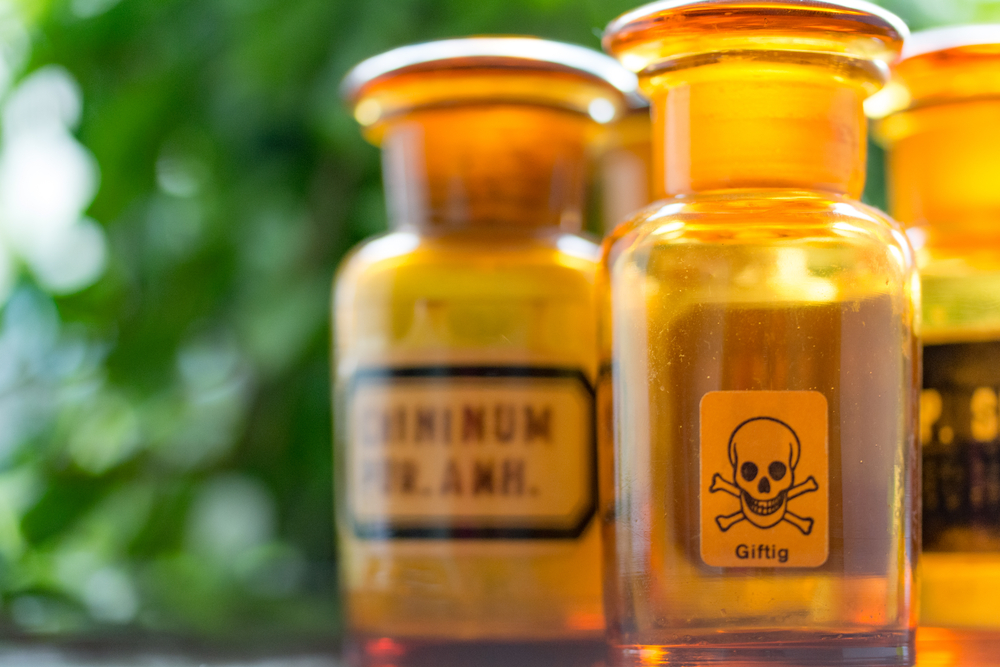
Cyanide ranks first as a pesticide, but it is not the only way through which you can poison yourself. Organic cyanides are highly toxic if ingested. These salts can also be absorbed percutaneously and the most dangerous is hydrogenated cyanide gas. Another source of cyanide is found in the kernel of some fruits, such as apricots and almonds. The action of cyanide is quite specific: it blocks cytochrome oxidase so that metabolism stops.
Symptoms appear in a short time. Initially, the patient experiences dizziness and agitation, followed by headache, tachycardia, and chest tightness. Other symptoms that occur are mental confusion, ataxia, weakness, and collapse.
Diagnosis and treatment
As for diagnosis , it is necessary to measure plasma cyanide levels, but in cases of acute poisoning it is not possible to wait for the results of these investigations. As a first measure, an amyl nitrite capsule should be broken under the patient’s roots, so that the volatile substance is inhaled making sure that the patient breathes by avoiding mouth-to-mouth respiration. The treatment involves dicobalt edetate, which is found to be the most effective. An alternative treatment is the injection of sodium nitrate and sodium thiosulfate.
Source: Vadecum of poisoning therapy by Roy Goulding