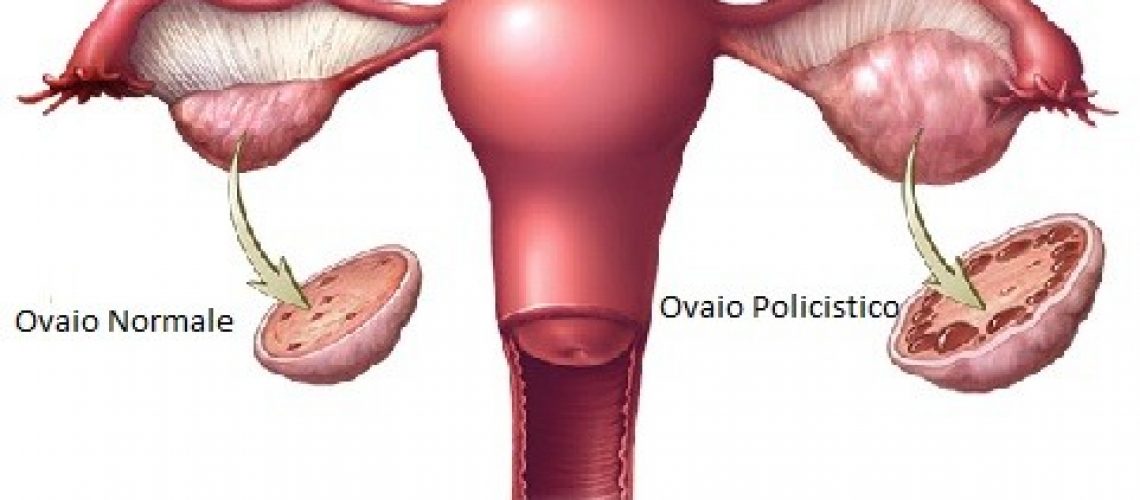
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) causes important cosmetic, metabolic, and reproductive health effects in women. It is characterized by enlarged ovaries, the presence of multiple ovarian cysts, and endocrinological and metabolic changes (hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and subsequent hyperinsulinemia).
PCOS affects 5-10% of women, originates in the pubertal period, and is considered the most common endocrine disruption in childbearing age.