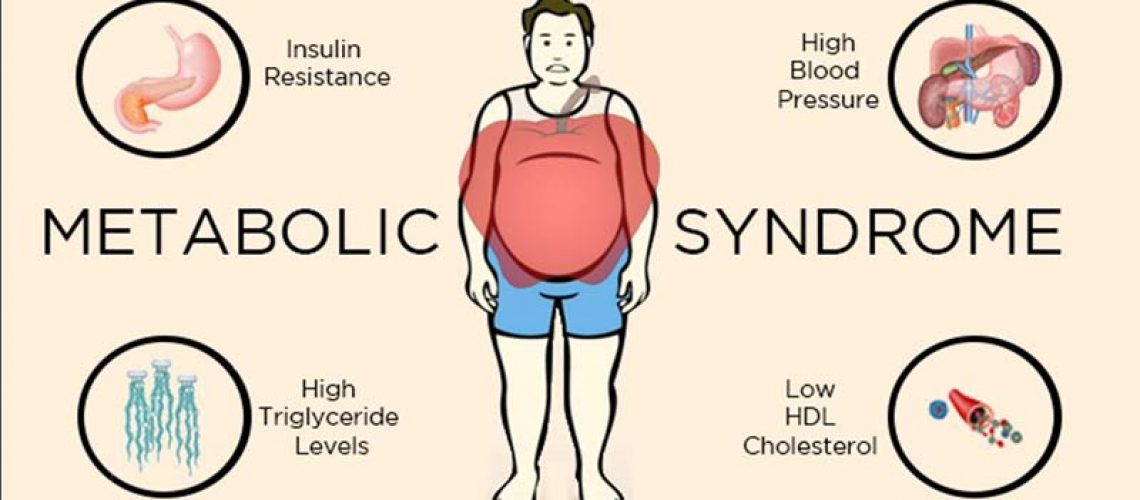
Metabolic syndrome is a set of abnormalities that can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and beyond. It is characterized through the presence of at least three of these factors: increased waist circumference, hypertriglyceridemia, reduced HDL cholesterol, increased blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. The most important pathogenetic hypothesis explaining metabolic syndrome is the0insurgence of insulin resistance related to increased circulating free fatty acids. An increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines has also been found in patients with metabolic syndrome. The increase of metabolic syndrome in the population is definitely related to obesity, sedentarism and the general aging of the population itself.
Dietary advice
Diet therapy for patients with Metabolic Syndrome aims to correct the metabolic changes present, thus obesity, insulin resistance, impaired carbohydrate tolerance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. The diet to be followed should be low in calories and consist mainly of complex carbohydrates and low in simple sugars. Regarding fat intake, reduction of saturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids and cholesterol is necessary. Fats to be preferred include monounsaturated fats so olive oil. To improve blood pressure values, the diet must also include reducing sodium intake, keeping in mind that many of the high-fat foods are also high in sodium.
Source: Handbook of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition by Franco Contaldo et al.