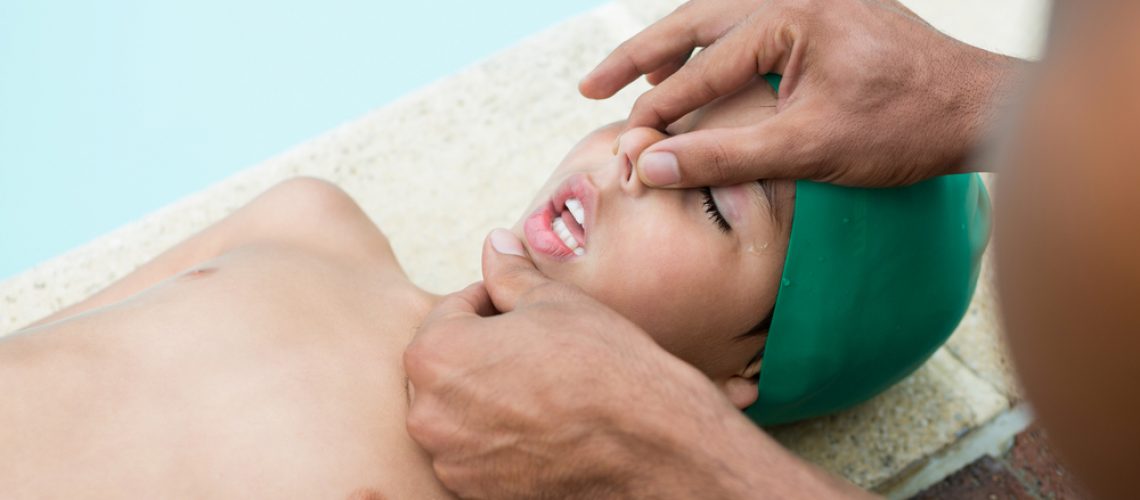
In pediatric age often respiratory arrest precedes cardiac arrest. The causes can be of different nature: respiratory, cardiological, neurological, from shock, from drugs, metabolic imbalances, or environmental causes. The signs are: absence of arterial pulses, absence of respiratory activity, state of unconsciousness, extreme pallor and cyanosis. It is necessary to place on a plane rigid in dorsal decubitus with moderate cable hyperextension. Liberating the airway from secretions or food, lift the chin and practice two Insufflations with mouth-to-mouth respiration, begin cardiac massage external.
If there is no rapid recovery of cardiac activity give the child a syringe of adrenaline. If the result after 10 minutes is negative, proceed with baking soda. Clinical monitoring will consist of pupillary reactivity, peripheral pulse assessment, skin color, skin temperature, diuresis, blood glucose, azotemia, electrolycemia and blood count.
Source: Mediserve‘s Medical Emergencies in Pediatrics.