Mumps is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by a virus belonging to the Paramyxovirus family, which localizes to the salivary glands and the first airways (pharynx, larynx, and trachea).
How does it manifest itself?
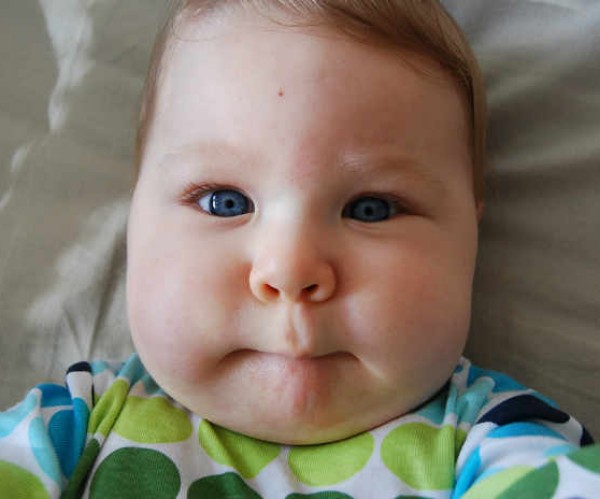
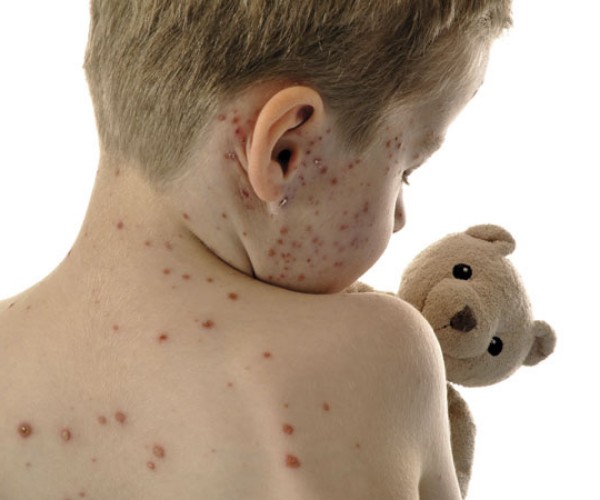
The enlargement of the parotid glands, located under the ear pinnae, behind the angle of the jaw, gives the face the characteristic appearance from which the popular name of “mumps“.
The incubation period is highly variable between 12 and 25 days and is generally free of symptoms except sometimes accompanied by malaise, loss of appetite, chilliness, fever, headache, muscle pain. Symptoms begin with fever, often high that persists for 4-5 days, auricular region pain, muscle aches, headache, and swelling of one or both parotids, resulting in pain during chewing and swallowing.
The involvement is initially of only one gland but in most cases (75%), in about 2 days, the parotid gland on the opposite side is also involved. Approximately one-third of parotitic virus infections do not manifest in a clinically overt form, but only with nonspecific respiratory tract symptomatology. Swelling of the parotid glands lasts approximately one week, and healing occurs in 10-12 days. Swelling and redness of the orifice of Stenone’s duct is often present.