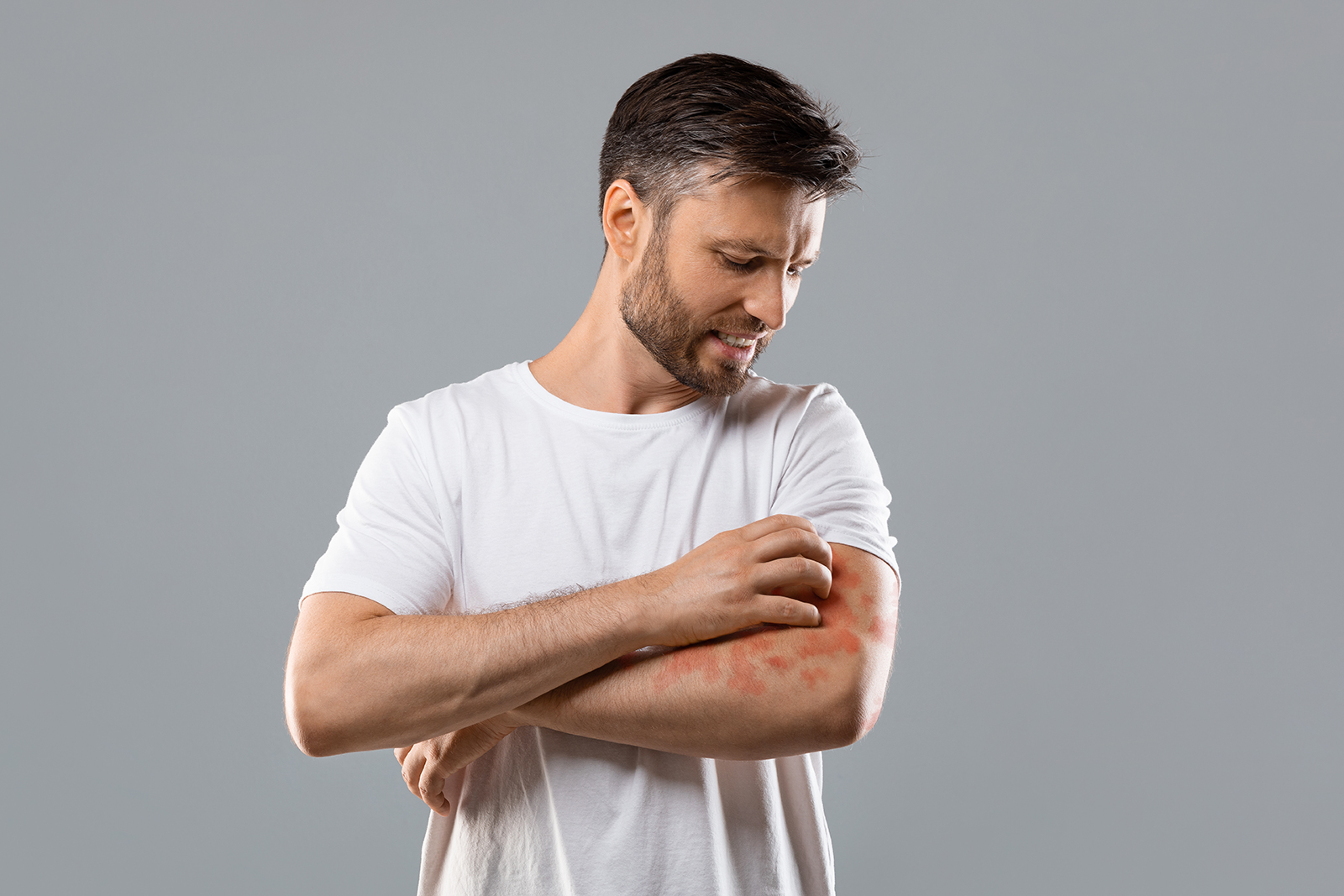
Ivy, oak and sumac plants cause an allergic reaction, and often resulting in a rash, in half of adults. A proportion of these individuals have a skin reaction, and only in 15-25% of cases is edema and eruption of blisters observed. Allergic people can come into contact with this plant through clothing, shoes, from contact with animal hair or through smoke from burning plants. There is no risk in touching the liquid contained in the vesicles. Symptoms include itching, erythema, edema, and blisters, depending on the form through which one is infected. Severity is certainly important, but so is the extent of the affected skin; in fact, the larger it is, the greater the need for medical treatment.
What to do?
- Those who know they are allergic and have come in contact with a poisonous plant should act immediately. Many victims do not realize the contact until many hours or even days later. The moment the itching and rash appears, use soap and water to clean the skin or apply alcohol. Rinse to remove solubilized material.
- For mild forms, 4 different methods can be used: tablets soaked in Burow’s solution, calamine or zinc oxide lotion, warm water mixed with two cups of colloidal vein flour, and baking soda paste.
- For mild-to-moderate forms, however, treat the skin as for the mild form. Apply cortisone ointment and for itching soak the affected area in warm water.
- For severe forms, use an oral corticosteroid or apply a corticosteroid ointment or cream and cover with a clear plastic sheet.
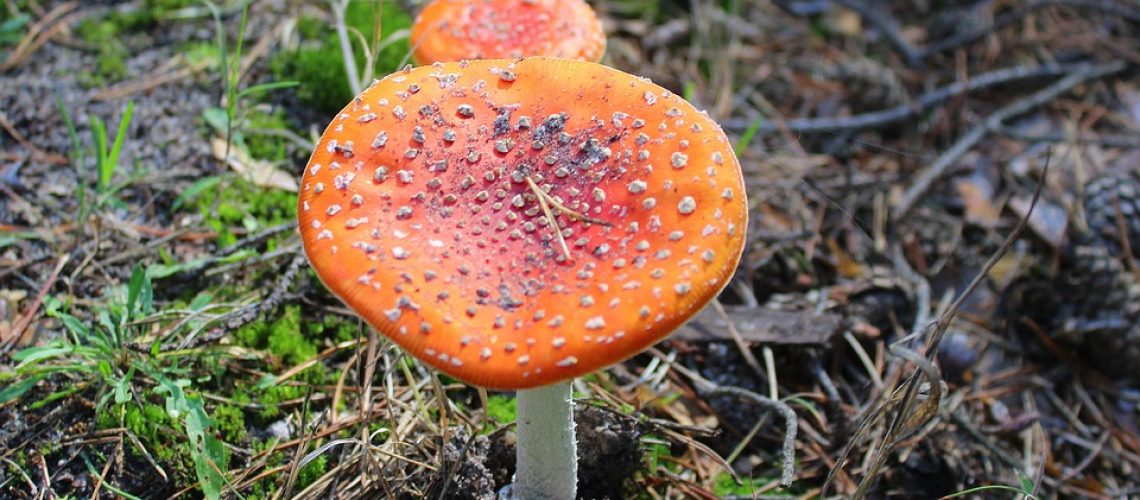
Mushrooms
In Italy, among the most poisonous substances are mushrooms. They cause long incubation syndromes and short incubation syndromes.
What to do?
- In case of phalloid syndrome, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain appear after a period of 6 to 20 hours. Treatment consists of gastrolusion with vegetable charcoal. This involves antibiotic therapy with forced diuresis.
- In case of anticholinergic syndrome, the symptoms are dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. Later, delirium, hallucinations, coma, and respiratory depression appear. Therapy consists of gastrolusion treatment with activated charcoal, sedation, and fluid therapy.
- Tearing, miosis, rhinorrhea, broncho-spasm, vomiting, hypotension, tremors and paresthesias appear 2 hours after ingestion in the case of cholinergic syndrome. Treat the syndrome with gastroluxis.
Source: Mediserve‘s Pocket Guide to First Aid.