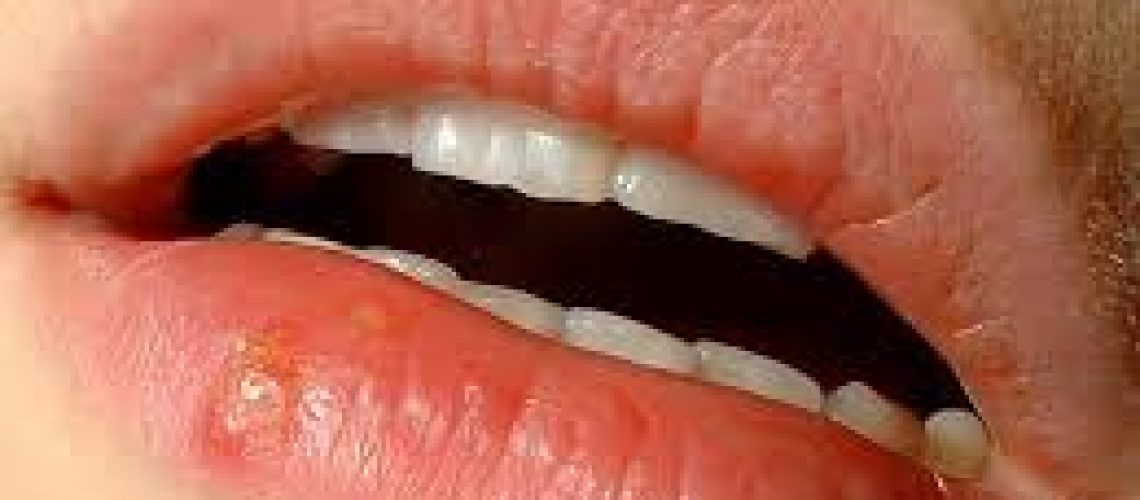
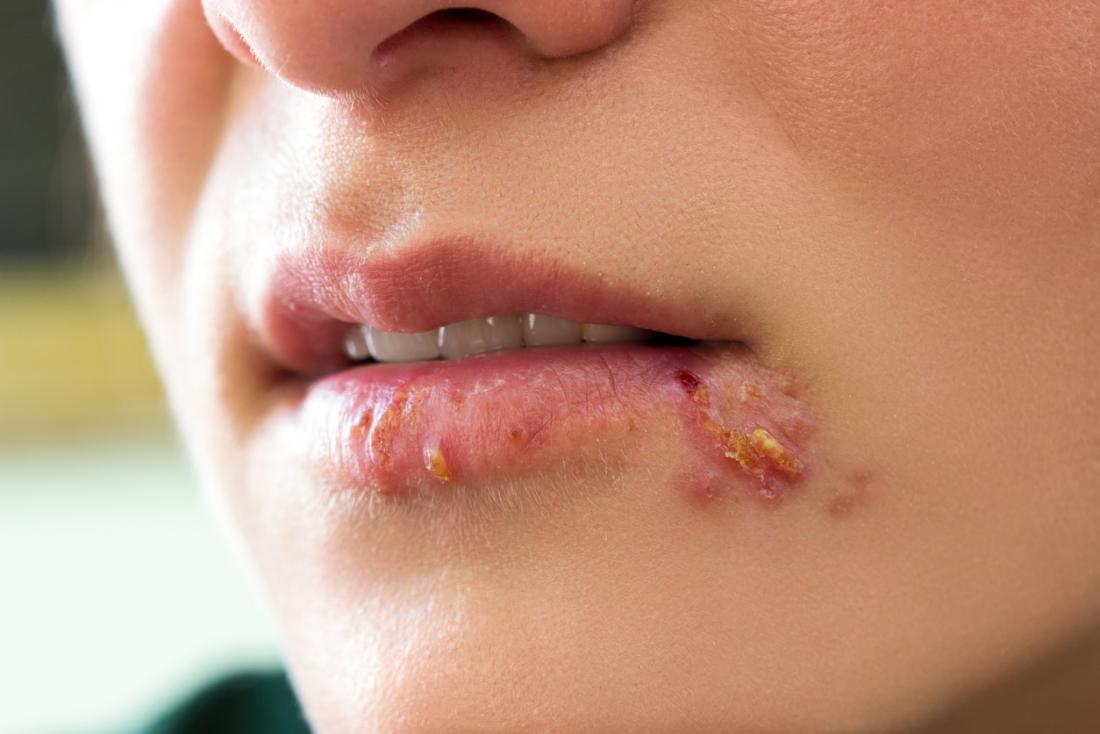
Herpes simplex viruses (human herpes virus types 1 and 2, HHV-1 and 2) commonly cause a relapsing infection affecting skin, mouth, lips, eyes, and genitalia. Common serious variants include encephalitis, meningitis, neonatal herpes, and disseminated infections in immunocompromised patients. Mucocutaneous infections manifest as clusters of small, painful, erythematous-based blisters. Diagnosis is clinical; laboratory confirmation can be obtained through culture tests, PCR (polymerase chain reaction), direct immunofluorescence, or serologic tests. Therapy is symptomatic; antiviral treatment with acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir is useful in severe infections and, if started early, in primary or recurrent infections.

Anal fissures: symptoms and causes
Anal fissure is a wound, usually a linear or oval-shaped ulceration, several millimeters long and located at the level of the outer muco-cutaneous margin of the anus. It can occur