Habitat
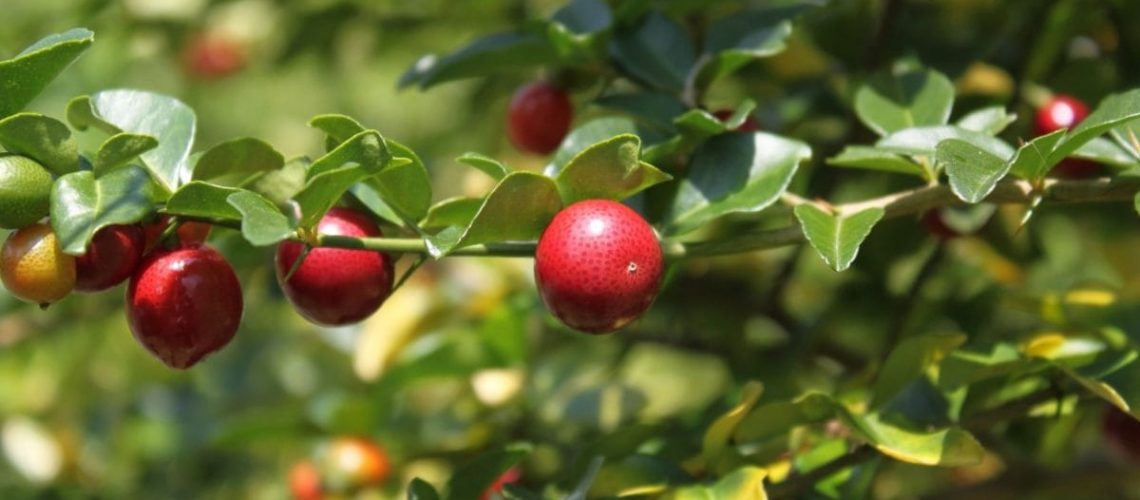
The cranberry shrub originally grew in the sandy soils and swamps of North America. Today, as we know, it is widespread and cultivated in many states of the union for food purposes. The cranberry requires exposure to shade, abundant watering and moist, cool soil. The ideal habitat, therefore consists of the combination of soil and hydrogeological features, typical of the marshy areas of Massachusetts. Natural swamps came into being 10,000 years ago through the melting of glaciers. Rock fragments of different sizes and organic materials have settled on the surface of the glacial boiler cavities, making them impermeable and preventing materials from seeping into the water table. These natural cavities filled with water and organic material and generated the ideal environment for the cranberry. The cultivation of these fruits also requires a support system, which mimics the conditions of the natural habitat. Unlike common farmland, cranberry soil does not require tillage, only small additions of sand and organic material. Every 2-5 years a mixture of dead leaves and sand is added to the base of the plants to reinvigorate the crop. Vaccinium macrocarpon is adapted to low temperatures, but not to frost. Being a swamp plant, cranberry prefers submerged soils. Flooding is done at the end of the growing season, and through good drainage, plant development is ensured.
Production cycle
The cranberry production cycle lasts 16 months. New buds sprout in July of the previous year of harvest, buds develop during summer and fall with bud formation on vertical shoots. From August, the first stages of flower budding can be seen, and until October there continue to be changes. As temperatures drop, the dormancy phase begins, lasting until spring for a variable length of time.
The development cycle ends with flowering and fruit ripening as temperatures rise and days become longer. During June the branches elongate as new leaves form, and by the end of the month most are open and the fields take on the appearance of a pink carpet. Between June and July, bees pollinate the flowers and young berries. From this time until harvest, the ripening cycle coincides with the beginning of the next year’s new growth cycle. By September, the berries begin to turn red, and 80 days after flowering, maturity is complete.
Cultivation
Cranberry cultivation requires special environmental conditions. Although it is a cold-hardy plant, it can only grow and survive in the presence of a combination of factors. Cranberry prefers sandy soils with rich hummus and has a decidedly acidic reaction.
One of the decisive factors to the development of cultivation plants is the soil, which must be moist and well drained. Growers prepare soil suitable for crop needs by stratifying sand, peat, gravel and clay. Historically, crops were planted in wetlands characterized by an abundance of slow-moving water, which created an oxygen-poor and inhospitable environment for bacteria. Currently, cranberry fields are located in flat areas, and topsoil is dug up to dig a ditch and within which 10-20 centimeters of clean sand is poured. The bases are also drained with ditch reinforcement bricks. In addition to retaining water, this prevents the irrigation device from running over shrubs. Ditches are important for both flooding and drainage. Cranberry planting is done by resting the branches on the new layers of sand, burying them with a special tool. Often during the first year, the soil of the bases, is treated with nitrogen-based fertilizer. In autumn the fields are flooded with water to facilitate harvesting and in winter to protect the plants from low temperatures. On fields where ice forms, some trucks dump a thin layer of sand, which helps fight pests. Sand is added every 3-5 years, which not only helps vine growth but also slows the development of weeds and insects.
Source: The Cranberry – A fruit that never ceases to amaze by Mediserve