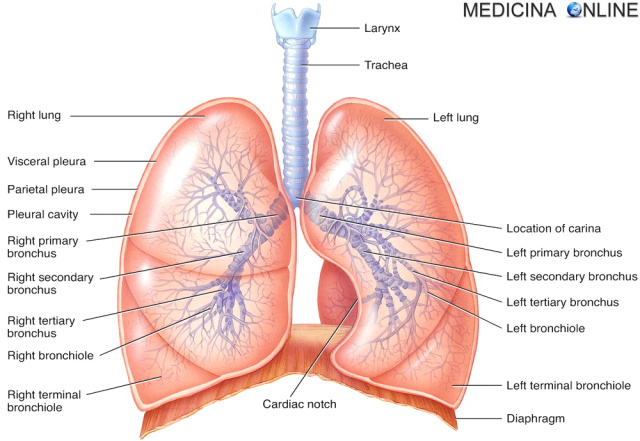
A condition of “respiratory failure” is present when the respiratory system is unable to ensure efficient gas exchanges through the lungs, preventing the maintenance of an adequate balance between oxygen (O2) and/or carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood.
When only low plasma O2 concentration is present, there is “hypoxemic” (type I or partial) respiratory failure, commonly found in association with lung diseases such as pneumonia or pulmonary edema. When a higher-than-normal plasma CO2 concentration is also present, we speak of “hypercapnic” (type II or total) respiratory failure, typically associated with severe/advanced forms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
Excess CO2, which in plasma is transformed into carbonic acid (H2CO3) and hydrogen carbonate (HCO3-), promotes a decrease in blood pH from neutral to weakly acidic. This condition is partially corrected by the kidneys, which “buffers” the pH of the blood, bringing it back toward neutrality, by increasing the plasma concentration of HCO3- (which is more reabsorbed by the renal tubule rather than excreted with urine).
However, when respiratory failure and increased plasma CO2 concentration are significant, the renal homeostatic mechanism is no longer sufficient to ensure a neutral blood pH, and so-called “respiratory acidosis” is established, a condition that is in effect a medical emergency since most of the body’s basic physiological functions are set to take place in the presence of a blood pH around 7.3-7.4.
Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic: the former arises quickly and suddenly (for example, due to chest trauma or epiglottis edema on an allergic basis); the latter has a more gradual onset and may persist for months or years, worsening abruptly due to extemporaneous phenomena such as acute respiratory inflammation or infection (as occurs, for example, during COPD or pulmonary fibrosis flare-ups).
Those with chronic respiratory failure often also have what is known as “pulmonary heart,” a cardiac condition characterized by dilatation of the right ventricle of the heart, resulting in impaired pump function and onset of right heart failure.