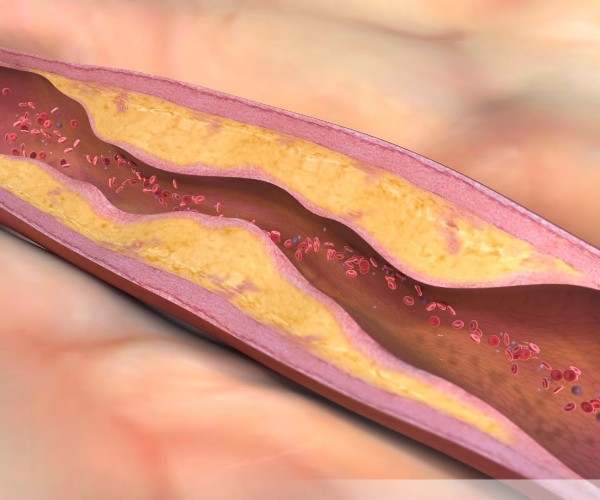
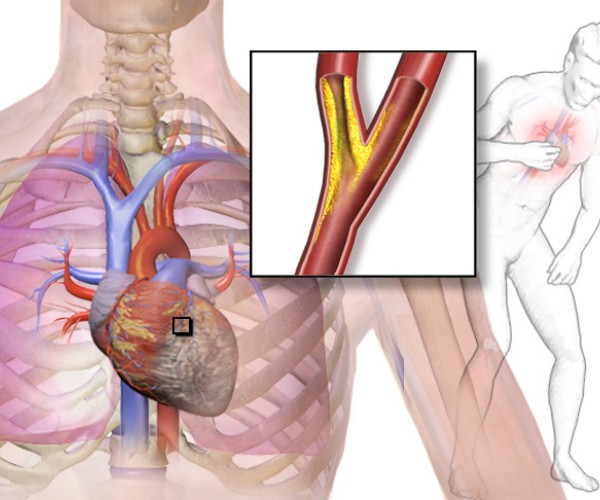
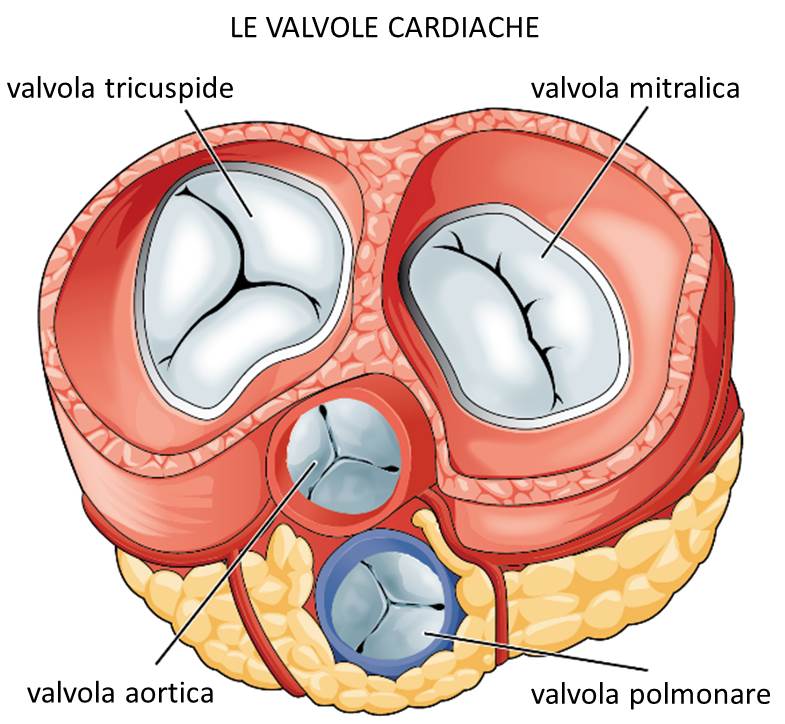
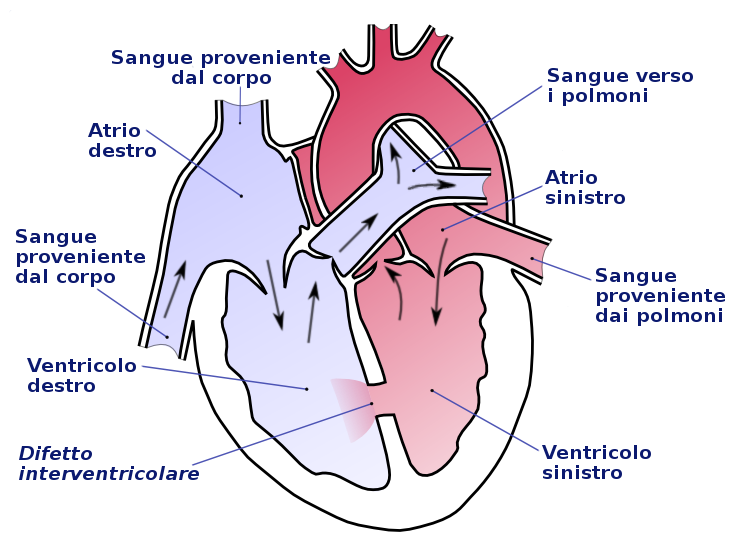
Coronarography, also known as coronary angiography, is an invasive radiological technique used in cardiology to visualize the course and condition of the coronary arteries (the arterial vessels that surround the heart and ensure the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle), especially when there is a strong suspicion of stenosis due to atherosclerotic plaques or partial occlusions due to clots (thrombosis) associated with a high risk of cardiac ischemia or aneurysms at risk of rupture.
If, the stenosis or aneurysm is confirmed by the investigation, in some cases, it is possible to intervene in real time during coronarography with angioplasty techniques to correct the coronary alteration present and thus prevent possible acute cardiovascular events. If immediate correction is not feasible, the information obtained from coronary angiography is valuable in planning the most appropriate hemodynamic or surgical intervention.
Description
Coronarography involves the insertion of a flexible catheter into an artery in the arm that is advanced into the blood vessel to the point near the coronary arteries where it is to release the contrast agent. Once the opaque X-ray contrast agent has spread throughout the coronary bed to be visualized, the patient undergoes a cardiac X-ray that will provide an image of the course of the arteries that surround the heart, highlighting any obstructions and abnormalities.
The examination is performed while the patient is awake and only partially sedated to facilitate relaxation during the procedure while still allowing the patient to interact with the physicians (e.g., answer questions), while local anesthesia is administered to reduce pain at the catheter insertion site. Throughout the evaluation, the patient undergoes electrocardiographic and pressure monitoring, and the amount of blood oxygen (pO2), indicative of cardiopulmonary function, is assessed.
The performance of coronarography takes, on average, about an hour, but its duration may increase in the case of blood vessels that are difficult to navigate (for example, due to subjective stenosis or tortuosity) and, most importantly, when other hemodynamic procedures, such as angioplasty, are implemented in addition to diagnostic evaluation. At the end of the procedure, the catheter is removed and the incision site closed with simple pressure or a clip.
When needed
Coronary angiography is performed only when diagnostic imaging techniques or other noninvasive evaluations, such as echocardiogram and echodoppler (at rest or under stress) or cardiac MRI, are inadequate or sufficient to clarify the origin of clinically highlighted symptoms and signs or when correction of the coronary defect present at the same time as coronarography (e.g., reopening of a semi-occluded vessel with application of a coronary stent) is deemed plausible.
This cautious use of coronary angiography is related to the fact that performing the examination has low but not zero operative risks, mainly related to the need to navigate the arteries with a catheter to the coronary arteries to be examined and to administer a contrast agent. In contrast, the use of low doses of X-rays, which are needed to highlight heart vessels, is essentially harmless.
The main indications for performing coronarography include:
- Symptoms indicative of coronary artery disease, such as angina pectoris or anginal pain in the arm;
- Finding of chest, neck/mandibular, chest or arm pain not explained by other tests;
- Increased symptoms of already diagnosed angina (unstable angina);
- Presence of congenital heart defects;
- Presence of defects at a heart valve;
- Heart failure already diagnosed;
- Detection of alterations in other blood vessels or thoracic trauma;
- Abnormal outcomes in other cardiac evaluations (in particular, stress testing).
In addition, coronarography can be used to better plan for surgery (percutaneous or open) or angioplasty and to monitor outcomes over time (follow-up), in order to highlight early possible recurrences of the initial coronary alteration (e.g., re-stenosis of a vessel at the same location where a stent has already been applied or in another area of the coronary vessels).
Special Warnings
Angiography is an invasive procedure that requires a series of preliminary assessments before it can be performed and is managed in the interventional hemodynamics room in the same manner as minor surgery.
After the procedure is completed, it is necessary to remain several hours under monitoring until cardiac and general conditions are stable. If there is no special underlying clinical criticality (e.g., a very advanced age or diseases that increase the risk of complications, such as diabetes) and the procedure is performed without any problems, coronarography can be performed in the day hospital, and the patient can return to his or her home the same day. Conversely, an overnight hospitalization may be required.
After the examination, it is recommended to drink plenty to promote elimination of the contrast medium from the bloodstream (unless otherwise medically indicated), not to perform strenuous exertion or activities for a few days, and not to rub or touch the small wound at the catheter insertion site until it is completely healed.