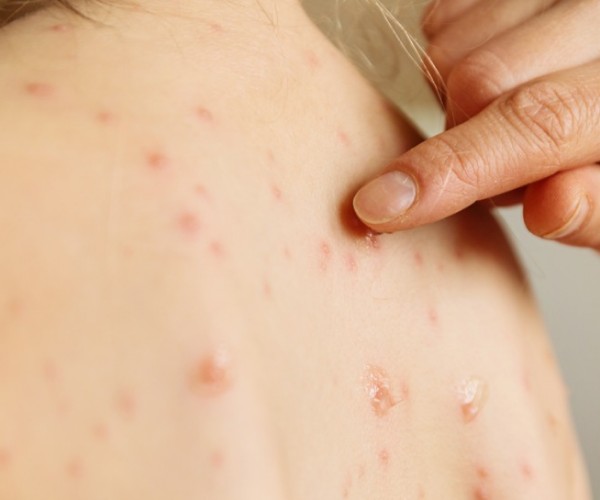
A sting from a wasp, bee or hornet is almost always painful, although sometimes the hornet sting may prove to be the one that causes the most intense painful reaction. Stings by these insects occur by a stinger that inoculates an irritating venom. In hypersensitive individuals, and it causes more or less severe allergic reactions. Most people who are not allergic to stings will show only mild symptoms during and after a wasp sting. Initial sensations may include sharp pain or burning at the puncture site. Redness, swelling and itching may also occur. Among normal reactions, it is likely that a mild skin elevation around the puncture site may develop. A small white mark may be visible in the middle of the rise where the stinger pierced the skin. Usually, the pain and swelling recedes within a few hours after the puncture. The more pronounced local reactions and symptoms associated with a sting from bees or other insects can be varied and bothersome especially for people allergic to wasp stings, but they do not have life-threatening symptoms, such as anaphylactic shock. Major local reactions to wasp stings include extreme redness and swelling that increase for two to three days after the sting. Nausea and vomiting may also occur. Most of the time, local reactions subside on their own within a week or so.
It is advisable to inform your doctor if you are affected by a large local reaction after an insect bite. You may need to take an over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamine medication to reduce discomfort. Having a great local reaction after a wasp sting for once does not necessarily mean that we will react to future stings in the same way. It might happen to have a strong reaction but without necessarily being affected by the same symptoms. However, a more significant local reaction might be the way the body habitually responds to insect bites. Of course, one must try to avoid being stung, so it is better to move relative to the insect’s flight area, also avoiding getting rid of it by trying to eliminate it as it would increase the risk of being stung. In addition, care should be taken to ensure that you are not near an insect nest, from which particularly aggressive swarms could emerge.
The most severe allergic reactions to wasp stings are referred to as anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis occurs when the body experiences shock in response to wasp venom.
Most people who are in shock after a wasp sting experience it very quickly. It is important to seek immediate emergency care to treat anaphylaxis.
Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction to wasp stings include:
- severe swelling of the face, lips, or throat;
- hives or itching in areas of the body not affected by the sting;
- breathing difficulties, such as wheezing or shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- sudden drop in blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea or vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- stomach cramps;
- weak or accelerated pulse.
It is possible that you may not experience all of these symptoms after a first sting, but it is likely on a new occasion you may experience only some of the symptoms. If you have experienced a history of anaphylaxis, you should carry a kit to protect yourself from the medical consequences of insect bites. The “kits ” contain adrenaline injections that one can self-administer after a wasp sting. Ready-to-use Adrenaline has several effects that help stabilize blood pressure, increase heart rate and strength, and help breathing return to normal.
Anaphylactic shock is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.