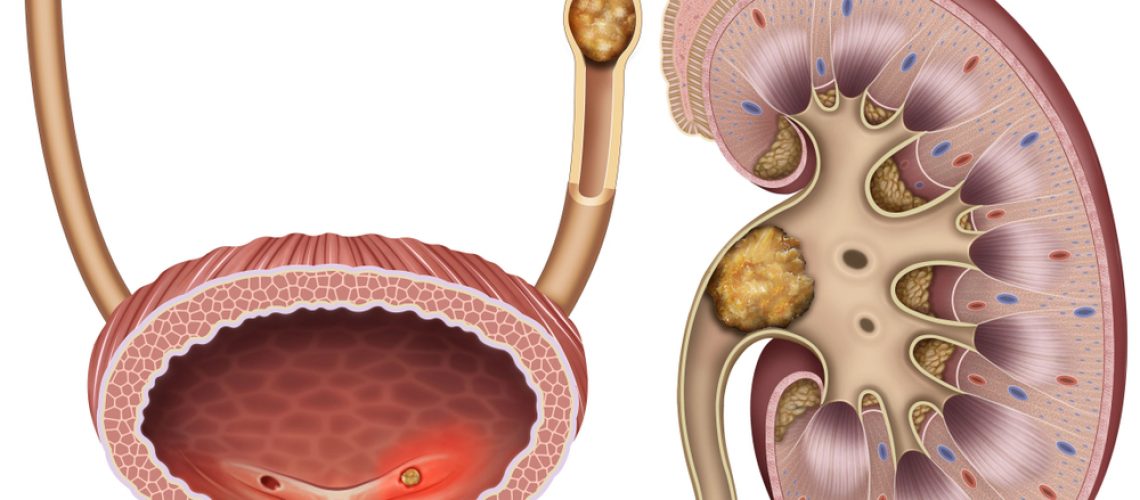
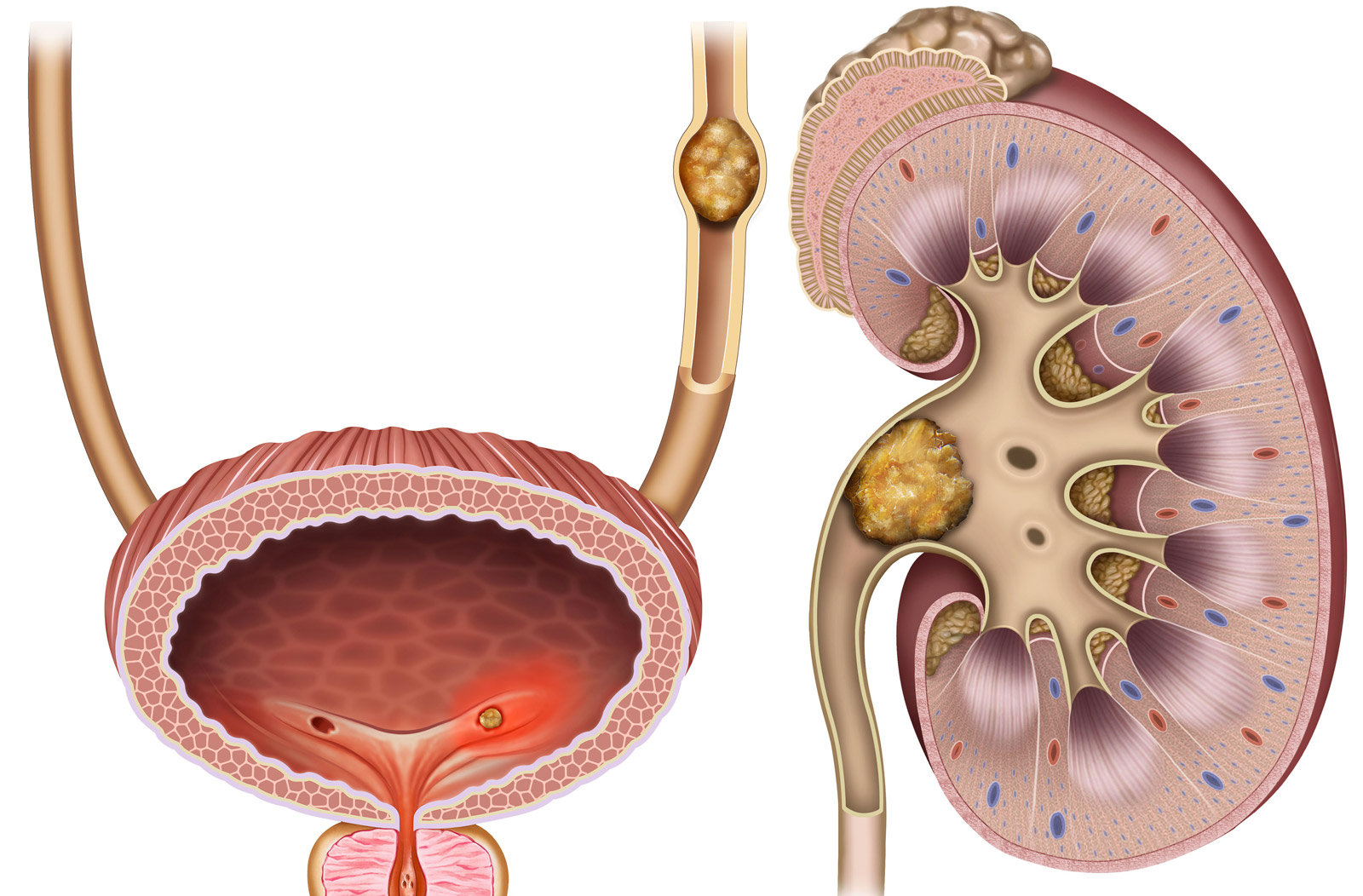
Renal calculosis is a disease due to the precipitation in the urinary tract of calcium salts. The genesis of kidney stones is mainly due to urine supersaturation of these insoluble salts, which first precipitate as crystals and then become actual stones. Urinary pH also favors the precipitation of uric acid crystals if it is acidic. Common causes include idiopathic hypercalciuria, hyperuricosuria, and hyperoxaluria.
About lipid malabsorption and the genesis of oxalate stones, it can be attributed to the binding of calcium with bile salts, which are reabsorbed in the intestine. Another cause of hypercalciuria is primary hyperparathyroidism.
- Dietary intervention seems to be very effective es Ipecially in the most common forms of kidney stones. In fact, having completed the diagnostic phase, it is appropriate to recommend increased hydration and dietary treatment to all patients with kidney stones as supportive therapy in reducing stone growth.
Source: Handbook of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition by Franco Contaldo et al.