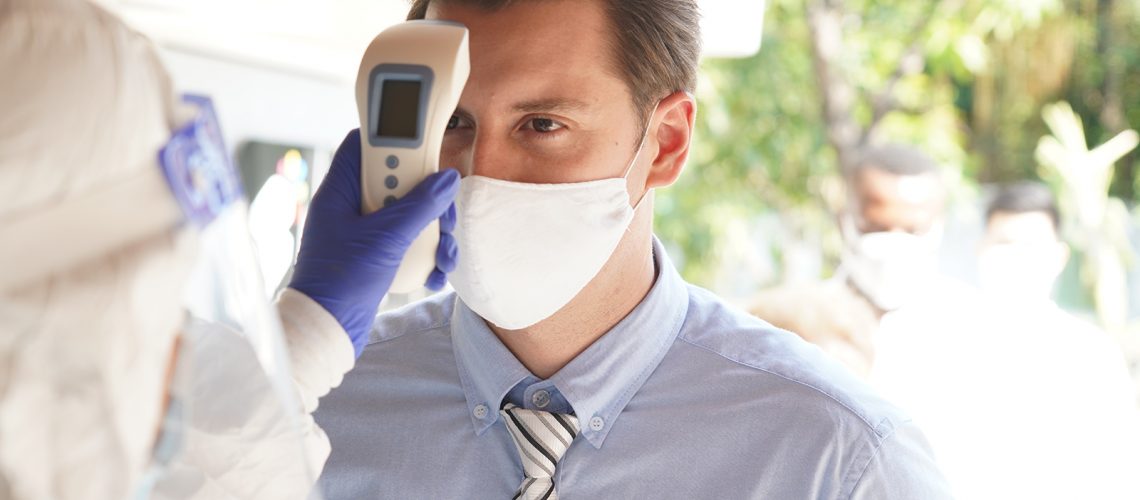
It is one of the items that came to the fore as a result of the Covid 19 outbreak, the remote thermoscanner, this kind of thermometer in the shape of a gun Which is used to measure the temperature of people intending to enter premises such as banks, offices, bars, and restaurants, already bitten by the mask and anxious to be assessed by the instrument as “fit” and thus unfebrile and noninfectious.
It is one technical tool that thanks to the infrared is Capable of detecting temperature at a distance from the subject initially used only in special environments as the triage inhospital,laborators limited admission, airports, and then became in common use at the entrance to all public places, where people with fever and Covid 19 symptoms are to be prevented from entering.
This particular thermometer has proved very popular with physicians and health care personnel precisely because of the speed of the measurement procedure, which in certain situations is particularly useful that speed with which one pulls the trigger and the temperature of the subject under investigation instantly appears on the monitor.
It also proves very useful in taking the temperature of children, who are usually restless, precisely because of the very short time required.
But how does a thermoscanner work? The instrument is an infrared laser that can detect the electromagnetic thermal radiation emitted by the human body by converting it into degrees of temperature, without physically touching the person and remaining at a safe distance.
While these thermoscanner gauges are particularly effective and useful in times of pandemic, they are not evaluated by insiders as precision thermometers, but rather as practical and easy-to-use detectors in emergencies and events such as epidemics, arguing that thermoscanners usually report temperatures at least one degree lower than mercury or digital thermometers, due to interference from the environment where the measurement takes place and also other factors related to materials in the context of the emitted beam.
From the point of view of safety, make sure that a sanitary type thermoscanner is used for temperature measurement one and not a type suitable for industrial purposes.
In addition, it is especially necessary to be cautious when using a thermoscanner by directing the measurement beam away from the eyes, either to the top of the forehead or to another body surface such as a wrist , arm or hand , surfaces equally good for detection.
The Thermoscanner Laser thermometers are equipped with a processor that allows the analysis of the radiation coming out of the body and to calculate the actual temperature from the actual signal measured by the instrument (which will then be processed according to a function in order to define the body temperature).
The measurement is made from the evaluation of the signal received from the instrument sensor, the temperature of theenvironment in which the instrument is located, and theemissivity of the material.
The emissivity of the material plays a very important role (in the case of human skin it is 0.98), and if not set correctly in the instrument, measurement errors could occur.
But is it possible to perform this measurement under any condition? Of course not, crucial is that temperature measurement conditions are carried out in environments with conditions as homogeneous as possible. Every object emits electromagnetic radiation that, being invisible to the human eye, could be present on the body where you want to measure temperature which would begin to reflect radiation from other thermal objects that would inevitably lead to an incorrect temperature measurement.
Another error is related to the presence of disturbances between the thermoscanner and the body to be measured; just think of the dust or dirt that might be present on the thermoscanner lens and that would lead to the detection of a temperature different from the real one (since the instrument would also tend to measure the radiation emitted by dust and/or dirt). It is imperative, therefore, that the environment where the measurement takes place is free of all these elements of error in order to ensure that the temperature measured is indeed the right one and to avoid the possibility of the person walking around with unnoticed febrile symptoms or generating an alarm for a person who is instead perfectly healthy.
According to physicians, theuse of these laser thermometers is suboptimal because they tend to measure a temperature that is generically lower than the actual temperature being influenced by the factors previously listed, a thesis also supported by James Lawler of the Global Center for Health Security at the University of Nebraska. If the measurement were taken under conditions as homogeneous as possible and measured over a large area such as the forehead at a reasonable distance, the temperature measurement on a healthy person would range between 33° and 34°, a value that tends to vary according to the person’s environmental and sweating conditions. All things being equal, a temperature difference of at least 1.5-2° will be appreciable between a healthy person and a sick person.
Thus, although there are a number of issues with these tools, their use is essential to try to counter and reduce the spread of the virus as much as possible and to ensure that people going about their daily lives are healthy people.