Vaginal candida is the purely female fungal infection that results from the out-of-control growth, at the level of the vagina, of the fungus Candida albicans.
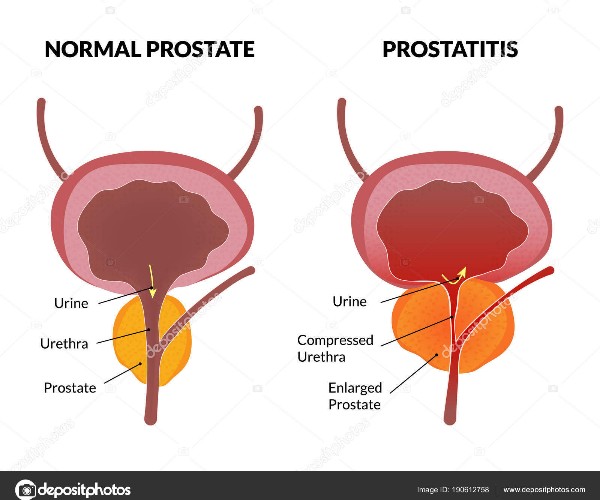
Promoted by conditions such as, for example, misuse of antibiotics, pregnancy, immunodepression, diabetes, and poor intimate hygiene, vaginal candida is typically responsible for pain and itching in the vulva, pain during sexual intercourse, and pain or burning during urination.
For the diagnosis of vaginal candida, an objective examination and history are generally sufficient; however, at some junctures, more extensive diagnostic tests, such as vaginal swab, blood test, or urine test, are also needed.
Treatment of vaginal candida revolves around the use of antifungal drugs available in cream or tablet form for oral or vaginal use.