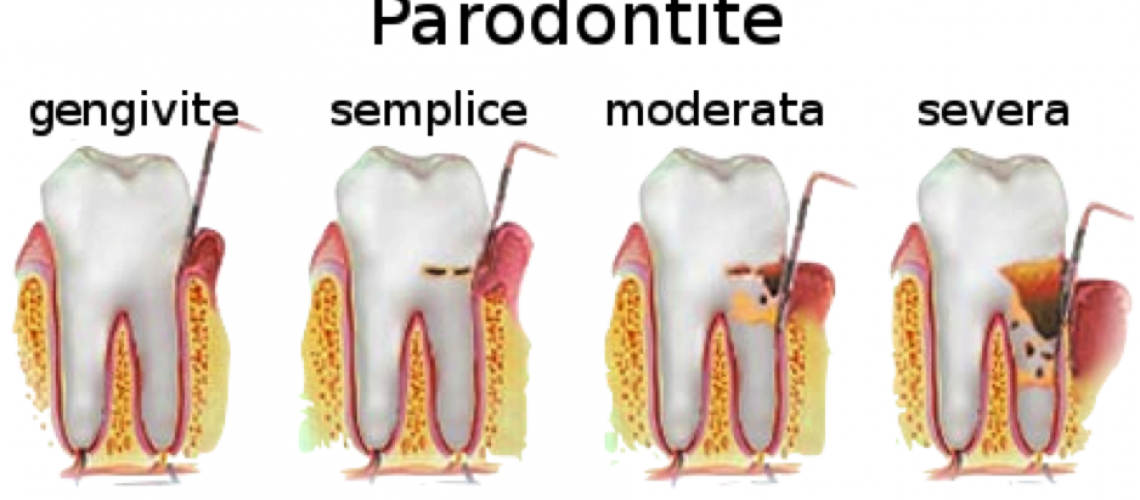
Periodontitis, also called periodontal disease, begins with bacterial growth in the mouth and can end-if not properly treated-with tooth lossdue to destruction of the tissue surrounding the teeth.
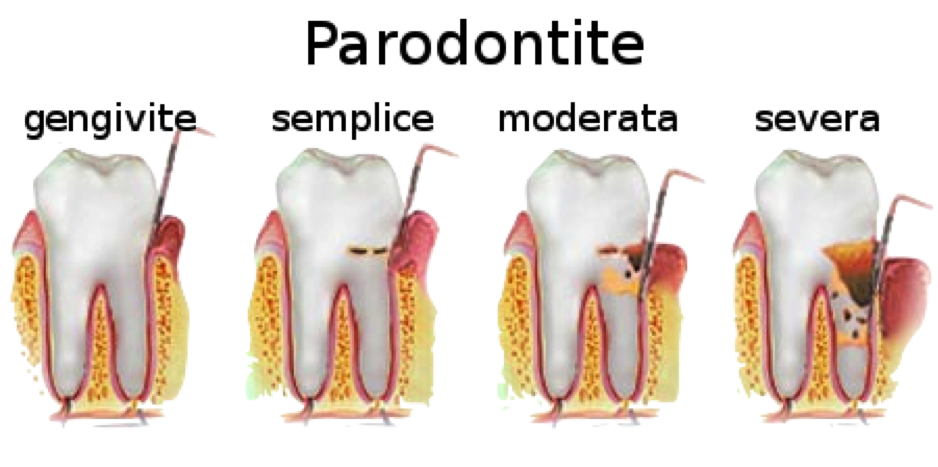
Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) usually precedes periodontitis, but not all gingivitis progresses to periodontitis.
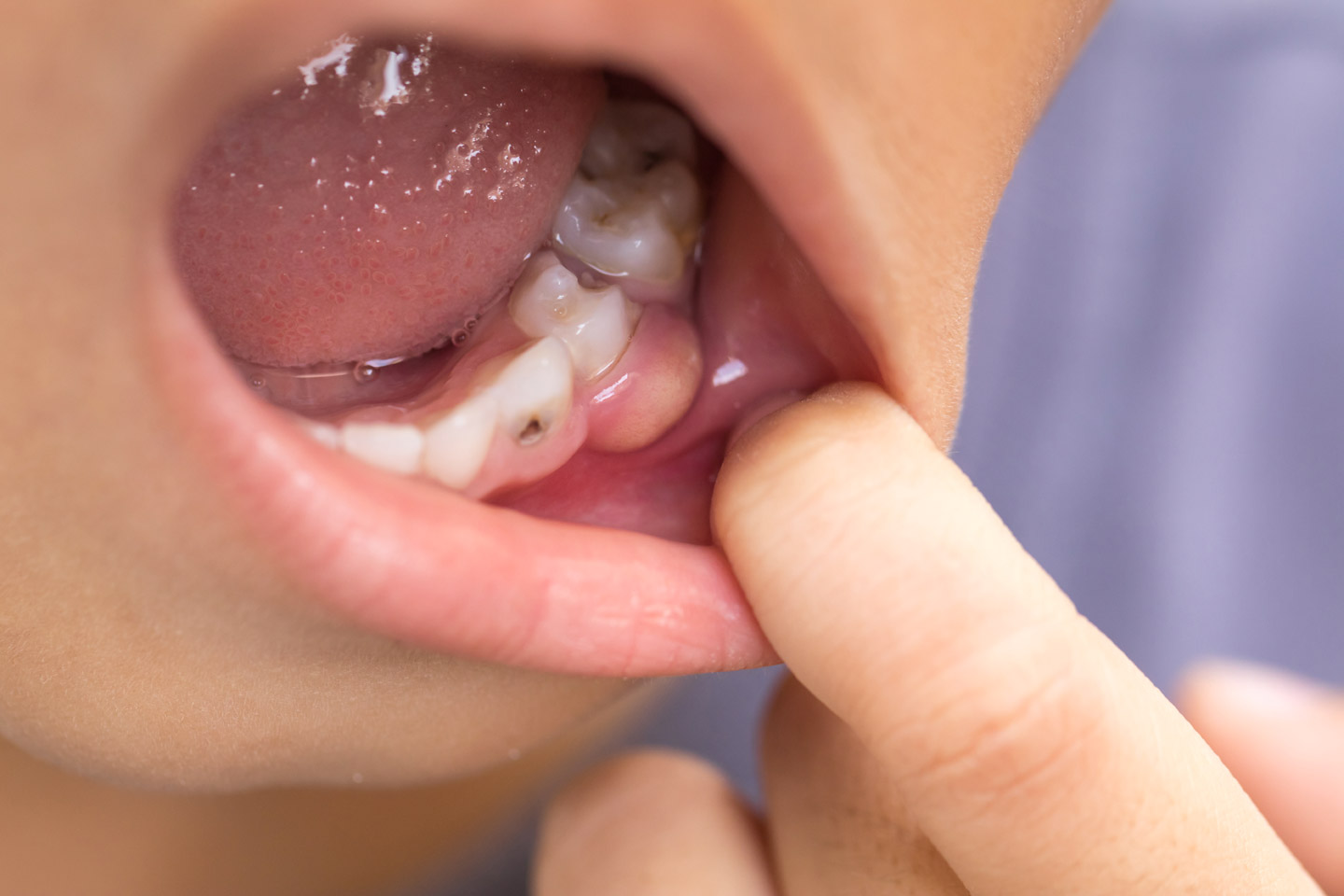
In the early stage of gingivitis, bacteria in plaque accumulate, causing the gums to become inflamed and bleed easily when brushing the teeth. At this stage, although the gums may be irritated, the teeth are still firm and there is no irreversible tissue damage.
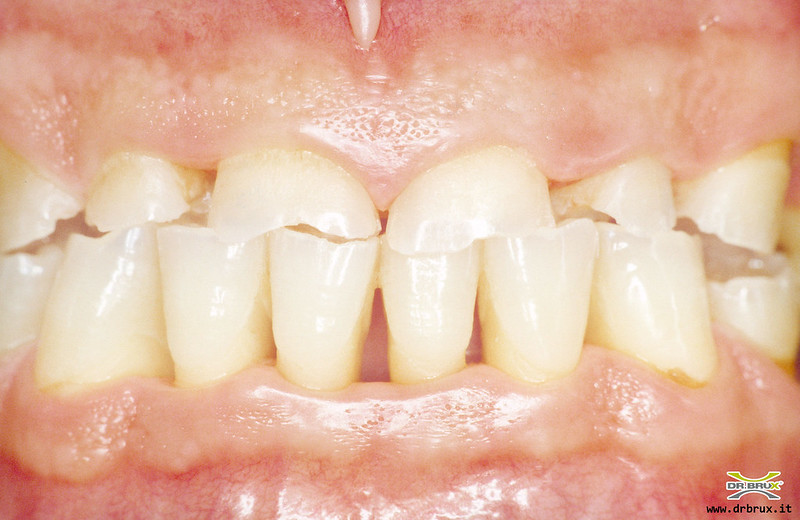
When gingivitis goes untreated, it can evolve into periodontitis, in which the inner layer of the gingiva pulls away from the teeth and forms periodontal pockets-these small spaces between teeth and gums collect debris and can become infected.
As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more and more gum and bone tissue is destroyed. When this happens, the teeth are no longer anchored, they become loose, and tooth loss occurs.
Periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.