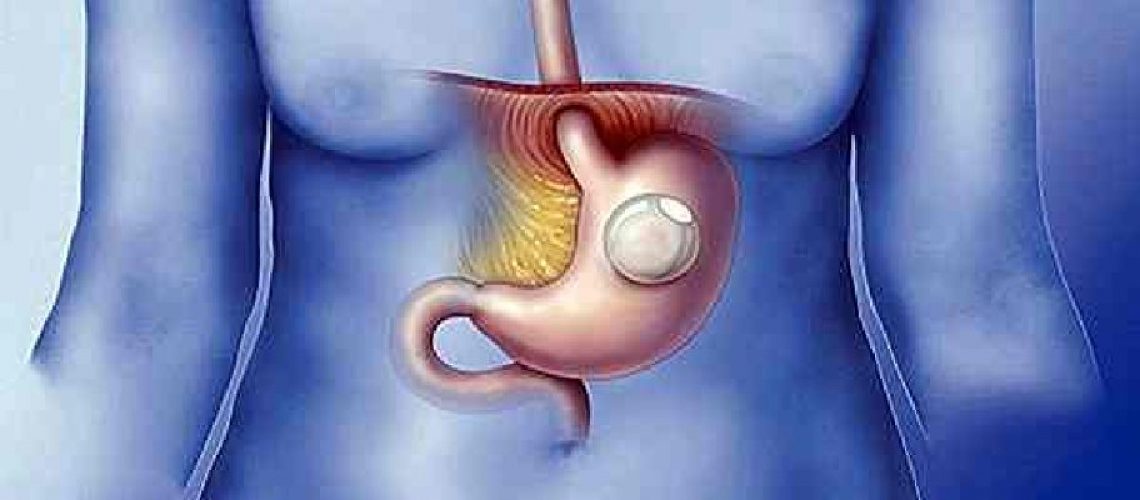
The intragastric balloon is inserted through endoscopic intervention into the stomach. It induces a partial filling of the stomach, causing the subject to feel full, which turns him or her away from food. There are two types of intragastric balloon:
- BIB, insufflable with sterile saline solution
- Insufflable with air
They have an average volume of 500 cc, are made of silicone and have a smooth surface and radiopaca. It must necessarily be removed after a maximum of 8 months.
Directions For intragastric balloon insertion:
- BMI <30 on psychological and clinical-nutritional indication
- BMI 30-35 with Obesity-related complications
- BMI 35-50 also as a test to be used in the pre-surgical patient to identify the type of intervention
- BMI >50 in Patients with serious clinical conditions that are not candidates for surgery surgical.
Criteria exclusion:
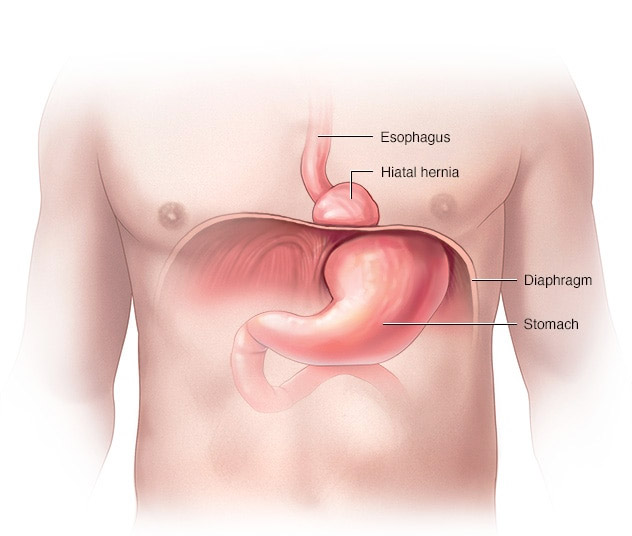
- Medico-surgical: reflux, ulcer, gastrolesive drugs, obesity secondary to endocrine disease, pregnancy or lactation, esophageal disease, hiatal hernia
- Nutritional: sweet easters
- Psychological: psychiatric illness, bulimia, alcoholism, poor follow-up reliability, drug addiction.
Source: Handbook of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition by Franco Contaldo et al.