Anaphylactic shock is the acute allergic reaction to exposure to allergens to which the patient had become sensitized, leading to The rapid release of mediators from mast cells and basophils. The anaphylactoid reaction, to which the child is subjected causes the same symptoms as an allergy and is treated through the same therapy.
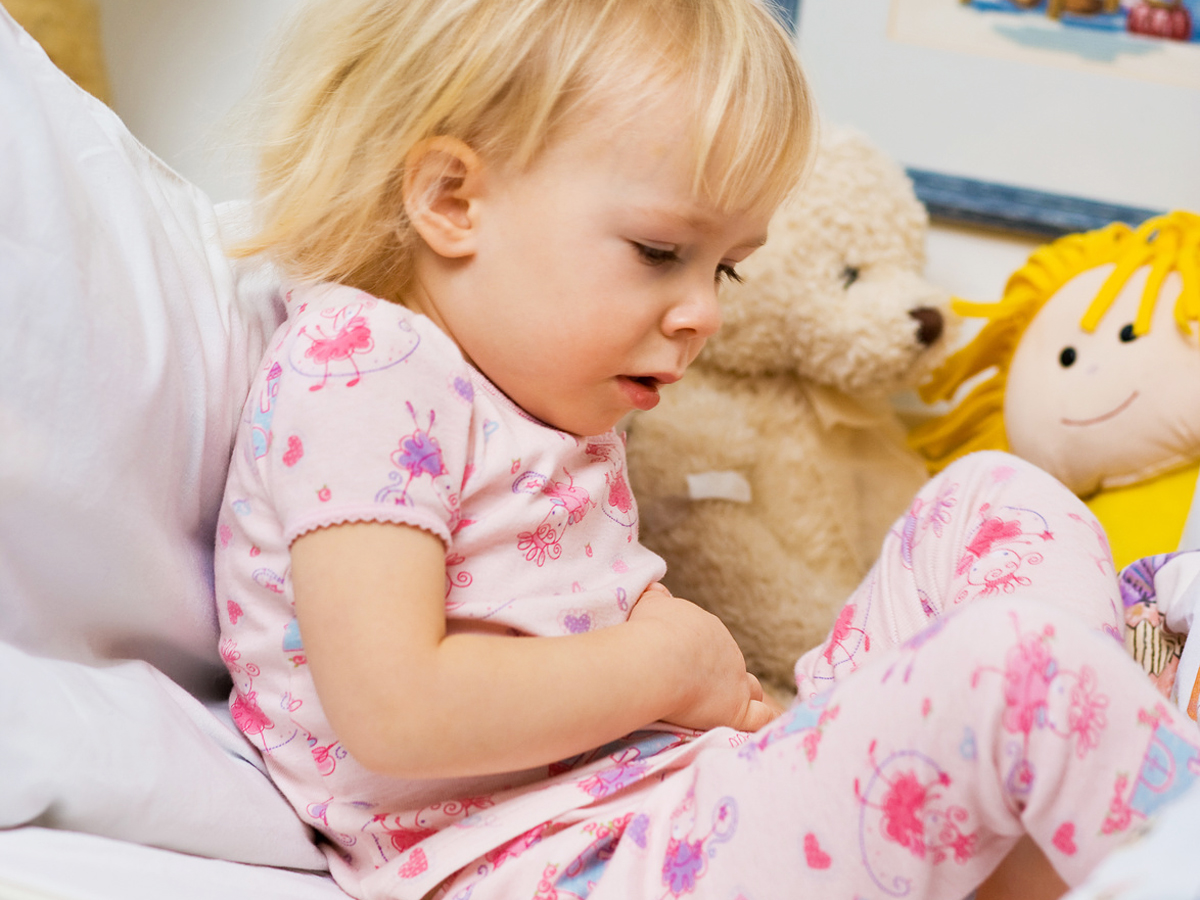
Symptoms occur immediately after exposure to the allergen. The most common symptoms are tingling sensation, itching and feeling of heat on the scalp, palms of the hands and soles of the feet, oral itching, constricted feeling in the throat, hoarseness, swollen feeling in the lips and tongue.
It is necessary to immediately remove the child from the cause of shock and proceed with some tests. In addition, it is important to administer oxygen, elevate the little patient’s limbs, and inject adrenaline.
Source: Mediserve‘s Medical Emergencies in Pediatrics.