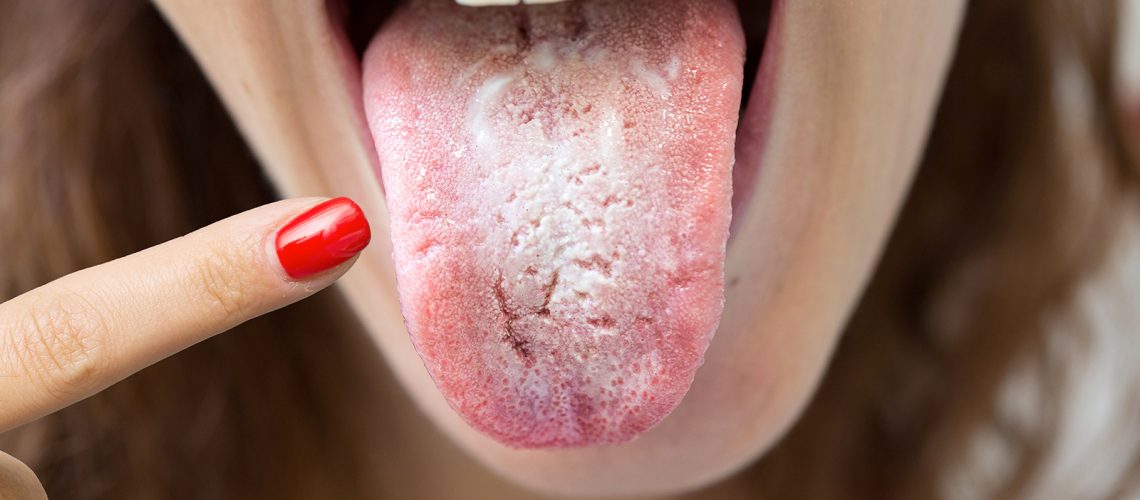
Also known as
oral thrush
, this condition is considered a minor, insignificant problem that can resolve itself
spontaneously. When the problem is more extensive and articulated there is the oral candidiasis, which carries risk factors and complications when the condition has manifested with its signs and symptoms, but there are nevertheless preventive measures that can be taken to prevent it from occurring.
Risk factors and complications
If appropriate treatment is not undertaken, this condition can develop into a chronic condition that can cause discomfort and anorexia. Rarely,oropharyngeal infection leads to systemic candidiasis.
Risk factors include:
- Impaired salivary gland function.
- The administration of medications (some medications can promote candidiasis).
- The use of dentures.
- A diet rich in carbohydrates.
- Habits like smoking.
- Diseases such as siabetes, Cushing’s syndrome, malignancies, reduced immune defense.
Oral candidiasis, when left untreated can result in more severe systemic candida infections, with spread to the esophagus or other parts of the body, especially in cases of decreased immune defenses.
Prevention
There are some measures and behaviors that can help reduce the risk of developing candida infections:
- make mouth rinses, especially after using a drug inhaler such as corticosteroids.
- Adequate and assiduous dental hygiene with brushing and flossing to remove food debris.
- Remove any removable dentures during the nighttime hours , taking care that they are always properly fitted and do not create irritation inside the mouth.
- Avoid sugary foods that can promote candida development.
- Keep blood glucose under control at all times. Saliva may also become more sugary predisposing the mouth to candida growth.