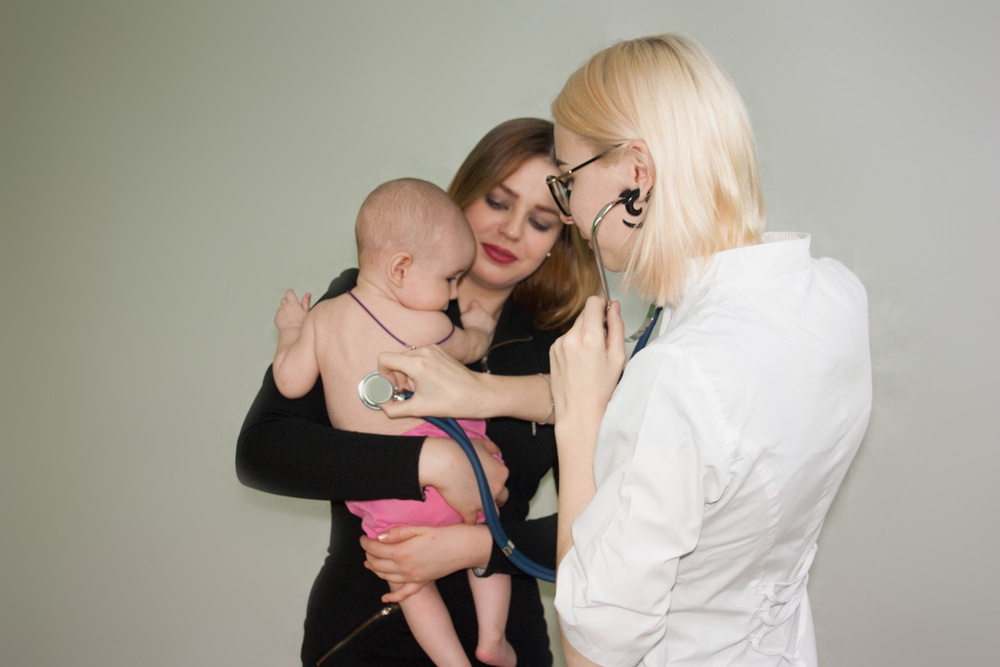
Meningitis is one of the neurological diseases most commonly acquired during childhood. It is the infection of the meninges due to the penetration of pathogens into the subarachnoid space and causes the increase of leukocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment should be immediate, keeping in mind that clinical signs are often nonspecific.
Symptoms usually include fever, symptoms of endocranial hypertension, hypertonic-antalgic symptoms, psychic sphere symptoms, symptoms associated with breathing and digestion, and neurovegetative symptoms.
The lumbar procedure must be performed to confirm that it is meningitis. It is also very important to immediately perform culture examination on pharynx and nostrils, blood cultures, urine examination, and coagulation tests.
Sometimes lumbar puncture may not be performed, especially when the patient has severe cardiac and respiratory compromise, signs of andocranial hypertension, and severe skin infection in the area of execution.
Source: Mediserve‘s Medical Emergencies in Pediatrics.