Infection with
vaginal candidiasis
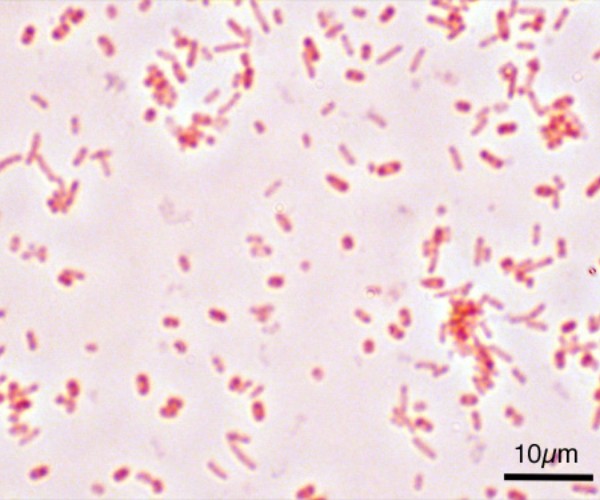
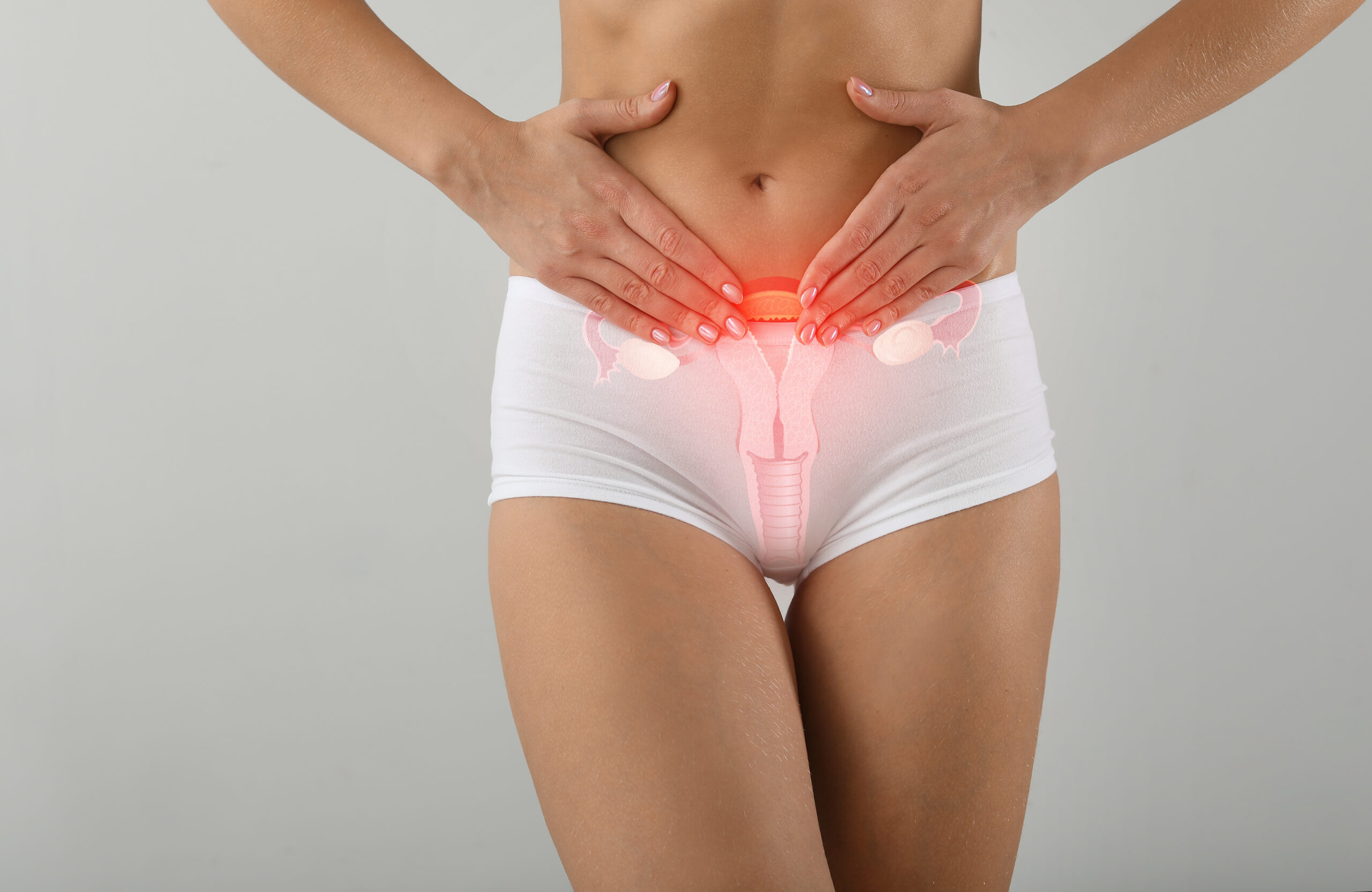
is a fungal infection that causes irritation, discharge, and intense itching of the vagina and vulva; it is also called vaginal candidiasis and usually every woman has been affected at least a few times in her lifetime.
A vaginal yeast infection does not fall under sexually transmitted diseases, but there is a risk of candidiasis infection during a first time as sexual intercourse, with the possibility that the infection may localize to the mouth or genitals, due to the type of sexual intercourse.
Usually this type of infection is effectively treatable with drugs that eradicate fungal yeasts. In cases of recurrent infections or refractory to treatment, longer courses of treatment should be administered.
Symptoms
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis may occur more or less intensely:
- Itching and irritation of vagina and vulva.
- Discomfort and burning during sexual intercourse, or when urinating.
- Redness and swelling of the vulva.
- Vaginal pain and soreness.
- vaginal eruption.
- Thick, white, odorless vaginal discharge.
A complicated yeast infection can occur in the following cases:
- If you complain of severe signs and symptoms, such as extensive redness, swelling, and itching, sometimes with irritation or sores.
- If the infection is recurrent, such as 3-4 times in a year.
- If you are pregnant.
- If you have diabetes, uncontrolled.
- If you have an immunodeficiency condition.
Symptoms
The symptomatology of infection can range from mild to moderate if elements such as:
- Itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva.
- A burning sensation, especially during intercourse.
- Redness and swelling of the vulva.
- Vaginal pain and soreness.
Diagnosis
Formulating the diagnosis of a yeast infection for the physician goes through a few steps:
- Collection of information and data on the patient’s medical history, past vaginal infections or sexually transmitted infections.
- Performance of a pelvic examination, an objective examination of the external genitalia to observe any signs of infection.
- Intravaginal and cervix investigation, observation of the uterus.
- Test vaginal secretions by taking a sample of vaginal fluid for the type of fungus responsible for the infection in order to be able to identify the most effective treatment.
Treatment
Treatment for yeast infections depends on the severity and frequency of infections.
- One-week administration of antifungal drugs; there are both over-the-counter and prescription drugs in the form of tablets, creams.
- For more severe cases, a single-dose oral fluconazole medication may be effective, which cannot be taken if the patient is pregnant.