Sore throat from Virus or Streptococcus?
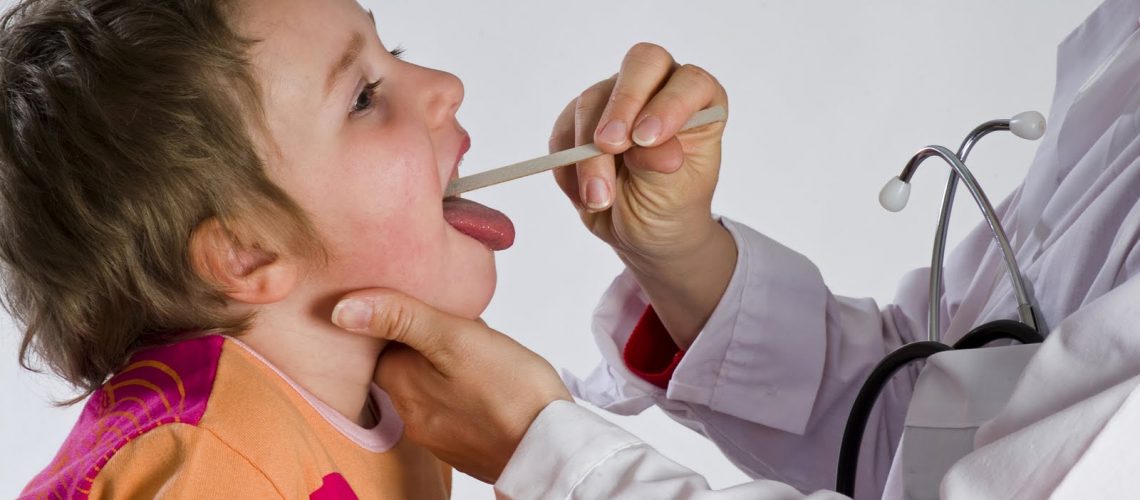
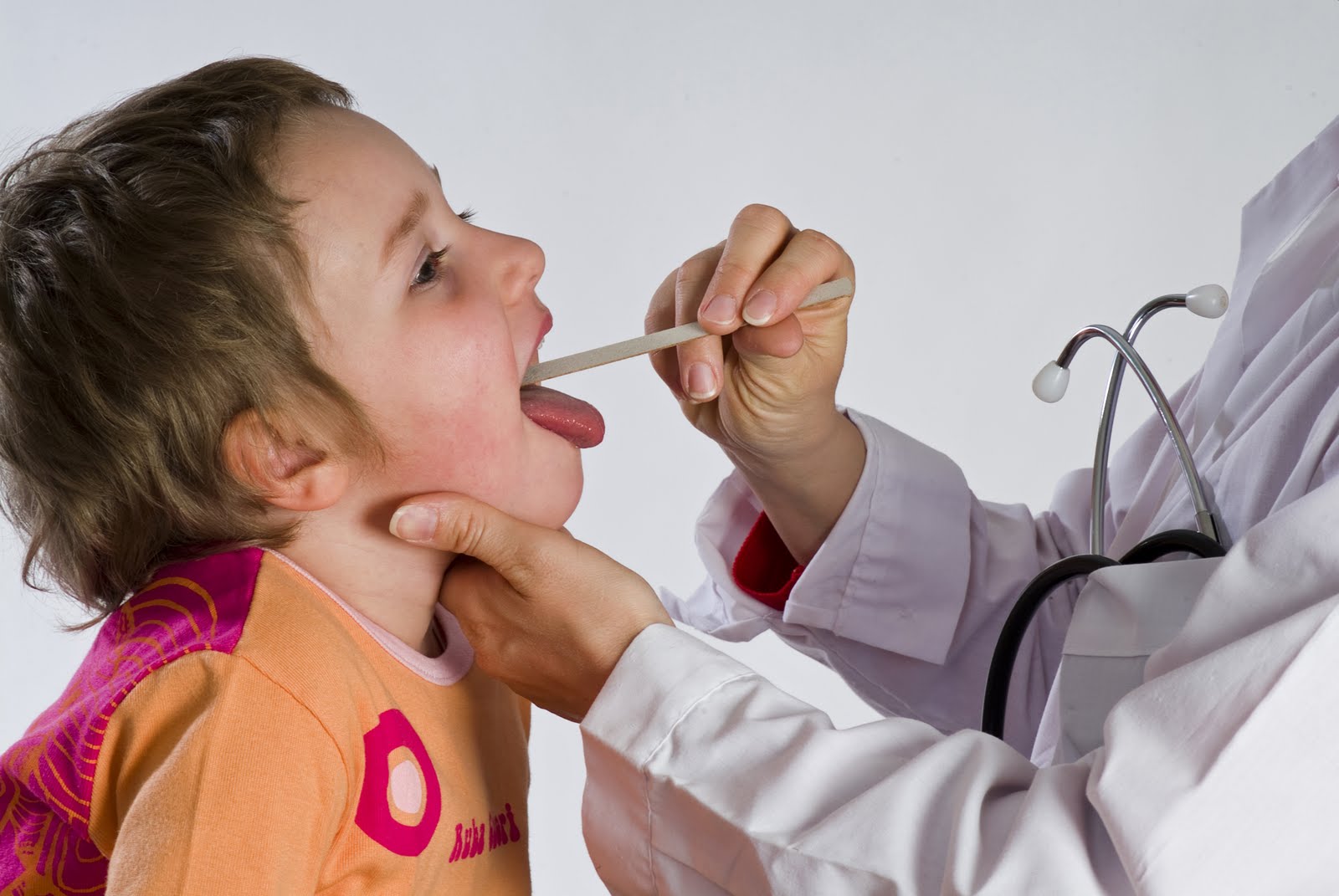
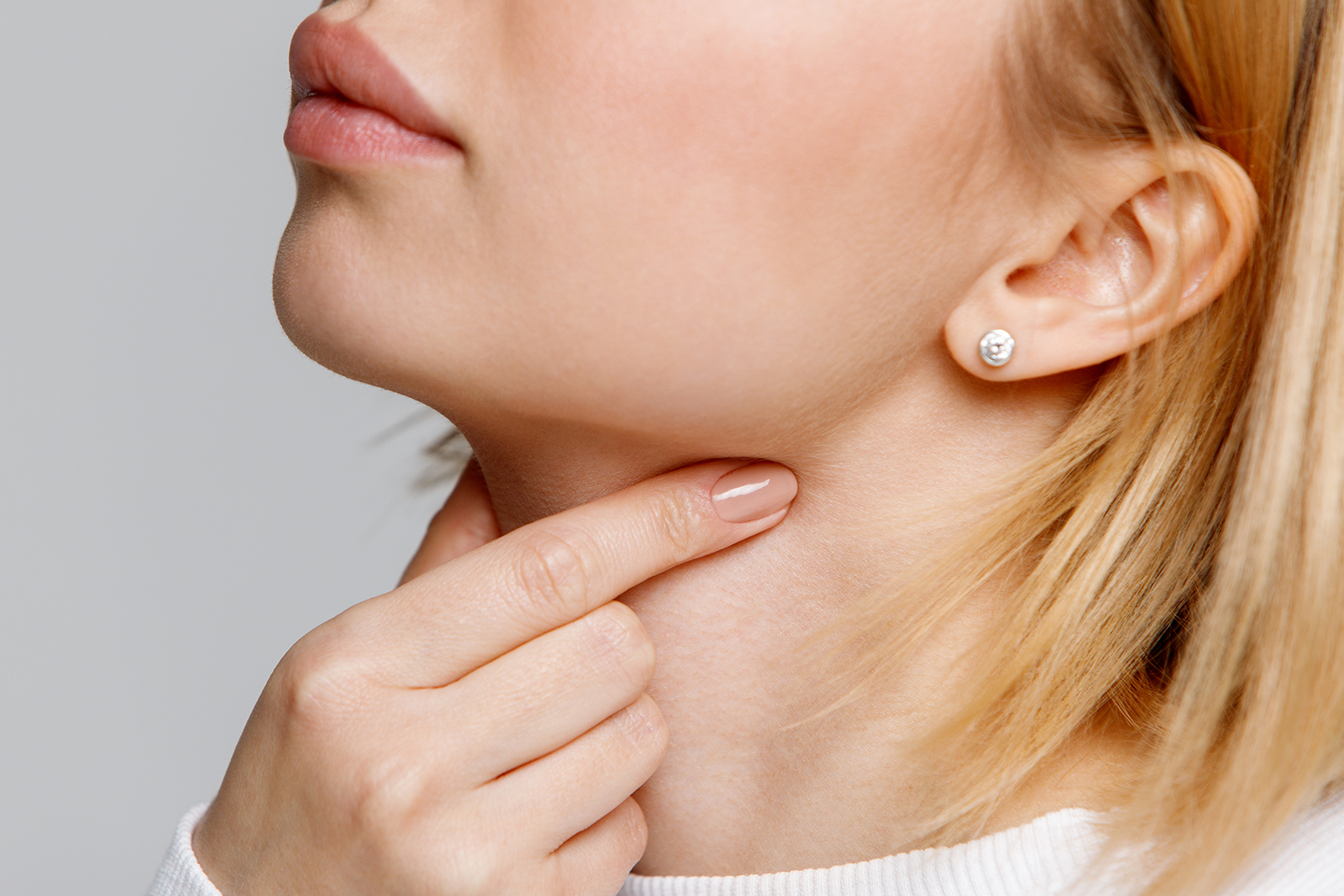
Sore throat is among the most common symptoms in children and adults. In most cases, it is a trivial viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, and does not need treatment. If, on the other hand, the sore throat is caused by streptococcus bacteria, antibiotic treatment becomes necessary.
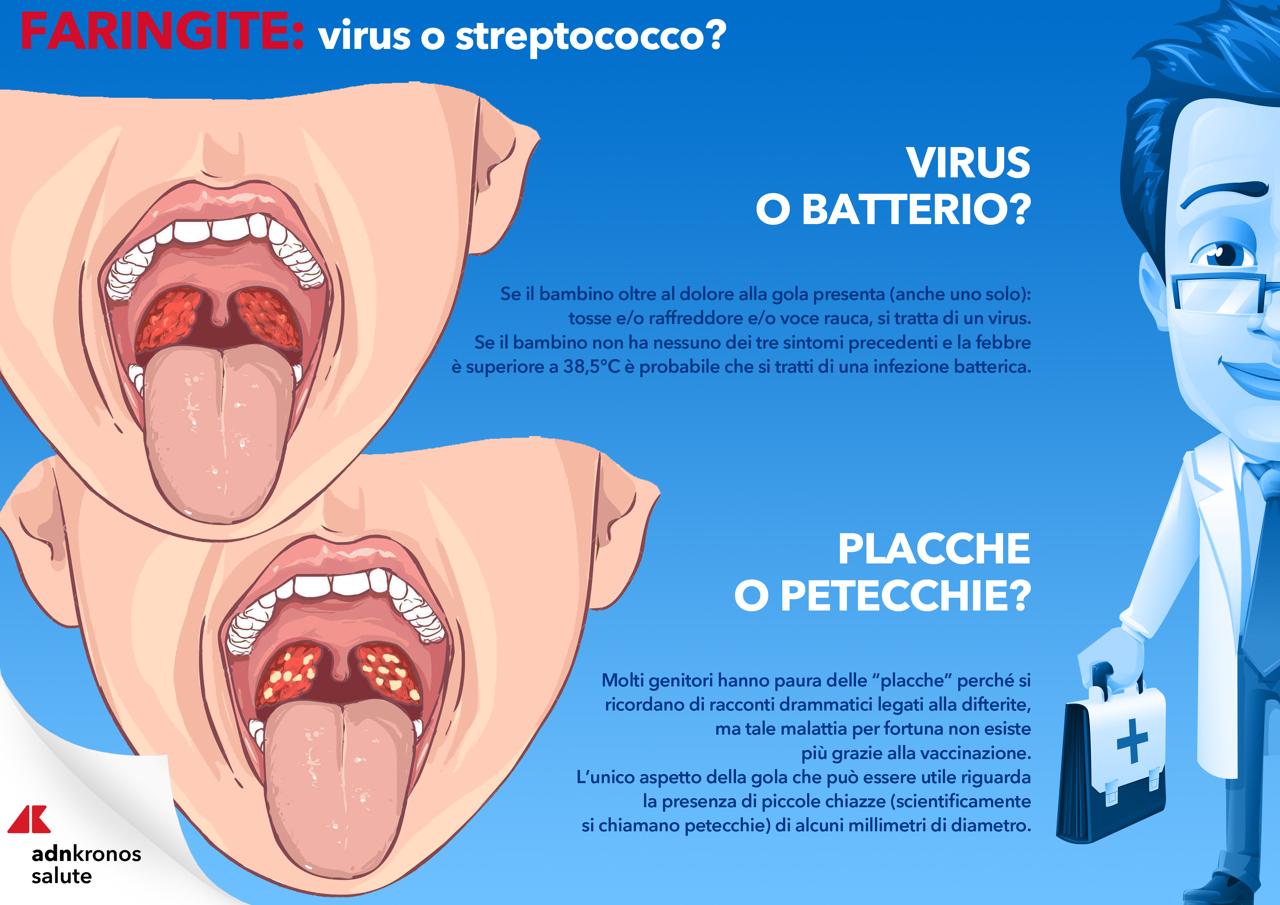
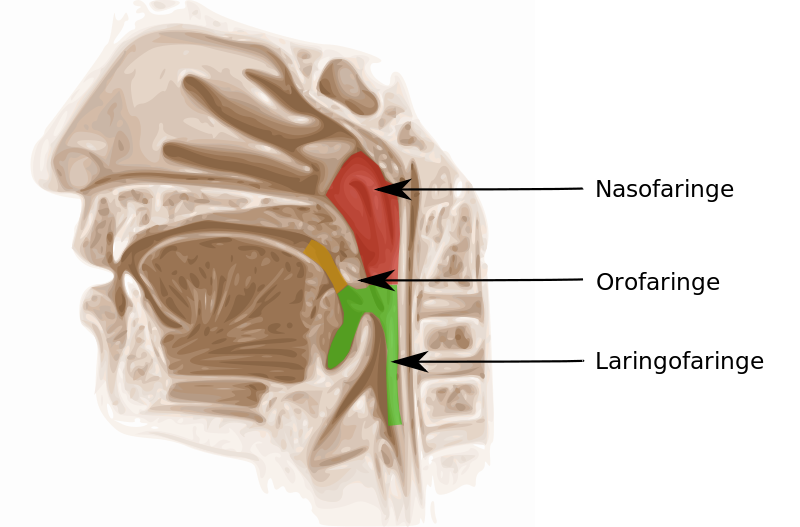
The inflammation may involve the pharynx (pharyngitis) or even the tonsils (pharyngotonsillitis), causing pain. The tonsils may appear increased in volume, reddened, and covered with a whitish material (exudate). These are the so-called “plates”, caused by the immune system’s reaction to the infection. However, their presence on the tonsils does not mean that the infection is bacterial, that is, caused by streptococcus, but can instead be viral in origin, as in the case of mononucleosis. Typically, when pharyngitis and pharyngotonsillitis are caused by viruses, they are accompanied by other typical signs of viral diseases, such as colds, conjunctivitis, hoarseness, or diarrhea.
Source: AdnKronos Health
The antibiotic, therefore, should be taken only if plaques are a result of the presence of streptococcus, which should be ascertained by resorting to pharyngeal swabbing, which is a swab that is taken by vigorously rubbing a cotton swab on the oropharynx and the surface of both tonsils, avoiding touching other parts of the oral cavity or contaminating it with saliva.
Streptococcus is a spherical (coconut) bacterium of which there are several types, many of which do not cause diseases. In some cases, however, they can cause pharyngotonsillitis, otitis, meningitis, pneumonia, infection generalized and endocaritis (infections of the internal cavities or valves of the heart). Also scarlet fever, the rheumatic disease and an inflammation of the kidney (glomerulonephritis) are attributable to streptococcus.
Today, streptococcal infections are no longer scary, but complications should not be underestimated, especially since the misuse of inappropriate antibiotic therapies has produced “resistances” that are weakening the effectiveness of law enforcement. Antibiotic therapy of streptococcal pharyngitis should begin within 9 days of the onset of sore throat, but not before swabbing, the microbiological examination of the pharyngeal cavity. Therapy can shorten and alleviate frequent sore throats, but is mainly aimed at preventing complications.