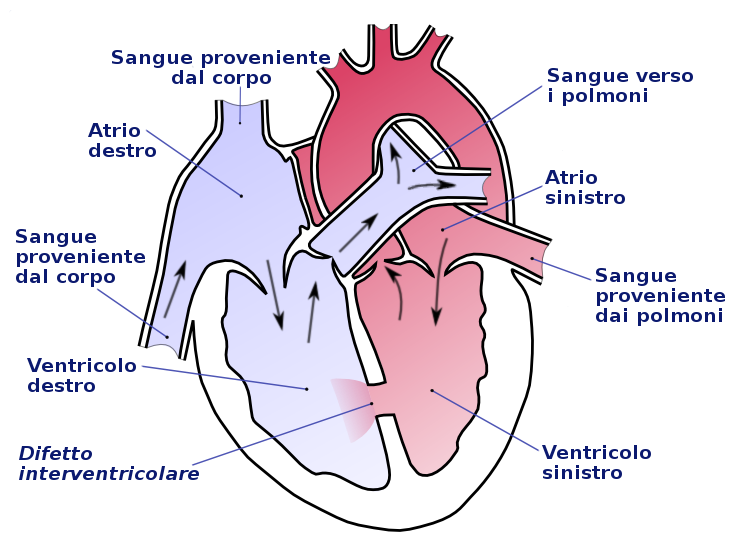
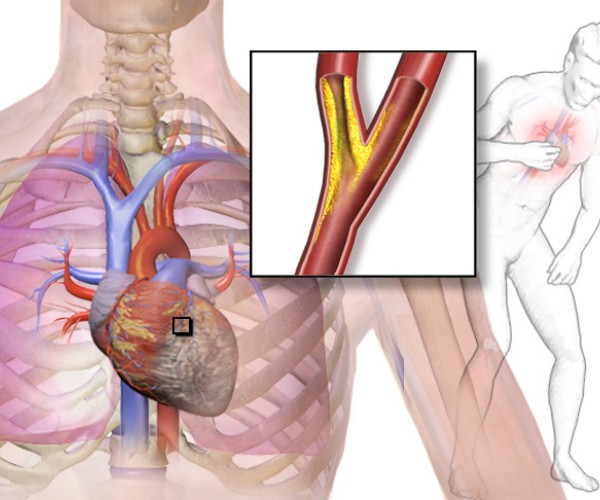
Cardiac Arrest causes immediate widespread ischemia in the body with cellular reactions within the various organs impairing their function and sometimes even thwarting resuscitation maneuvers for circulatory restoration.
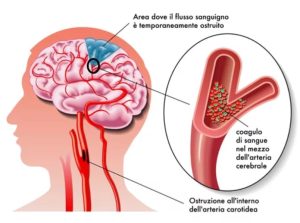
Consequences of cardiac arrest are provoked cells and the appearance of edema. Which pose a significant risk to the brain due to the considerable reduction in cerebral circulation.
Signs of abnormalities in brain function can be observed in patients undergoing resuscitation, long after the event. With various symptoms affecting the nervous system.
Consequences of cardiac arrest are also the alteration of electrolyte balance, which then accounts for the formation of cellular edema, or even the onset of thrombotic phenomena at the microvascular level.
DIFFUSE ISCHEMIA