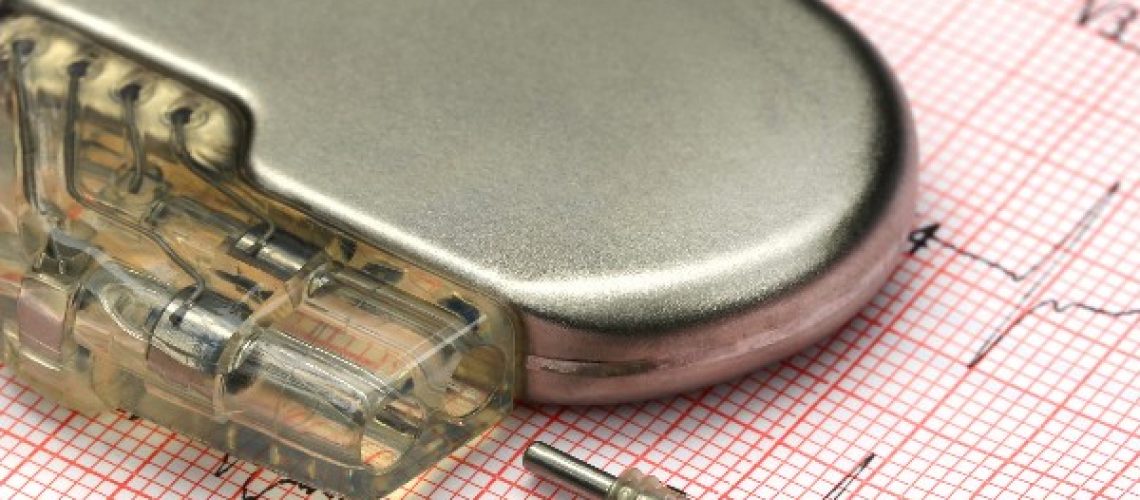
Each pace-maker consists of two basic parts: a pulse generator varying in size from one to a few cm (newer devices are getting smaller), which is usually implanted under the front of the left shoulder, in the hollow under the collarbone; and one or two electrodes that are run from the generator down to the heart muscle and placed in well-defined locations depending on the conduction defect present and resynchronization needs.
Pacemaker application involves a relatively simple procedure, lasting one to a few hours (depending on the type of device applied and the patient’s characteristics), usually performed through small incisions and with electrode insertion by “endovascular” means (i.e., moving the leads with the electrodes inside veins that reach the atria and/or cardiac ventricles, usually the subclavian vein or left cephalic vein).
The procedure can be somewhat more delicate and complex, and take longer, when a biventricular pacemaker must be applied to simultaneously support the contraction of both ventricles and the pumping function of the heart in patients with heart failure.
In this case, the application of the pace-maker is also called “cardiac resynchronization therapy” (CRT).
The average hospital stay after surgery is about 24-48 hours, unless the clinical picture is particularly delicate and such that a longer hospitalization is warranted.
Causes
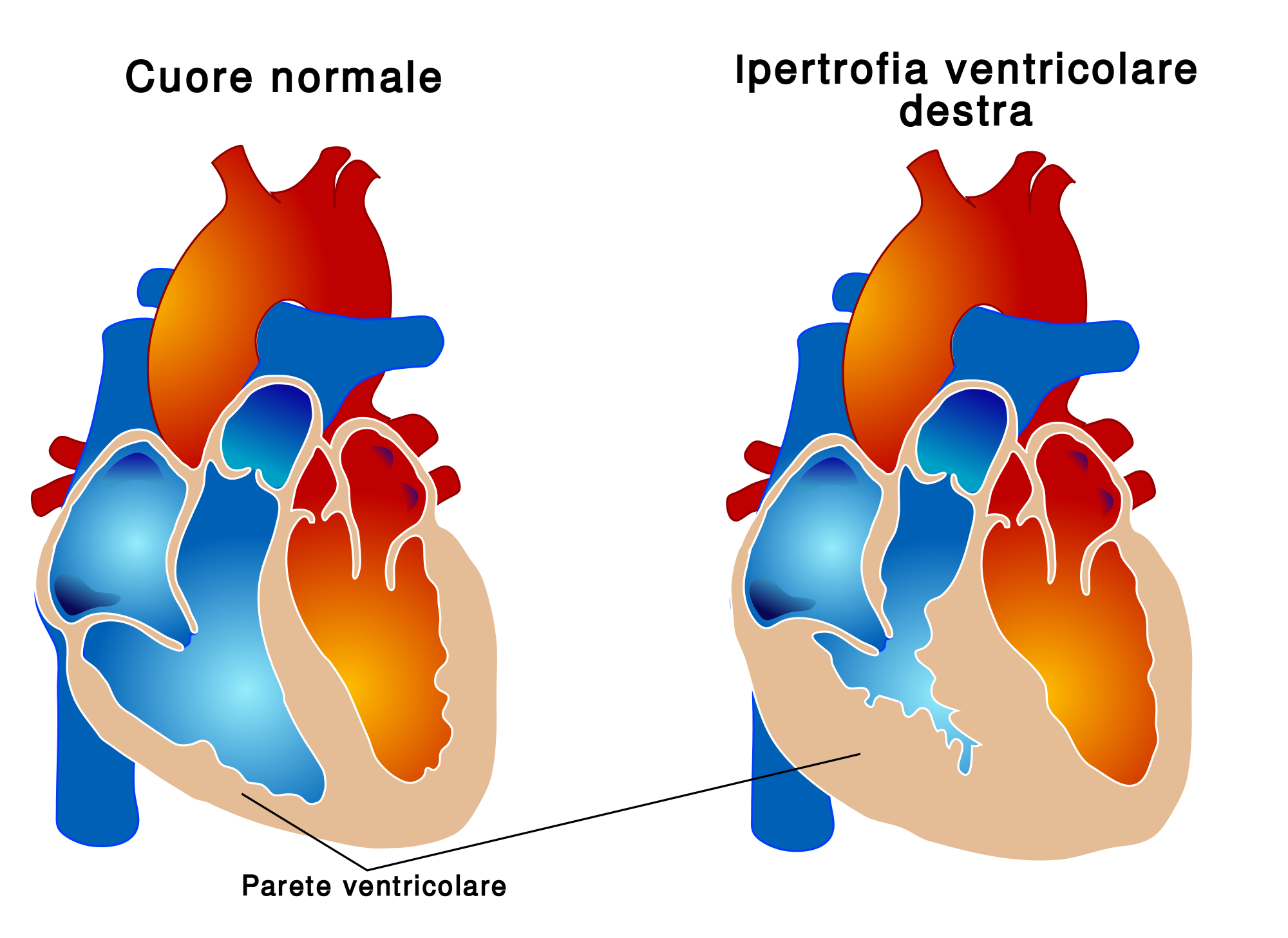
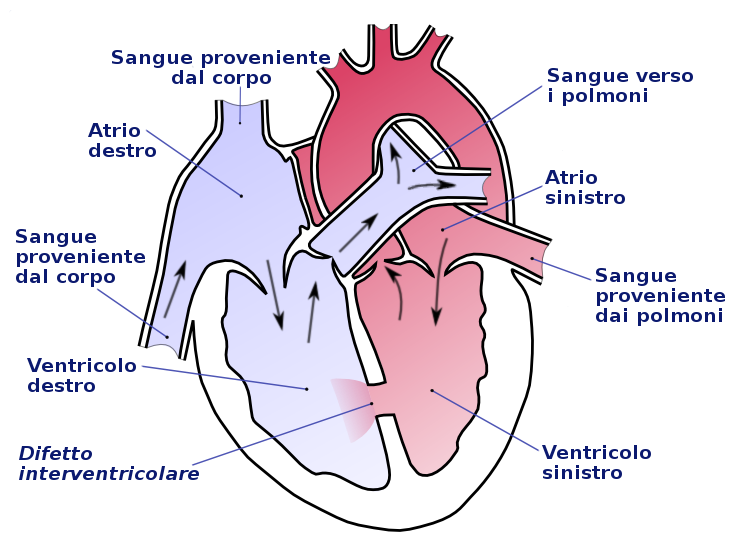
A pace-maker is an electronic device used to normalize an altered heartbeat due to defects in the conduction of the electrical stimulus through the heart muscle and the resulting deficient and/or imperfectly coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles or to support insufficient contraction activity of the heart.
There are different types of pace-makers: single-chamber, dual-chamber, bi-ventricular or associated with a defibrillator.
Each device has a different activity and is intended for patients with different heart diseases.
The application can be permanent (with replacement of the device after 5-7 years, due to depletion of the internal battery) or temporary (when the alteration of heart rhythm is related to acute circumstances that resolve over time (post-infarction period or after surgery/overdose of drugs or substances harmful to the heart muscle).
Symptoms
The application of a pace-maker may be necessary in the presence of acute or, more often, chronic alterations of the heartbeat of various origins and nature, which are not adequately compensated by available drug therapies and which are such that they interfere with daily activities or expose the patient to the risk of cardiac arrest.
The single- or dual-chamber pacemaker is applied when only the right ventricle or both the right atrium and right ventricle need to be paced in a coordinated manner, for example, in patients presenting with bradycardia (slowing of heart rate).
The biventricular pace maker is applied in patients with moderate-severe heart failure.
Especially in the latter case, when there is a significant risk of ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest in addition to the altered heart rhythm, a device that integrates the activities of a pace-maker and defibrillator can be applied: the former will be constantly functioning in relation to cardiac pacing needs, while the latter will only come into operation if the device itself detects the immediate need.
Diagnosis
The Diagnosis leading to the intervention of pacemaker application takes into account the findings made about the situation of the heart and the detected dear heart beat. As the pacemaker is apparatus an electronic that is given in aid of proper and continuous cardiac activity, it should be considered , before resorting to this device the patient’s diagnostic picture should be taken into careful consideration.
Therefore, if the diagnosis ascertains that the heart rhythm should be regularized to avoid disturbance caused to the patient by bradycardia , heart failure, or even atrial fibrillation.
Given that the myocardium is the muscle of the heart responsible for the impulses that generate the contractions of the atria and ventricle necessary for the heartbeat.
The correct heart rate refers to the sinus node, where the magnitude of the beat is assessed, which must be between 60 and 100 beats per minute to ensure a good sinus rhythm.
Alteration of sinus rhythm can generate a Cardiac Arrhythmia, which may be at a lower or more accelerated rate.
In such a case, the diagnosis should take into account that ivarious symptoms described by the patient such as fatigue, shortness of breath, possible syncope, would direct the treating physician to suggest implantation of a pacemaker.
Among the lifestyles
The application of a pace-maker may be necessary in the presence of acute or, more often, chronic alterations of the heartbeat of various origins and nature, which are not adequately compensated by available drug therapies and which are such that they interfere with daily activities or expose the patient to the risk of cardiac arrest.
The single- or dual-chamber pacemaker is applied when only the right ventricle or both the right atrium and right ventricle need to be paced in a coordinated manner, for example, in patients presenting with bradycardia (slowing of heart rate).
The biventricular pace maker is applied in patients with moderate-severe heart failure.
Especially in the latter case, when there is a significant risk of ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest in addition to the altered heart rhythm, a device that integrates the activities of a pace-maker and defibrillator can be applied: the former will be constantly functioning in relation to cardiac pacing needs, while the latter will only come into operation if the device itself detects the immediate need.