Antibiotic resistance continues to grow globally, and in Italy, the situation is among the most severe in Europe, with many fearsome bacteria now unassailable by most available antibiotics. According to data from theEuropean Center for Diseases Prevention and Control (ECDC), our country accounts for 1/3 of all deaths (10,000 deaths/year) related to antibiotic resistance on the European territory: in the EU/EAA area, a situation of similar severity affects only Greece, Croatia, Bulgaria and Hungary.
In addition to recommending that fewer and better antibiotics be used on the market to preserve their effectiveness and trying to identify new drugs that are more active against bacteria (long, complex, and rarely successful work), researchers are testing the possibility of enhancing the action of current antibiotics or restore their bacteriostatic/bactericidal activity by combining them with other compounds.
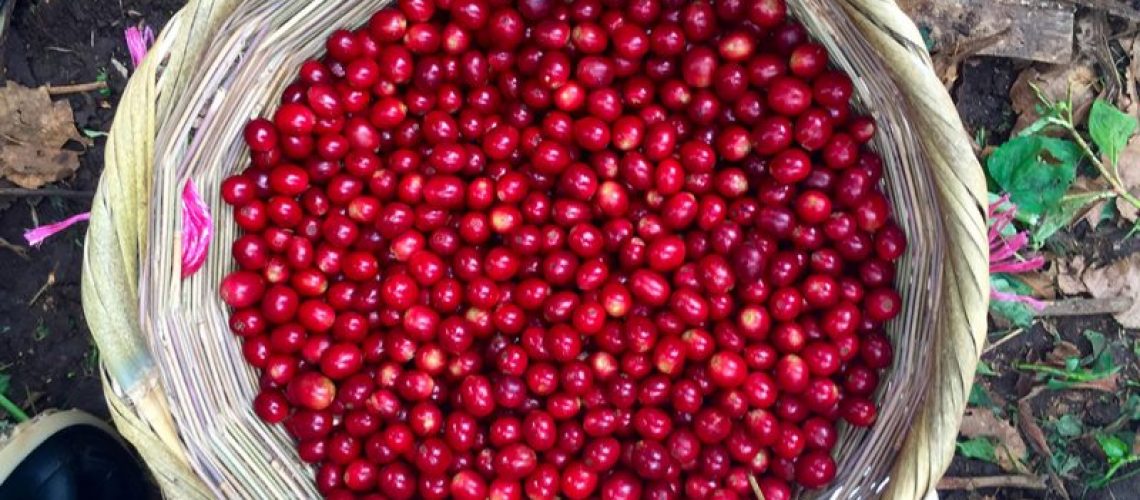
Among such strategies that could help overcome the problem is one based on a protein found in the inviting red berries of the cranberry: plant also known as “American cranberry” or “American oxycock” and has long been exploited for its favorable action against inflammation of the female lower urinary tract (in addition to any specific therapy indicated by the doctor).
In particular, a study published in Advance Science indicates that the pro-anthocyanidin protein (c-PAC) contained in cranberry is able to interfere with two important resistance mechanisms developed by pathogenic microorganisms: selective membrane permeability, which allows bacteria to not absorb or to absorb in minimal amounts the antibiotic that should kill them; and active “pumping” outward from the bacterial cell of antibiotic molecules that have already been absorbed, before they can do damage. By reducing the effectiveness of these two defensive mechanisms, c-PAC would have the effect of increasing the response to antibiotics by pathogenic microorganisms.
L’protective effect of c-PAC has been shown in in vitro and in vivo tests on some of the bacteria most dangerous to human health in case of infection and most frequently resistant to available drugs, such as Escherichia coli (mainly responsible for severe and life-threatening gastrointestinal infections, especially in children, the elderly, and people with reduced immune defenses), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (the cause of difficult-to-fight airway, urinary, and eye infections, severe otitis, endocarditis, and often fatal septicemia); and Proteus mirabilis (mainly at the origin of severe urinary tract infections).
In the case of E. coli and P. aeruginosa, c-PAC has been shown not only to prevent the development of tetracycline resistance, but also to reduce the tendency of these bacteria to form biofilms on the surface of target organs. The formation of biofilms, i.e., dense and compact patches of bacteria tightly adhered to mucous membranes and interacting with each other, is a colonization mechanism that microorganisms use to increase their ability to survive, reducing the ability of drugs to attack and kill them. Hindering biofilm formation, therefore, amounts to making bacteria more isolated and fragile.
Whether this initial evidence can be converted into a combination drug containing an antibiotic and the cranberry protein remains to be evaluated, but the avenue opened is certainly interesting and gives cause for hope.
Source
Maisuria VB et al. Proanthocyanidin Interferes with Intrinsic Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Advance Science 2019; doi:10.1002/advs.201802333 (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/advs.201802333)